The Republic of South Africa is a unitary parliamentary democratic republic. The President of South Africa serves both as head of state and as head of government. The President is elected by the National Assembly and must retain the confidence of the Assembly in order to remain in office. South Africans also elect provincial legislatures which govern each of the country's nine provinces.

Pieter Willem Botha, was a South African politician. He served as the last prime minister of South Africa from 1978 to 1984 and the first executive state president of South Africa from 1984 to 1989.

The Democratic Party (DP) was the name of the South African political party now called the Democratic Alliance. Although the Democratic Party name dates from 1989, the party existed under other labels throughout the apartheid years, when it was the Parliamentary opposition to the ruling National Party's policies.

The National Party, also known as the Nationalist Party, was a political party in South Africa from 1914 to 1997, which was responsible for the implementation and much of the deconstruction of apartheid rule. The party was an Afrikaner ethnic nationalist party, which initially promoted the interests of Afrikaners but later became a stalwart promoter and enactor of white supremacy, for which it is best known. It first became the governing party of the country in 1924. It merged with its rival, the SAP, during the Great Depression, and a splinter faction became the official opposition during World War II and returned to power. With the National Party governing South Africa from 4 June 1948 until 9 May 1994, the country for the bulk of this time was only a de jure or partial democracy, as from 1958 onwards non-white people were barred from voting. In 1990, it began to style itself as simply a South African civic nationalist party, and after the fall of apartheid in 1994, attempted to become a moderate conservative one. The party's reputation was damaged irreparably by perpetrating apartheid, and it rebranded itself as the New National Party in 1997 before eventually dissolving in 2005.

The United Party was a political party in South Africa. It was the country's ruling political party between 1934 and 1948.

The Conservative Party of South Africa was a far-right South African political party that sought to preserve many aspects of apartheid in the system's final decade, and formed the official opposition in the white-only House of Assembly in the last seven years of minority rule. It declined quickly after apartheid ended, before being merged with the Freedom Front in 2004.
The Senate was the upper house of the Parliament of South Africa between 1910 and its abolition from 1 January 1981, and between 1994 and 1997.

The Herstigte Nasionale Party is a South African political party which was formed as a far-right splinter group of the now defunct National Party in 1969. The party name was commonly abbreviated as HNP, evoking the Herenigde Nasionale Party, although colloquially they were also known as the Herstigtes. The party is, unlike other splinter factions from the National Party, still active but politically irrelevant.

The United National South West Party was a political party in South West Africa, the local counterpart of the South African United Party but founded eight years earlier and merged into the latter in 1971. It was formed through a merger of National Party of South West Africa and the South West Party, in order to counter the influence of the German League in South West Africa. The first congress of UNSWP was held in Windhoek on 1–2 April 1927.

General elections were held in South Africa on 15 September 1910 to elect the 121 members of the House of Assembly. They were the first general election after the Union of South Africa was created on 31 May 1910.
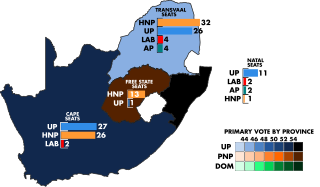
General elections were held in South Africa on 26 May 1948. They represented a turning point in the country's history, as despite receiving just under half of the votes cast, the United Party and its leader, incumbent Prime Minister Jan Smuts, were ousted by the Herenigde Nasionale Party (HNP) led by D. F. Malan, a Dutch Reformed cleric.

General elections were held in South Africa on 15 April 1953. The elections consolidated the position of the National Party under D. F. Malan, which won an absolute majority of the 156 elected seats in the House of Assembly, also receiving the most votes. Its first-time majority of the white electorate would be retained until the 1989 elections.
General elections were held in South Africa on 22 April 1970 to elect members of the 166-seat House of Assembly. Parliament was dissolved on 2 March and the deadline for the submission of candidates was 13 March.

General elections were held in South Africa on 7 July 1943 to elect the 150 members of the House of Assembly. The United Party of Jan Smuts won an absolute majority.
General elections were held in South Africa on 6 May 1987. The State of Emergency cast a cloud over the elections, which were again won by the National Party (NP) under the leadership of P. W. Botha, although for the first time it faced serious opposition from the right of the South African political spectrum. The election resulted in the creation of the Second Botha Cabinet, which held power until 1989.

General elections were held in South Africa on 6 September 1989, the last under apartheid. Snap elections had been called early by the recently elected head of the National Party (NP), F. W. de Klerk, who was in the process of replacing P. W. Botha as the country's president, and his expected program of reform to include further retreat from the policy of apartheid. The creation of the Conservative Party had realigned the NP as a moderate party, now almost certain to initiate negotiations with the black opposition, with liberal opposition openly seeking a new constitutional settlement on liberal democratic and federalist principles.

The Tricameral Parliament, officially the Parliament of the Republic of South Africa, was the legislature of South Africa between 1984 and 1994, established by the South African Constitution of 1983, which gave a limited political voice to the country's Coloured and Indian population groups. The majority African population group was however still excluded, their interests notionally represented in the governments of the black homelands, or "bantustans", of which they were formally citizens. As the bantustans were largely politically impotent, its principal effect was to further entrench the political power of the White section of the South African population.

The New Republic Party (NRP) was a South African political party. It was formed as the successor to the disbanded United Party (UP) in 1977 and as a merger with the smaller Democratic Party. It drew its support mainly from the then Province of Natal, and tried to strike a moderate course between the apartheid policy of the ruling National Party (NP) and the liberal policies of the Progressive Federal Party (PFP).
Although the Democratic Alliance of South Africa in its present form is fairly new, its roots can be traced far back in South African political history, through a complex sequence of splits and mergers.
The Coloured vote constitutional crisis, also known as the Coloured vote case, was a constitutional crisis that occurred in the Union of South Africa during the 1950s as the result of an attempt by the Nationalist government to remove coloured voters in the Union's Cape Province from the common voters' rolls. It developed into a dispute between the judiciary and the other branches of government over the power of Parliament to amend an entrenched clause in the South Africa Act and the power of the Appellate Division to overturn the amendment as unconstitutional. The crisis ended when the government enlarged the Senate and altered its method of election, allowing the amendment to be successfully enacted.

















