
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorized that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation and to increase employment. Additionally, it is designed to try to keep GDP growth at 2%–3% and the unemployment rate near the natural unemployment rate of 4%–5%. This implies that fiscal policy is used to stabilize the economy over the course of the business cycle.

The Federal Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund and Federal Disability Insurance Trust Fund are trust funds that provide for payment of Social Security benefits administered by the United States Social Security Administration.

Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget of a government, private company, or individual. Government deficit spending was first identified as a necessary economic tool by John Maynard Keynes in the wake of the Great Depression. It is a central point of controversy in economics, as discussed below.

A government budget is a financial statement presenting the government's proposed revenues and spending for a financial year. The government budget balance, also alternatively referred to as general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the overall difference between government revenues and spending. A positive balance is called a government budget surplus, and a negative balance is a government budget deficit. A budget is prepared for each level of government and takes into account public social security obligations.
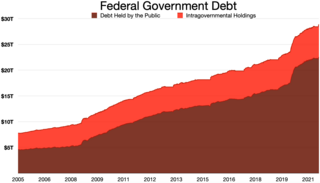
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

Proposition 57 was a California ballot proposition on the March 2, 2004 primary election ballot. It was passed with 4,056,313 (63.4%) votes in favor and 2,348,910 (36.6%) against. The proposition authorized the state to sell $15 billion in long-term bonds to pay off accumulated deficits. Proposition 57 went into effect only because Proposition 58 also passed.

A country's gross government debt is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit occurs when a government's expenditures exceed revenues. Government debt may be owed to domestic residents, as well as to foreign residents. If owed to foreign residents, that quantity is included in the country's external debt.

Proposition 60A was an amendment of the Constitution of California, enacted in 2004, relating to funds from the sale of government property. It was proposed by the California Legislature and approved by the voters in a referendum held as part of the November 2004 election, by a majority of 73%.
A balanced budget amendment is a constitutional rule requiring that a state cannot spend more than its income. It requires a balance between the projected receipts and expenditures of the government.

The California special election of 2005 was held on November 8, 2005 after being called by Governor Arnold Schwarzenegger on June 13, 2005.
PAYGO is the practice in the United States of financing expenditures with funds that are currently available rather than borrowed.

The United States federal budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levels—from 98 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.

California's state elections were held November 3, 1992. Necessary primary elections were held on March 3. Up for election were all the seats of the State Assembly, 20 seats of the State Senate, and fifteen ballot measures.

Proposition 1A was a defeated California ballot proposition that appeared on the May 19, 2009 special election ballot. It was a constitutional amendment that would have increased the annual contributions to the state's rainy day fund. The proposition was legislatively referred to voters by the State Legislature.

Proposition 1C was a defeated California ballot proposition that appeared on the May 19, 2009 special election ballot. The measure was a legislatively referred constitutional amendment that would have made significant changes to the operation of the State Lottery.

Deficit reduction in the United States refers to taxation, spending, and economic policy debates and proposals designed to reduce the Federal budget deficit. Government agencies including the Government Accountability Office (GAO), Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the Office of Management and Budget (OMB),and the U.S. Treasury Department have reported that the federal government is facing a series of important long-run financing challenges, mainly driven by an aging population, rising healthcare costs per person, and rising interest payments on the national debt.

In California state elections, 2014 was the first year in which the top statewide offices were elected under the nonpartisan blanket primary, pursuant to Proposition 14, which passed with 53% voter approval in June 2010. Under this system, which first went into effect during the 2012 election year, all candidates will appear on the same ballot, regardless of party. In the primary, voters may vote for any candidate, regardless of their party affiliation. The top two finishers, regardless of party, then advance to face each other in the general election in November.

California state elections in 2018 were held on Tuesday, November 6, 2018, with the primary elections being held on June 5, 2018. Voters elected one member to the United States Senate, 53 members to the United States House of Representatives, all eight state constitutional offices, all four members to the Board of Equalization, 20 members to the California State Senate, and all 80 members to the California State Assembly, among other elected offices.
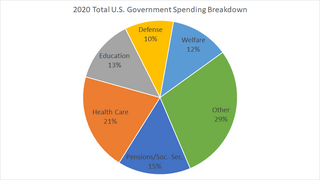
Government spending in the United States is the spending of the federal government of the United States, and the spending of its state and local governments.







