
An airliner is a type of aircraft for transporting passengers and air cargo. Such aircraft are most often operated by airlines. Although the definition of an airliner can vary from country to country, an airliner is typically defined as an airplane intended for carrying multiple passengers or cargo in commercial service. The largest of them are wide-body jets which are also called twin-aisle because they generally have two separate aisles running from the front to the back of the passenger cabin. These are usually used for long-haul flights between airline hubs and major cities. A smaller, more common class of airliners is the narrow-body or single-aisle. These are generally used for short to medium-distance flights with fewer passengers than their wide-body counterparts.

Emirates is one of two flag carriers of the United Arab Emirates. Based in Garhoud, Dubai, the airline is a subsidiary of The Emirates Group, which is owned by the government of Dubai's Investment Corporation of Dubai. It is the largest airline in the Middle East, operating over 3,600 flights per week from its hub at Terminal 3 of Dubai International Airport. It operates to more than 150 cities in 80 countries across six continents on its fleet of nearly 300 aircraft. Cargo activities are undertaken by Emirates SkyCargo.

Singapore Airlines is the flag carrier of the Republic of Singapore with its hub located at Changi Airport, and a member of the Star Alliance. The airline is notable for highlighting the Singapore Girl as its central figure in the corporate branding segment. Widely renowned as one of the best carriers, airline is ranked as a 5-star airline by Skytrax, and it has also been ranked as the world's best airline five times. The airline operates a variety of Boeing and Airbus aircraft, including the A350, 787, 777, A380, and 737.

The Airbus A380 is a very large wide-body airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and only full-length double-deck jet airliner. Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was announced in 1990 to challenge the dominance of the Boeing 747 in the long-haul market. The then-designated A3XX project was presented in 1994; Airbus launched the €9.5 billion ($10.7 billion) A380 programme on 19 December 2000. The first prototype was unveiled in Toulouse on 18 January 2005, with its first flight on 27 April 2005. It then obtained its type certificate from the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) on 12 December 2006.

A wide-body aircraft, also known as a twin-aisle aircraft and in the largest cases as a jumbo jet, is an airliner with a fuselage wide enough to accommodate two passenger aisles with seven or more seats abreast. The typical fuselage diameter is 5 to 6 m. In the typical wide-body economy cabin, passengers are seated seven to ten abreast, allowing a total capacity of 200 to 850 passengers. Seven-abreast aircraft typically seat 160 to 260 passengers, eight-abreast 250 to 380, nine- and ten-abreast 350 to 480. The largest wide-body aircraft are over 6 m (20 ft) wide, and can accommodate up to eleven passengers abreast in high-density configurations.
Condor Flugdienst GmbH, usually shortended to Condor, is a German leisure airline established in 1955 with Frankfurt Airport being its main base. Condor offers scheduled flights to leisure destinations and operates, from Germany, medium-haul flights to the Mediterranean Basin and the Canary Islands as well as long-haul flights to destinations in Africa, Asia, North America, South America and the Caribbean. Whereas medium-haul flights are operated from many German airports, long-haul flights usually depart from Frankfurt, with a few rotations operated from Düsseldorf and Munich. Condor also operates charter flights.

Etihad Airways is the national airline of the United Arab Emirates and one of the two major airlines in the country. Its head office is in Khalifa City, Abu Dhabi, near Zayed International Airport. The airline commenced operations in November 2003, and is the second-largest airline in the UAE after Emirates. The name Etihad is the Arabic word for 'Union'.

The Airbus A350 is a long-range, wide-body twin-engine jet airliner developed and produced by Airbus. The initial A350 design proposed by Airbus in 2004, in response to the Boeing 787 Dreamliner, would have been a development of the Airbus A330 with composite wings and new engines. Due to inadequate market support, Airbus switched in 2006 to a clean-sheet "XWB" design, powered by two Rolls-Royce Trent XWB high bypass turbofan engines. The prototype first flew on 14 June 2013 from Toulouse, France. Type certification from the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) was obtained in September 2014, followed by certification from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) two months later.

Business class is a travel class available on many commercial airlines and rail lines, known by brand names which vary, by airline or rail company. In the airline industry, it was originally intended as an intermediate level of service between economy class and first class, but many airlines now offer business class as the highest level of service, having eliminated first class seating. Business class is distinguished from other travel classes by the quality of seating, food, drinks, ground service and other amenities. In commercial aviation, full business class is usually denoted 'J' or 'C' with schedule flexibility, but can be many other letters depending on circumstances.
Economy class, also called third class, coach class, steerage, or to distinguish it from the slightly more expensive premium economy class, standard economy class or budget economy class, is the lowest travel class of seating in air travel, rail travel, and sometimes ferry or maritime travel. Historically, this travel class has been called tourist class or third class on ocean liners.

In-flight entertainment (IFE) refers to the entertainment available to aircraft passengers during a flight. In 1936, the airship Hindenburg offered passengers a piano, lounge, dining room, smoking room, and bar during the 2+1⁄2-day flight between Europe and America. After World War II, food and drink services were offered, and movies were projected onto big screens viewable by all passengers on long flights. In 1985 the first personal audio player became available for purchase, and noise cancelling headphones were introduced in 1989. During the 1990s, the demand for better IFE was a major factor in the design of aircraft cabins. Before then, entertainment came via audio headphone sockets and airline-provided headphones providing music of various genres and the soundtrack of projected movies. Now, in most aircraft, personal IFE display screens are available at most seats, offering entertainment and flight information such as a moving map, speed, and altitude. The advent of small entertainment and communication devices also allows passengers to also use their own devices, subject to regulations to prevent them interfering with aircraft equipment.

An airline seat is a seat on an airliner in which passengers are accommodated for the duration of the journey. Such seats are usually arranged in rows running across the airplane's fuselage. A diagram of such seats in an aircraft is called an aircraft seat map.

An aircraft cabin is the section of an aircraft in which passengers travel. Most modern commercial aircraft are pressurized, as cruising altitudes are high enough such that the surrounding atmosphere is too thin for passengers and crew to breathe.

Airport check-in is the process whereby an airline approves airplane passengers to board an airplane for a flight. Airlines typically use service counters found at airports for this process, and the check-in is normally handled by an airline itself or a handling agent working on behalf of an airline. Passengers usually hand over any baggage that they do not wish or are not allowed to carry in the aircraft's cabin and receive a boarding pass before they can proceed to board their aircraft.

Premium economy class, also known by brand names which vary by company, is a travel class offered on many airlines. It is usually positioned between standard economy class and business class in terms of price, comfort, and available amenities. In 1991, EVA Air was the first to introduce Evergreen Class, becoming the first airline to offer this class of service. It was widely acknowledged that the premium economy class has become a standard reflection of what the economy class was like several decades ago. In some countries, this class has emerged as a response from governments and companies requiring economy class for travel done by staff.
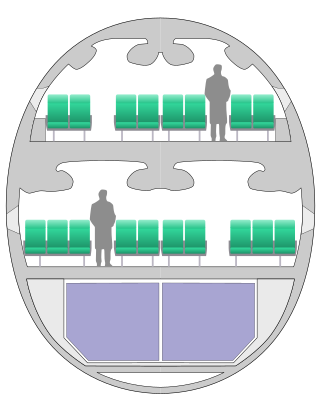
The Airbus A380 has two full-length decks of 49.9 metres (164 ft), though the upper deck has a slightly reduced usable length of 44.93 metres (147.4 ft) due to the curvature of the front fuselage and the front staircase. The widths of the main deck and upper deck measure 6.50 metres (21.3 ft) and 5.80 metres (19.0 ft) respectively.
An exit row is a row of seats on board a commercial airliner that is next to an emergency exit. Exit rows may be next to overwing exits or full-sized exit doors.
Lufthansa operates a mainline fleet consisting of Airbus narrow and widebody and Boeing widebody aircraft. The mainline fleet is composed of seven different aircraft families: the Airbus A320, Airbus A330, Airbus A340, Airbus A350, Airbus A380, Boeing 747 and Boeing 787 Dreamliner. Additionally, Lufthansa currently has orders placed for new Airbus A320neo, Airbus A350 and Boeing 777X aircraft. They have also placed an order for 40 Boeing 737 MAX aircraft with an optional 60, making it the first order of Boeing single aisle aircraft in 40 years. In the following years, the 777X will replace all Boeing 747-400 aircraft in the fleet, and the 787 and A350 will replace all remaining Airbus A340 aircraft.

Qantas Flight 7 (QF7/QFA7) and Qantas Flight 8 (QF8/QFA8) are flights operated by Australian airline Qantas between Sydney Airport and Dallas/Fort Worth International Airport, which, from 2013 to 2016, were the longest regularly scheduled non-stop commercial flights in the world. As of January 2024, they are the 11th longest regularly scheduled non-stop commercial flights in the world as measured by great-circle distance—13,804 kilometres, which is over one third of the distance around Earth.

First class is a travel class on some passenger airliners intended to be more luxurious than business class, premium economy, and economy class. Originally all planes offered only one class of service, with a second class appearing first in 1955 when TWA introduced two different types of service on its Super Constellations.

















