Related Research Articles

The Burgundians were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and were later moved into the empire, in eastern Gaul. They were possibly mentioned much earlier in the time of the Roman Empire as living in part of the region of Germania that is now part of Poland.

The Marcomanni were a Germanic people that established a powerful kingdom north of the Danube, somewhere near modern Bohemia, during the peak of power of the nearby Roman Empire. According to Tacitus and Strabo, they were Suebian.

The Suebi were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own names such as the Marcomanni, Quadi, Hermunduri, Semnones, and Lombards. New groupings formed later, such as the Alamanni and Bavarians, and two kingdoms in the Migration Period were simply referred to as Suebian.

The Irminones, also referred to as Herminones or Hermiones, were a large group of early Germanic tribes settling in the Elbe watershed and by the first century AD expanding into Bavaria, Swabia, and Bohemia. Notably this included the large sub-group of the Suevi, that itself contained many different tribal groups, but the Irminones also included for example the Chatti.

The Quadi were a Germanic people who lived approximately in the area of modern Moravia in the time of the Roman Empire. The only surviving contemporary reports about the Germanic tribe are those of the Romans, whose empire had its border on the River Danube just to the south of the Quadi. They associated the Quadi with their neighbours the Marcomanni, and described both groups as having entered the region after the Celtic Boii had left it deserted. The Quadi may later have contributed to the "Suebian" group who crossed the Rhine with the Vandals and Alans in the 406 Crossing of the Rhine, and later founded a kingdom in northwestern Iberia.

Legio I Minervia was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in AD 82 by emperor Domitian (r. 81–96), for his campaign against the Germanic tribe of the Chatti. Its cognomen refers to the goddess Minerva, the legion's protector. There are still records of the I Minervia in the Rhine border region in the middle of the 4th century. The legion's emblem is an image of goddess Minerva.

The Lugii were a large tribal confederation mentioned by Roman authors living in ca. 100 BC–300 AD in Central Europe, north of the Sudetes mountains in the basin of upper Oder and Vistula rivers, covering most of modern southern and middle Poland.

Legio III Italica was a legion of the Imperial Roman army founded in 165 AD by the emperor Marcus Aurelius for his campaign against the Marcomanni tribe. The cognomen Italica suggests that the legion's original recruits were drawn for the defence of Italy. The legion was still active in Raetia and other provinces in the early 5th century.
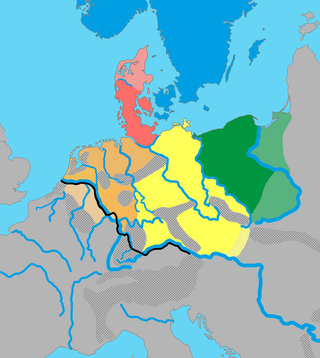
The Istvaeones were a Germanic group of tribes living near the banks of the Rhine during the Roman Empire which reportedly shared a common culture and origin. The Istaevones were contrasted to neighbouring groups, the Ingaevones on the North Sea coast, and the Herminones, living inland of these groups.

The Hermunduri, Hermanduri, Hermunduli, Hermonduri, or Hermonduli were an ancient Germanic tribe, who occupied an inland area near the source of the Elbe river, around what is now Bohemia from the first to the third century, though they have also been speculatively associate with Thuringia further north. According to an old proposal based on the similarty of the names, the Thuringii may have been the descendants of the Hermunduri. At times, they apparently moved to the Danube frontier with Rome. Claudius Ptolemy mentions neither tribe in his geography but instead the Teuriochaemae, who may also be connected to both.

The Juthungi were a Germanic tribe in the region north of the rivers Danube and Altmühl in what is now the modern German state of Bavaria.
The Limes Germanicus is the name given in modern times to a line of frontier fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubdued Germanic tribes from the years 83 to about 260 AD. The Limes used either a natural boundary such as a river or typically an earth bank and ditch with a wooden palisade and watchtowers at intervals. A system of linked forts was built behind the Limes.

The Varisci were a Germanic tribe, the presumed prior inhabitants of a medieval district, Provincia Variscorum, the same as the Vogtland district of Saxony in Germany. They do not appear under that name exactly in ancient history, however, but rather come on stage boldly and abruptly in the Germania of Tacitus as the Naristi, with manuscript variants of Narisci and Varisti. Perhaps the historical name of the mediaeval province is to be regarded as the final authority, but there are other possibilities:

The Ravenna Cosmography is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Textual evidence indicates that the author frequently used maps as his source.

The Buri were a Germanic tribe mentioned in the Germania of Tacitus, where they initially "close the back" of the Marcomanni and Quadi of Bohemia and Moravia. It is said that their speech and customs were like those of the Suebi. Such a statement implies that the Buri had recently come from the direction of the Baltic Sea, as other Germanic settlers in Bohemia and Moravia were newcomers, having driven out the Celtic Boii, or more likely absorbing and incorporating them after defeating them in battle and establishing a new authority. In Tacitus, the Buri are not linked to the Lugii.
Laeti, the plural form of laetus, was a term used in the late Roman Empire to denote communities of barbari ("barbarians"), i.e. foreigners, or people from outside the Empire, permitted to settle on, and granted land in, imperial territory on condition that they provide recruits for the Roman military. The term laetus is of uncertain origin. It means "lucky" or "happy" in Latin but may derive from a non-Latin word. It may derive from a Germanic word meaning "serf" or "half-free colonist". Other authorities suggest the term was of Celtic or Iranian origin.

Serbinum, also known as Serbitium or Serbicium, was an ancient Roman city in the province of Pannonia. It was situated in the location of present-day Gradiška in northern Bosnia and Herzegovina.
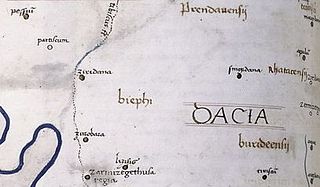
Zurobara was a Dacian town located in the northwest of today's Romanian Banat. It was positioned by the Tibiscus (Timiș) river, north of Sarmizegetusa Regia and south of Ziridava.
Caenophrurium was a settlement in the Roman province of Europa, between Byzantium and Heraclea Perinthus. It appears in late Roman and early Byzantine accounts. Caenophrurium translates as the "stronghold of the Caeni", a Thracian tribe.
References
- ↑ Agustí Alemany, Sources on the Alans: A Critical Compilation (Brill, 2000), pp. 52–53.
- ↑ Ludwig Rübekeil, "Tufa und Armilausini: Namen und Appellativa im römisch-germanischen Sprachkontakt", Beiträge zur Geschichte der deutschen Sprache und Literatur 142, 2 (2020): 185–213.