
H. Lundbeck A/S is a Danish international pharmaceutical company engaged in the research, development, manufacturing, marketing and sale of pharmaceuticals across the world. The company’s products are targeted at brain diseases, including depression, schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and migraine.
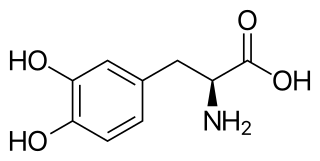
l-DOPA, also known as levodopa and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine. l-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. In some plant families, l-DOPA is the central precursor of a biosynthetic pathway that produces a class of pigments called betalains. l-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.

Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended because of widespread drug resistance. It acts as a nicotinic antagonist, dopamine agonist, and noncompetitive NMDA antagonist. The antiviral mechanism of action is antagonism of the influenzavirus A M2 proton channel, which prevents endosomal escape.

Rasagiline is an irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase-B used as a monotherapy to treat symptoms in early Parkinson's disease or as an adjunct therapy in more advanced cases.

Nalmefene is a medication that is used in the treatment of opioid overdose and alcohol dependence. Nalmefene belongs to the class of opioid antagonists and can be taken by mouth, administered by injection, or delivered through nasal administration.

Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor from the phenyltropane family of drugs, which is being developed for the treatment of obesity. Tesofensine was originally developed by a Danish biotechnology company, NeuroSearch, who transferred the rights to Saniona in 2014.
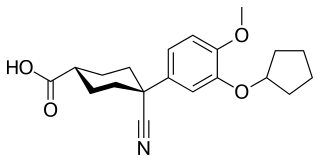
Cilomilast is a drug which was developed for the treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is orally active and acts as a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor.

Droxidopa is a synthetic amino acid precursor which acts as a prodrug to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Unlike norepinephrine, droxidopa is capable of crossing the protective blood–brain barrier (BBB).

Nepicastat is an inhibitor of dopamine beta-hydroxylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine.
Vedolizumab, sold under the brand name Entyvio, is a monoclonal antibody medication developed by Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for the treatment of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It binds to integrin α4β7, blocking the α4β7 integrin results in gut-selective anti-inflammatory activity.

TopoTarget was a Copenhagen-based biotechnology company focused on the discovery and development of drugs and therapies to treat cancer. In 2014, it merged with BioAlliance Pharma and is now part of Onxeo.

Pimavanserin, sold under the brand name Nuplazid, is an atypical antipsychotic which is approved for the treatment of Parkinson's disease psychosis and is also being studied for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease psychosis, schizophrenia, agitation, and major depressive disorder. Unlike other antipsychotics, pimavanserin is not a dopamine receptor antagonist.
Bagadilico, Basal Ganglia Disorders Linnaeus Consortium, is a research group in Lund, Sweden, and a Linnaeus environment, supported by the Swedish Research Council. The group comprises about 120 researchers at either Lund University or Lund University Hospital.

Losmapimod (GW856553X) is an investigational drug being developed by Fulcrum Therapeutics for the treatment of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD); a phase III clinical trial is pending approval. Losmapimod selectively inhibits enzymes p38α/β mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which are modulators of DUX4 expression and mediators of inflammation.

Acorda Therapeutics, Inc. is an American biotechnology company based in Pearl River, New York. The company develops therapies that improve neurological function in people with Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis and other neurological disorders. Acorda Therapeutics manufactures and markets the drugs Inbrija and Ampyra (dalfampridine) in the United States.

A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly referred to as a PDE4 inhibitor, is a drug used to block the degradative action of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is a member of the larger family of PDE inhibitors. The PDE4 family of enzymes are the most prevalent PDE in immune cells. They are predominantly responsible for hydrolyzing cAMP within both immune cells and cells in the central nervous system.

Brexpiprazole, sold under the brand name Rexulti among others, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder, schizophrenia, and agitation associated with dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. It is an atypical antipsychotic.
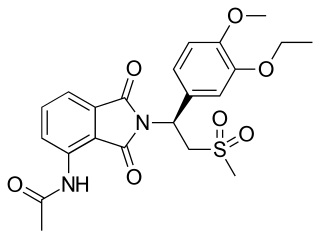
Apremilast, sold under the brand name Otezla among others, is a medication for the treatment of certain types of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. The drug acts as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and inhibits spontaneous production of TNF-alpha from human rheumatoid synovial cells. It is taken by mouth.

Spark Therapeutics, Inc. is a developer of gene therapy treatments, which treat debilitating genetic diseases. It is a subsidiary of Hoffmann-La Roche.

Phenserine is a synthetic drug which has been investigated as a medication to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD), as the drug exhibits neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects.

















