Hydrobromic acid is a strong acid formed by dissolving the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide (HBr) in water. "Constant boiling" hydrobromic acid is an aqueous solution that distills at 124.3 °C (255.7 °F) and contains 47.6% HBr by mass, which is 8.77 mol/L. Hydrobromic acid has a pKa of −9, making it a stronger acid than hydrochloric acid, but not as strong as hydroiodic acid. Hydrobromic acid is one of the strongest mineral acids known.
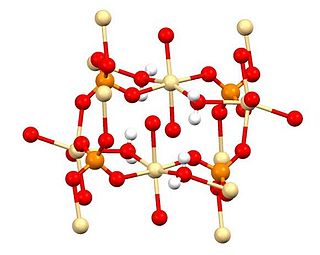
Cadmium sulfate is the name of a series of related inorganic compounds with the formula CdSO4·xH2O. The most common form is the monohydrate CdSO4·H2O, but two other forms are known CdSO4·8⁄3H2O and the anhydrous salt (CdSO4). All salts are colourless and highly soluble in water.

Hydrogen bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula HBr. It is a hydrogen halide consisting of hydrogen and bromine. A colorless gas, it dissolves in water, forming hydrobromic acid, which is saturated at 68.85% HBr by weight at room temperature. Aqueous solutions that are 47.6% HBr by mass form a constant-boiling azeotrope mixture that boils at 124.3 °C. Boiling less concentrated solutions releases H2O until the constant-boiling mixture composition is reached.

Cadmium chloride is a white crystalline compound of cadmium and chloride, with the formula CdCl2. This salt is a hygroscopic solid that is highly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol. The crystal structure of cadmium chloride (described below), is a reference for describing other crystal structures. Also known are CdCl2•H2O and the hemipenahydrate CdCl2•2.5H2O.

Cadmium fluoride (CdF2) is a mostly water-insoluble source of cadmium used in oxygen-sensitive applications, such as the production of metallic alloys. In extremely low concentrations (ppm), this and other fluoride compounds are used in limited medical treatment protocols. Fluoride compounds also have significant uses in synthetic organic chemistry. The standard enthalpy has been found to be -167.39 kcal. mole−1 and the Gibbs energy of formation has been found to be -155.4 kcal. mole−1, and the heat of sublimation was determined to be 76 kcal. mole−1.

Cadmium oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CdO. It is one of the main precursors to other cadmium compounds. It crystallizes in a cubic rocksalt lattice like sodium chloride, with octahedral cation and anion centers. It occurs naturally as the rare mineral monteponite. Cadmium oxide can be found as a colorless amorphous powder or as brown or red crystals. Cadmium oxide is an n-type semiconductor with a band gap of 2.18 eV at room temperature.

Zinc bromide (ZnBr2) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnBr2. It is a colourless salt that shares many properties with zinc chloride (ZnCl2), namely a high solubility in water forming acidic solutions, and good solubility in organic solvents. It is hygroscopic and forms a dihydrate ZnBr2·2H2O.

Chromyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula CrO2Cl2. It is a reddish brown compound that is a volatile liquid at room temperature, which is unusual for transition metal compounds.

Arsenic tribromide is the inorganic compound with the formula AsBr3. This pyramidal molecule is the only known binary arsenic bromide. AsBr3 is noteworthy for its very high refractive index of approximately 2.3. It also has a very high diamagnetic susceptibility. The compound exists as colourless deliquescent crystals that fume in moist air.

Copper(II) bromide (CuBr2) is a chemical compound that forms an unstable tetrahydrate CuBr2·4H2O. It is used in photographic processing as an intensifier and as a brominating agent in organic synthesis.
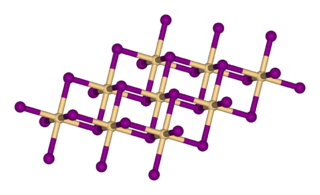
Cadmium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula CdI2. It is a white hygroscopic solid. It also can be obtained as a mono- and tetrahydrate. It has few applications. It is notable for its crystal structure, which is typical for compounds of the form MX2 with strong polarization effects.
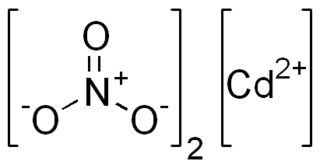
Cadmium nitrate describes any of the related members of a family of inorganic compounds with the general formula , the most commonly encountered form being the tetrahydrate. The anhydrous form is volatile, but the others are colourless crystalline solids that are deliquescent, tending to absorb enough moisture from the air to form an aqueous solution. Like other cadmium compounds, cadmium nitrate is known to be carcinogenic.

Copper(I) bromide is the chemical compound with the formula CuBr. This diamagnetic solid adopts a polymeric structure akin to that for zinc sulfide. The compound is widely used in the synthesis of organic compounds and as a lasing medium in copper bromide lasers.

Beryllium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BeBr2. It is very hygroscopic and dissolves well in water. The compound is a polymer with tetrahedral coordinated Be centres.

Cadmium(I) tetrachloroaluminate is the inorganic compound with the formula Cd2[AlCl4]2, a tetrachloroaluminate of cadmium(I). It was the first compound reported (1961) that contained cadmium in the +1 oxidation state and features a cadmium–cadmium bond.

Cadmium acetate is the chemical compound with the formula Cd(O2CCH3)2(H2O)2. The compound is marketed both as the anhydrous form and as a dihydrate, both of which are white or colorless. Only the dihydrate has been verified by X-ray crystallography.

Cadmium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(CN)2. It is a white crystalline compound that is used in electroplating. It is very toxic, along with other cadmium and cyanide compounds.
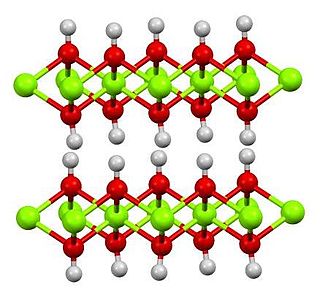
Cadmium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Cd(OH)2. It is a white crystalline ionic compound that is a key component of nickel–cadmium battery.

Chromium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrBr3. It is a dark colored solid that appears green in transmitted light but red with reflected light. It is used as a precursor to catalysts for the oligomerization of ethylene.

Chromium(II) bromide is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula CrBr2. Like many metal dihalides, CrBr2 adopts the "cadmium iodide structure" motif, i.e., it features sheets of octahedral Cr(II) centers interconnected by bridging bromide ligands. It is a white solid that dissolves in water to give blue solutions that are readily oxidized by air.























