
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard.

Adobe Flash was, except in China, a multimedia software platform used for production of animations, rich internet applications, desktop applications, mobile apps, mobile games, and embedded web browser video players.

Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. Based on the PostScript language, each PDF file encapsulates a complete description of a fixed-layout flat document, including the text, fonts, vector graphics, raster images and other information needed to display it. PDF has its roots in "The Camelot Project" initiated by Adobe co-founder John Warnock in 1991. PDF was standardized as ISO 32000 in 2008. The last edition as ISO 32000-2:2020 was published in December 2020.

Wolfram Mathematica is a software system with built-in libraries for several areas of technical computing that allow machine learning, statistics, symbolic computation, data manipulation, network analysis, time series analysis, NLP, optimization, plotting functions and various types of data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other programming languages. It was conceived by Stephen Wolfram, and is developed by Wolfram Research of Champaign, Illinois. The Wolfram Language is the programming language used in Mathematica. Mathematica 1.0 was released on June 23, 1988 in Champaign, Illinois and Santa Clara, California.

Stephen Wolfram is a British-American metamathematician, mathematician, computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and theoretical physics. In 2012, he was named a fellow of the American Mathematical Society.
Sarah Flannery was, at sixteen years old, the winner of the 1999 Esat Young Scientist Exhibition for her development of the Cayley–Purser algorithm, based on work she had done with researchers at Baltimore Technologies during a brief internship there. The project, entitled "Cryptography – A new algorithm versus the RSA", also won her the EU Young Scientist of the Year Award in 1999.

ZDNET is a business technology news website owned and operated by Red Ventures. The brand was founded on April 1, 1991, as a general interest technology portal from Ziff Davis and evolved into an enterprise IT–focused online publication.
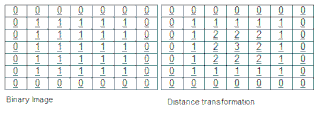
A distance transform, also known as distance map or distance field, is a derived representation of a digital image. The choice of the term depends on the point of view on the object in question: whether the initial image is transformed into another representation, or it is simply endowed with an additional map or field.

Wolfram Research, Inc. is an American multinational company that creates computational technology. Wolfram's flagship product is the technical computing program Wolfram Mathematica, first released on June 23, 1988. Other products include WolframAlpha, Wolfram SystemModeler, Wolfram Workbench, gridMathematica, Wolfram Finance Platform, webMathematica, the Wolfram Cloud, and the Wolfram Programming Lab. Wolfram Research founder Stephen Wolfram is the CEO. The company is headquartered in Champaign, Illinois, United States.
gridMathematica is a software product sold by Wolfram Research which extends the parallel processing capabilities of its main product Mathematica.

The Wolfram Demonstrations Project is an organized, open-source collection of small interactive programmes called Demonstrations, which are meant to visually and interactively represent ideas from a range of fields. It is hosted by Wolfram Research, whose stated goal is to bring computational exploration to a large population. At its launch, it contained 1300 demonstrations but has grown to over 10,000. The site won a Parents' Choice Award in 2008.
Natural-language programming (NLP) is an ontology-assisted way of programming in terms of natural-language sentences, e.g. English. A structured document with Content, sections and subsections for explanations of sentences forms a NLP document, which is actually a computer program. Natural language programming is not to be mixed up with natural language interfacing or voice control where a program is first written and then communicated with through natural language using an interface added on. In NLP the functionality of a program is organised only for the definition of the meaning of sentences. For instance, NLP can be used to represent all the knowledge of an autonomous robot. Having done so, its tasks can be scripted by its users so that the robot can execute them autonomously while keeping to prescribed rules of behaviour as determined by the robot's user. Such robots are called transparent robots as their reasoning is transparent to users and this develops trust in robots. Natural language use and natural-language user interfaces include Inform 7, a natural programming language for making interactive fiction, Shakespeare, an esoteric natural programming language in the style of the plays of William Shakespeare, and Wolfram Alpha, a computational knowledge engine, using natural-language input. Some methods for program synthesis are based on natural-language programming.
NetCDF is a set of software libraries and self-describing, machine-independent data formats that support the creation, access, and sharing of array-oriented scientific data. The project homepage is hosted by the Unidata program at the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). They are also the chief source of netCDF software, standards development, updates, etc. The format is an open standard. NetCDF Classic and 64-bit Offset Format are an international standard of the Open Geospatial Consortium.
WolframAlpha is an answer engine developed by Wolfram Research. It is offered as an online service that answers factual queries by computing answers from externally sourced data.

Conrad Wolfram is a British technologist and businessman known for his work in information technology and mathematics education reform. In June 2020, Wolfram released his first book, The Math(s) Fix: An Education Blueprint for the AI Age.

The Wolfram Language is a proprietary, general high-level multi-paradigm programming language developed by Wolfram Research. It emphasizes symbolic computation, functional programming, and rule-based programming and can employ arbitrary structures and data. It is the programming language of the mathematical symbolic computation program Mathematica.

A notebook interface or computational notebook is a virtual notebook environment used for literate programming, a method of writing computer programs. Some notebooks are WYSIWYG environments including executable calculations embedded in formatted documents; others separate calculations and text into separate sections. Notebooks share some goals and features with spreadsheets and word processors but go beyond their limited data models.

Project Jupyter is a project to develop open-source software, open standards, and services for interactive computing across multiple programming languages.













