Related Research Articles
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) is an Internet standard that extends the format of email messages to support text in character sets other than ASCII, as well as attachments of audio, video, images, and application programs. Message bodies may consist of multiple parts, and header information may be specified in non-ASCII character sets. Email messages with MIME formatting are typically transmitted with standard protocols, such as the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), the Post Office Protocol (POP), and the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP).

Portable Network Graphics is a raster-graphics file format that supports lossless data compression. PNG was developed as an improved, non-patented replacement for Graphics Interchange Format (GIF).
PCX, standing for PiCture eXchange, is an image file format developed by the now-defunct ZSoft Corporation of Marietta, Georgia, United States. It was the native file format for PC Paintbrush and became one of the first widely accepted DOS imaging standards, although it has since been succeeded by more sophisticated image formats, such as BMP, JPEG, and PNG. PCX files commonly stored palette-indexed images ranging from 2 or 4 colors to 16 and 256 colors, although the format has been extended to record true-color (24-bit) images as well.
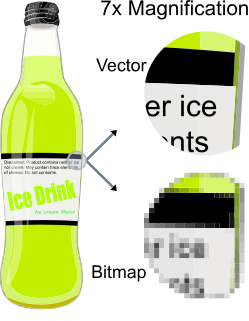
Vector graphics are computer graphics images that are defined in terms of points on a Cartesian plane, which are connected by lines and curves to form polygons and other shapes. Vector graphics have the unique advantage over raster graphics in that the points, lines, and curves may be scaled up or down to any resolution with no aliasing. The points determine the direction of the vector path; each path may have various properties including values for stroke color, shape, curve, thickness, and fill.

Tag Image File Format, abbreviated TIFF or TIF, is a computer file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and photographers. TIFF is widely supported by scanning, faxing, word processing, optical character recognition, image manipulation, desktop publishing, and page-layout applications. The format was created by the Aldus Corporation for use in desktop publishing. It published the latest version 6.0 in 1992, subsequently updated with an Adobe Systems copyright after the latter acquired Aldus in 1994. Several Aldus or Adobe technical notes have been published with minor extensions to the format, and several specifications have been based on TIFF 6.0, including TIFF/EP, TIFF/IT, TIFF-F and TIFF-FX.
The BMP file format, also known as bitmap image file, device independent bitmap (DIB) file format and bitmap, is a raster graphics image file format used to store bitmap digital images, independently of the display device, especially on Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems.
Truevision TGA, often referred to as TARGA, is a raster graphics file format created by Truevision Inc.. It was the native format of TARGA and VISTA boards, which were the first graphic cards for IBM-compatible PCs to support Highcolor/truecolor display. This family of graphic cards was intended for professional computer image synthesis and video editing with PCs; for this reason, usual resolutions of TGA image files match those of the NTSC and PAL video formats.

X PixMap (XPM) is an image file format used by the X Window System, created in 1989 by Daniel Dardailler and Colas Nahaboo working at Bull Research Center at Sophia Antipolis, France, and later enhanced by Arnaud Le Hors.
Animated Portable Network Graphics (APNG) is a file format which extends the Portable Network Graphics (PNG) specification to permit animated images that work similarly to animated GIF files, while supporting 24-bit images and 8-bit transparency not available for GIFs. It also retains backward compatibility with non-animated PNG files.
3GP is a multimedia container format defined by the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) for 3G UMTS multimedia services. It is used on 3G mobile phones but can also be played on some 2G and 4G phones.
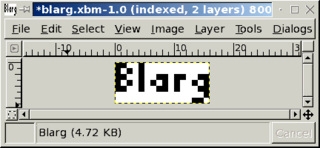
In computer graphics, the X Window System used X BitMap (XBM), a plain text binary image format, for storing cursor and icon bitmaps used in the X GUI. The XBM format is superseded by XPM, which first appeared for X11 in 1989.
The Cineon System was one of the first computer based digital film systems, created by Kodak in the early 1990s. It was an integrated suite of components consisting a Motion picture film scanner, a film recorder and workstation hardware with software for compositing, visual effects, image restoration and color management.
Netpbm is an open-source package of graphics programs and a programming library. It is used mainly in the Unix world, where one can find it included in all major open-source operating system distributions, but also works on Microsoft Windows, macOS, and other operating systems.

XnView is an image organizer and general-purpose file manager used for viewing, converting, organizing and editing raster images, as well as general purpose file management. It comes with built-in hex inspection, batch renaming and screen capture tools. It is licensed as freeware for private, educational and non-profit uses. For other uses, it is licensed as commercial software.
In the X Window System, the program xwd captures the content of a screen or of a window and optionally saves it into a file.
Radiance is a suite of tools for performing lighting simulation originally written by Greg Ward. It includes a renderer as well as many other tools for measuring the simulated light levels. It uses ray tracing to perform all lighting calculations, accelerated by the use of an octree data structure. It pioneered the concept of high-dynamic-range imaging, where light levels are (theoretically) open-ended values instead of a decimal proportion of a maximum or integer fraction of a maximum. It also implements global illumination using the Monte Carlo method to sample light falling on a point.
Silicon Graphics Image (SGI) or the RGB file format is the native raster graphics file format for Silicon Graphics workstations. The format was invented by Paul Haeberli. It can be run-length encoded (RLE). FFmpeg and ImageMagick, among others, support this format.

PCPaint was the first IBM PC-based mouse-driven GUI paint program. It was developed by John Bridges and Doug Wolfgram. It was later developed into Pictor Paint.
PICtor is an image file format developed by John Bridges, the principal author of PCPaint, the first Paintbrush program for the PC. It was also the native file format for Pictor Paint and Graphics Animation System for Professionals (GRASP) and became the first widely accepted DOS imaging standard.
This article presents a comparison of image viewers and image organizers which can be used for image viewing.
References
- ↑ Murray, James D.; vanRyper, William (May 1996). Encyclopedia of Graphics File Formats (Second ed.). O'Reilly. sunraster. ISBN 978-1-56592-161-0 . Retrieved 2014-02-27.
- ↑ .ras MIME type not registered at IANA
- ↑ McLaughlin, L., ed. (August 1990). "Print raster file". Line Printer Daemon Protocol. IETF. sec. 7.28. doi: 10.17487/RFC1179 . RFC 1179 . Retrieved 2014-03-13.
- ↑ Werner, Charles; Wegmüller, Urs; Strozzi, Tazio; Wiesmann, Andreas (October 2000). "Gamma SAR and interferometric processing software" (PDF). Retrieved 2014-03-12.
- ↑ Sofer, Nir. ".ras Extension" . Retrieved 2014-01-12.
- ↑ "File Type: Sun Raster Image". Windows File Association. Microsoft. 2013. Retrieved 2014-01-12.
- ↑ "Image Formats". FFmpeg General Documentation. 2014. Retrieved 2014-02-23.
- ↑ Murray, James D.; vanRyper, William (May 1996). Encyclopedia of Graphics File Formats (Second ed.). O'Reilly. sunicon. ISBN 978-1-56592-161-0 . Retrieved 2014-02-27.