
A hairstyle, hairdo, haircut or coiffure refers to the styling of hair, usually on the human head but sometimes on the face or body. The fashioning of hair can be considered an aspect of personal grooming, fashion, and cosmetics, although practical, cultural, and popular considerations also influence some hairstyles.

The crab louse or pubic louse is an insect that is an obligate ectoparasite of humans, feeding exclusively on blood. The crab louse usually is found in the person's pubic hair. Although the louse cannot jump, it can also live in other areas of the body that are covered with coarse hair, such as the perianal area, the entire body, and the eyelashes.
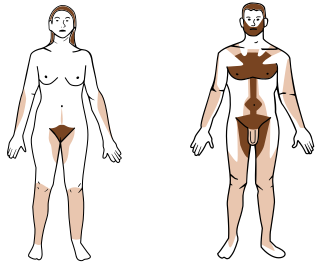
Hair removal, also known as epilation or depilation, is the deliberate removal of body hair or head hair.

Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring is not usually present. Hair loss in some people causes psychological distress.

A wig is a head covering made from human or animal hair, or a synthetic imitation thereof. The word is short for "periwig". Wigs may be worn to disguise baldness, to alter the wearer's appearance, or as part of certain professional uniforms.

Human hair color is the pigmentation of human hair follicles and shafts due to two types of melanin: eumelanin and pheomelanin. Generally, the more melanin present, the darker the hair. Its tone depends on the ratio of black or brown eumelanin to yellow or red pheomelanin. Levels of melanin can vary over time, causing a person's hair color to change, and it is possible for one person to have hair follicles of more than one color. Some hair colors are associated with some ethnic groups because of observed higher frequency of particular hair color within their geographical region, e.g. straight, dark hair amongst East Asians, Southeast Asians, Polynesians, some Central Asians, and Native Americans; a large variety of dark, fair, curly, straight, wavy or bushy amongst Europeans, West Asians, some Central Asians, and North Africans; and curly, dark, and uniquely helical hair amongst Sub Saharan Africans. Bright red hair is found in some European populations, and hair often turns gray, white, or "silver" with age.

An erogenous zone is an area of the human body that has heightened sensitivity, the stimulation of which may generate a sexual response, such as relaxation, sexual fantasies, sexual arousal and orgasm.

Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.

An eyebrow is an area of short hairs above each eye that follows the shape of the lower margin of the brow ridges of some mammals. In humans, eyebrows serve two main functions: first, communication through facial expression, and second, prevention of sweat, water, and other debris from falling down into the eye socket. It is common for people to modify their eyebrows by means of hair removal and makeup.

Hair coloring, or hair dyeing, is the practice of changing the color of the hair on humans' heads. The main reasons for this are cosmetic: to cover gray or white hair, to alter hair to create a specific look, to change a color to suit preference or to restore the original hair color after it has been discolored by hairdressing processes or sun bleaching.

Cosmetology is the study and application of beauty treatment. Branches of specialty include hairstyling, skin care, cosmetics, manicures/pedicures, non-permanent hair removal such as waxing and sugaring, and permanent hair removal processes such as electrology and intense pulsed light (IPL).

A hairbrush is a brush with rigid or light and soft spokes used in hair care for smoothing, styling, and detangling human hair, or for grooming an animal's fur. It can also be used for styling in combination with a curling iron or hair dryer.

Goose bumps, goosebumps or goose-pimples are the bumps on a person's skin at the base of body hairs which may involuntarily develop when a person is tickled, cold or experiencing strong emotions such as fear, euphoria or sexual arousal.

Hair conditioner is a hair care cosmetic product used to improve the feel, texture, appearance and manageability of hair. Its main purpose is to reduce friction between strands of hair to allow smoother brushing or combing, which might otherwise cause damage to the scalp. Various other benefits are often advertised, such as hair repair, strengthening, or a reduction in split ends.

Aders's duiker, also known as nunga in Swahili, kunga marara in Kipokomo and harake in Giriama, is a small, forest-dwelling duiker found only in Zanzibar and Kenya. It may be a subspecies of the red, Harvey's, or Peters's duiker or a hybrid of a combination of these. It is named after W. Mansfield Aders, a zoologist with the Zanzibar Government Service.

Dermatophytosis, also known as tinea and ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin, that may affect skin, hair, and nails. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. The types of dermatophytosis are typically named for area of the body that they affect. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time.
Artificial hair integrations, more commonly known as hair extensions, hair weaves, and fake hair add length and fullness to human hair. Hair extensions are usually clipped, glued, or sewn on natural hair by incorporating additional human or synthetic hair. These methods include tape-in extensions, clip-in or clip-on extensions, micro/nano rings, fusion method, weaving method, and wigs.

Auburn hair is a human hair color, a variety of red hair, most commonly described as reddish-brown in color. Auburn hair ranges in shades from medium to dark. It can be found with a wide array of skin tones and eye colors. The chemical pigments that cause the coloration of auburn hair are frequently pheomelanin with high levels of eumelanin; however, the auburn hair is due to a mutated melanocortin 1 receptor gene in Northwestern European people and by a mutated TYRP1 gene in the Melanesians and Austronesians, both genes that reduce the melanin production of the hair cells.

A kinocilium is a special type of cilium on the apex of hair cells located in the sensory epithelium of the vertebrate inner ear. Contrasting with stereocilia, which are numerous, there is only one kinocilium on each hair cell. The kinocilium can be identified by its apical position as well as its enlarged tip.

Markings on horses are usually distinctive white areas on an otherwise dark base coat color. Most horses have some markings, and they help to identify the horse as a unique individual. Markings are present at birth and do not change over the course of the horse's life. Most markings have pink skin underneath most of the white hairs, though a few faint markings may occasionally have white hair with no underlying pink skin. Markings may appear to change slightly when a horse grows or sheds its winter coat, however this difference is simply a factor of hair coat length; the underlying pattern does not change.



















