
Dartmouth Dam is a large rock-fill embankment dam with an uncontrolled chute spillway across the Mitta Mitta, Gibbo and Dart rivers, the Morass Creek and a number of small tributaries. The dam is located near Mount Bogong in the north-east of the Australian state of Victoria. The dam's purpose includes irrigation, the generation of hydro-electric power, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Dartmouth Reservoir, sometimes called Lake Dartmouth. The Dartmouth Power Station, a hydro-electric power station that generates power to the national grid, is located near the dam wall.

Hume Dam, formerly the Hume Weir, is a major dam across the Murray River downstream of its junction with the Mitta River in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's purpose includes flood mitigation, hydro-power, irrigation, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Lake Hume, formerly the Hume Reservoir. It is a gated concrete gravity dam with four earth embankments and twenty-nine vertical undershot gated concrete overflow spillways.

Burrendong Dam is a rock-fill embankment major gated dam with a clay core across the Macquarie River upstream of Wellington in the central west region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's purpose includes flood mitigation, irrigation, water supply and hydro-electric power generation. The dam impounds Lake Burrendong and is filled by the waters from the Macquarie, and Cudgegong rivers as well as Meroo Creek.

The Gariep Dam is located in South Africa, near the town of Norvalspont, bordering the Free State and Eastern Cape provinces. Its primary purpose is for irrigation, domestic and industrial use as well as for power generation. It the largest dam in South Africa.

Burrinjuck Dam is a heritage-listed major gated concrete-walled gravity hydro-electric dam at Burrinjuck, Yass Valley Shire, New South Wales, Australia. It has three spillways across the Murrumbidgee River located in the South West Slopes region of New South Wales, Australia. The dam's purpose includes flood mitigation, hydro-power, irrigation, water supply and conservation. The impounded reservoir is called Lake Burrinjuck. It was designed by Lawrence Augustus Burton Wade and built from 1907 to 1927 by Lane & Peters, Sydney. It is also known as Barren Jack Dam and Barrenjack. The property was owned by Department of Planning and Infrastructure. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is a masonry dam across the Krishna River at Nagarjuna Sagar which straddles the border between Palnadu district in Andhra Pradesh and Nalgonda district in Telangana. The dam provides irrigation water to the districts of Palnadu, Guntur, Nalgonda, Prakasam, Khammam, Krishna, and parts of West Godavari. It is also a source of electricity generation for the national grid.

The Srisailam Dam is constructed across the Krishna River in Nandyal district, Andhra Pradesh and Nagarkurnool district, Telangana near Srisailam temple town and is the 2nd largest capacity working hydroelectric station in India.

Lake Qaraoun is an artificial lake or reservoir located in the southern region of the Beqaa Valley, Lebanon. It was created near Qaraoun village in 1959 by building a 61 m-high (200 ft) concrete-faced rockfill dam in the middle reaches of the Litani River. The reservoir has been used for hydropower generation, domestic water supply, and for irrigation of 27,500 ha.

Ujjani Dam, also known as Bhima Dam or Bhima Irrigation Project, on the Bhima River, a tributary of the Krishna River, is an earthfill cum Masonry gravity dam located near Ujjani village of Madha Taluk in Solapur district of the state of Maharashtra in India.

Perunchani Dam is an irrigation dam at Perunchani, in Kalkulam Taluk, Kanyakumari District, in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is one of the dams of the Kodayar Irrigation System. As there was water deficiency in the Kodayar Irrigation System, Perunchani Dam was constructed in December 1952 to store flood water of the Paralayar River as an extension. It was built about 1 km (0.62 mi) upstream of the Puthen dam on the Paralayar River. The irrigation system became operational on 2 September 1953. It feeds the left bank irrigation canal system of the Puthen dam, which is the terminal structure of the system.
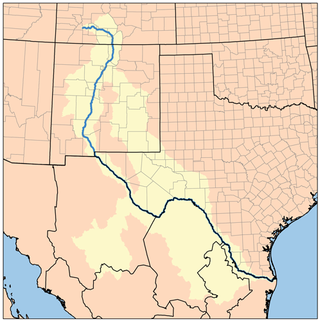
The Rio Grande Project is a United States Bureau of Reclamation irrigation, hydroelectricity, flood control, and interbasin water transfer project serving the upper Rio Grande basin in the southwestern United States. The project irrigates 193,000 acres (780 km2) along the river in the states of New Mexico and Texas. Approximately 60 percent of this land is in New Mexico. Some water is also allotted to Mexico to irrigate some 25,000 acres (100 km2) on the south side of the river. The project was authorized in 1905, but its final features were not implemented until the early 1950s.

Shihmen Dam is a major rock fill dam across the Dahan River in northern Taoyuan City. It forms the Shihmen Reservoir (石門水庫), Taiwan's third largest reservoir or artificial lake. It provides irrigation in Taoyuan, flood control for the Taipei Basin, and hydroelectricity and domestic water supply for more than three million people in northern Taiwan.

The Samarra Barrage is a multi-purpose barrage on the Tigris River adjacent (west) of Samarra and north of Baghdad, Iraq. The main purpose of the dam is to divert floodwater in the Tigris River to Lake Tharthar through the Tharthar depression along with irrigation and an 84 MW hydro-electricity station. It also serves to produce hydroelectric power and flood control – although the later has become less critical with the construction of the Mosul Dam upstream and several other large dams in Turkey.

Voëlvlei Dam is a dam located in the Western Cape, South Africa near the town of Gouda. The earth-fill wall is 2,910 metres (9,550 ft) long and 10 metres (33 ft) high. The reservoir covers an area of 1,524 hectares and has a capacity of 168,000 megalitres, making it the second-largest reservoir in the Western Cape Water Supply System. Water from the reservoir is supplied to water treatment works of the City of Cape Town and the West Coast District Municipality, and can also be released into the Berg River for agricultural purposes or to fill the Misverstand Dam.

Zengwen Dam, also spelled Tsengwen Dam, is a major earthen dam in Dapu Township, Chiayi County, Taiwan on the Zengwen River. It is the third tallest dam in Taiwan, and forms Zengwen Reservoir (曾文水庫), the biggest reservoir in Taiwan by volume. The dam stores water for irrigation of the Chianan Plain, Taiwan's most productive agricultural region, and provides flood control along the Zengwen River which flows through Tainan City. The dam supports a 50 megawatt hydroelectric power station.
Grahamstown Dam is a major off-stream earthfill Embankment dam with a controlled labyrinth spillway and baffle chute that stores water from the Williams River. The dam is located north of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. The dam's main purpose is water supply; it provides about 40 per cent of the potable water for the Hunter Region; and is its largest drinking water supply dam.

Wushantou Dam is an embankment dam in Guantian District, Tainan, Taiwan. The dam was designed by Yoichi Hatta and built between 1920 and 1930 during Japanese rule to provide irrigation water for the Chianan Plain as part of the Chianan Irrigation system. Because the natural flow of the Guantian River and other local streams was insufficient for irrigation of a planned 100,000 ha, a tunnel was constructed to divert water from the Zengwen River to fill the reservoir. In 1974, the Zengwen Dam was completed on the Zengwen River shortly above the diversion tunnel, stabilizing and reducing the sediment load of water flowing into Wushantou Reservoir.

The Bili-Bili Dam is located in Gowa Regency, South Sulawesi, Indonesia, on the Jeneberang River, about 30 km from the city of Makassar. It serves several purposes to include flood control, irrigation and hydroelectric power generation. The dam was constructed between 1991 and 1998.

The Deduru Oya Dam is an embankment dam built across the Deduru River in Kurunegala District of Sri Lanka. Built in 2014, the primary purpose of the dam is to retain for irrigation purposes approximately a billion cubic metres of water, which would otherwise flow out to sea. Site studies of the dam began in 2006 and construction started in 2008. It was ceremonially completed in 2014, with the presence of then President Mahinda Rajapaksa.


















