
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments: vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles.

The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Lymph is a clear fluid carried by the lymphatic vessels back to the heart for re-circulation. The Latin word for lymph, lympha, refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha".

In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle.

The right and left paratracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the neck situated lateral to the trachea and esophagus alongside the recurrent laryngeal nerve. They drain to the deep cervical lymph nodes.

The ansa cervicalis is a loop formed by muscular branches of the cervical plexus formed by branches of cervical spinal nerves C1-C3. The ansa cervicalis has two roots - a superior root and an inferior root - that unite distally, forming a loop. It is situated within the carotid sheath.
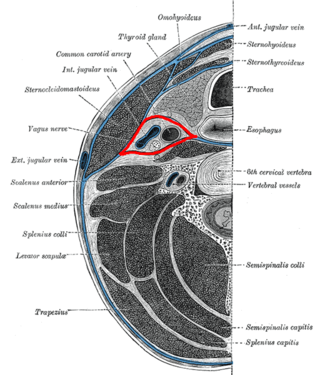
The carotid sheath is a condensation of the deep cervical fascia enveloping multiple vital neurovascular structures of the neck, including the common and internal carotid arteries, the internal jugular vein, the vagus nerve, and ansa cervicalis. The carotid sheath helps protects the structures contained therein.

The deep cervical fascia lies under cover of the platysma, and invests the muscles of the neck; it also forms sheaths for the carotid vessels, and for the structures situated in front of the vertebral column. Its attachment to the hyoid bone prevents the formation of a dewlap.
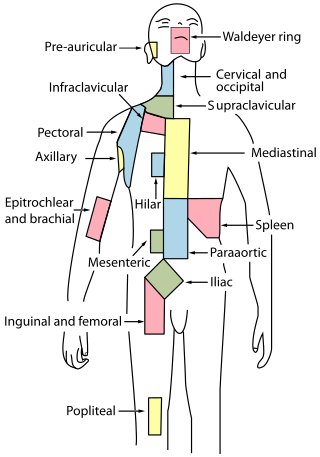
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammation.
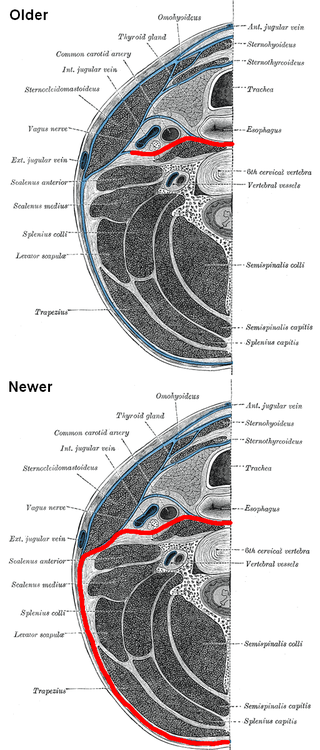
The prevertebral fascia is the layer of deep cervical fascia that surrounds the vertebral column. It is the deepest layer of deep cervical fascia.

The pretracheal fascia is a layer of the deep cervical fascia at the front of the neck. It attaches to the hyoid bone above, and - extending down into the thorax - blends with the fibrous pericardium below. It encloses the thyroid gland and parathyroid glands, trachea, and esophagus. It extends medially in front of the carotid vessels. It assists in forming the carotid sheath.

The jugular trunk is a lymphatic vessel in the neck. It is formed by vessels that emerge from the superior deep cervical lymph nodes and unite to efferents of the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes.

The inferior deep cervical lymph nodes are one of the two groups of the deep cervical lymph nodes.

The superior deep cervical lymph nodes are the deep cervical lymph nodes that are situated adjacent to the superior portion of the internal jugular vein. They drain either to the inferior deep cervical lymph nodes or into the jugular trunk.

The superficial cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes that lie near the surface of the neck.

The deep lateral cervical lymph nodes are found near the upper part of the internal jugular vein in the neck, lateral or posterior to the carotid sheath.

The pretracheal lymph nodes are lymph nodes located anterior to the trachea in the neck.

The parapharyngeal space, is a potential space in the head and the neck. It has clinical importance in otolaryngology due to parapharyngeal space tumours and parapharyngeal abscess developing in this area. It is also a key anatomic landmark for localizing disease processes in the surrounding spaces of the neck; the direction of its displacement indirectly reflects the site of origin for masses or infection in adjacent areas, and consequently their appropriate differential diagnosis.

The meningeal lymphatic vessels are a network of conventional lymphatic vessels located parallel to the dural venous sinuses and middle meningeal arteries of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). As a part of the lymphatic system, the meningeal lymphatics are responsible for draining immune cells, small molecules, and excess fluid from the CNS into the deep cervical lymph nodes. Cerebrospinal fluid, and interstitial fluid are exchanged, and drained by the meningeal lymphatic vessels.

Jonathan Kipnis is a neuroscientist, immunologist, and professor of pathology and immunology at the Washington University School of Medicine. His lab studies interactions between the immune system and nervous system. He is best known for his lab's discovery of meningeal lymphatic vessels in humans and mice, which has impacted research on neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis, neuropsychiatric disorders, such as anxiety, and neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism and Rett syndrome.















