
The large intestine, also known as the large bowel, is the last part of the gastrointestinal tract and of the digestive system in tetrapods. Water is absorbed here and the remaining waste material is stored in the rectum as feces before being removed by defecation. The colon is the longest portion of the large intestine, and the terms are often used interchangeably but most sources define the large intestine as the combination of the cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal. Some other sources exclude the anal canal.

The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine.

The ileum is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum.
Articles related to anatomy include:

In human anatomy, the mesentery, an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall, comprises the double fold of the peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines.

In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.
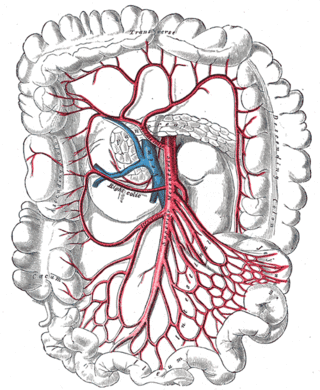
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas.

In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine. Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein that carries blood to the liver. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta.

In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the ascending colon is the part of the colon located between the cecum and the transverse colon.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon.

The left colic artery is a branch of the inferior mesenteric artery distributed to the descending colon, and left part of the transverse colon. It ends by dividing into an ascending branch and a descending branch; the terminal branches of the two branches go on to form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and a sigmoid artery (respectively).

The ileocolic artery is the lowest branch arising from the concavity of the superior mesenteric artery. It supplies the cecum, ileum, and appendix.
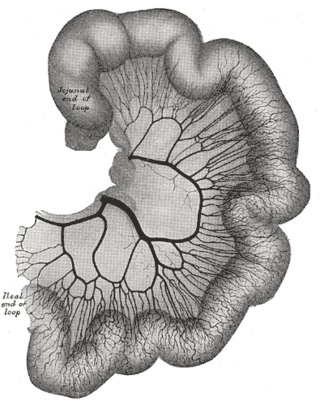
The intestinal arteries arise from the convex side of the superior mesenteric artery. They are usually from twelve to fifteen in number, and are distributed to the jejunum and ileum.

In the anatomy of the human digestive tract, there are two colic flexures, or curvatures in the transverse colon. The right colic flexure is also known as the hepatic flexure, and the left colic flexure is also known as the splenic flexure. Note that "right" refers to the patient's anatomical right, which may be depicted on the left of a diagram.

The midgut is the portion of the human embryo from which most of the intestines develop. After it bends around the superior mesenteric artery, it is called the "midgut loop". It comprises the portion of the alimentary canal from the end of the foregut at the opening of the bile duct to the hindgut, about two-thirds of the way through the transverse colon.

The appendicular artery, also known as the appendiceal artery, commonly arises from the terminal branch of the ileocolic artery, or less commonly from the posterior cecal artery or an ileal artery. It descends behind the termination of the ileum and enters the mesoappendix of the vermiform appendix. It runs near the free margin of the mesoappendix and ends in branches which supply the appendix.

The preaortic lymph nodes lie in front of the aorta, and may be divided into celiac lymph nodes, superior mesenteric lymph nodes, and inferior mesenteric lymph nodes groups, arranged around the origins of the corresponding arteries.

The inferior mesenteric lymph nodes consist of:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to human anatomy:


















