Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for human consumption, but water purification may also be carried out for a variety of other purposes, including medical, pharmacological, chemical, and industrial applications. The history of water purification includes a wide variety of methods. The methods used include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation; biological processes such as slow sand filters or biologically active carbon; chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination; and the use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light.

Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.
Flotation involves phenomena related to the relative buoyancy of objects.

Wastewater treatment is a process which removes and eliminates contaminants from wastewater and converts this into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes. The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater, the treatment plant is called a Sewage Treatment. For industrial wastewater, treatment either takes place in a separate Industrial wastewater treatment, or in a sewage treatment plant. Further types of wastewater treatment plants include Agricultural wastewater treatment and leachate treatment plants.

In colloidal chemistry, flocculation is a process by which colloidal particles come out of suspension to sediment in the form of floc or flake, either spontaneously or due to the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended, under the form of a stable dispersion and are not truly dissolved in solution.

The activated sludgeprocess is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It uses air and microorganisms to biologically oxidize organic pollutants, producing a waste sludge containing the oxidized material.

Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter, toxic pollutants or nutrients such as ammonia. Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants, and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system.

Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower grade ore than previously.

Sand filters are used as a step in the water treatment process of water purification.
Electrocoagulation (EC) is a technique used for wastewater treatment, wash water treatment, industrially processed water, and medical treatment. Electrocoagulation has become a rapidly growing area of wastewater treatment due to its ability to remove contaminants that are generally more difficult to remove by filtration or chemical treatment systems, such as emulsified oil, total petroleum hydrocarbons, refractory organics, suspended solids, and heavy metals. There are many brands of electrocoagulation devices available and they can range in complexity from a simple anode and cathode to much more complex devices with control over electrode potentials, passivation, anode consumption, cell REDOX potentials as well as the introduction of ultrasonic sound, ultraviolet light and a range of gases and reactants to achieve so-called Advanced Oxidation Processes for refractory or recalcitrant organic substances.
Sedimentation is a physical water treatment process using gravity to remove suspended solids from water. Solid particles entrained by the turbulence of moving water may be removed naturally by sedimentation in the still water of lakes and oceans. Settling basins are ponds constructed for the purpose of removing entrained solids by sedimentation. Clarifiers are tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation. Clarification does not remove dissolved species. Sedimentation is the act of depositing sediment.

Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option. A "primary treatment" step often precedes secondary treatment, whereby physical phase separation is used to remove settleable solids. During secondary treatment, biological processes are used to remove dissolved and suspended organic matter measured as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). These processes are performed by microorganisms in a managed aerobic or anaerobic process depending on the treatment technology. Bacteria and protozoa consume biodegradable soluble organic contaminants while reproducing to form cells of biological solids. Secondary treatment is widely used in sewage treatment and is also applicable to many agricultural and industrial wastewaters.

Fine bubble diffusers are a pollution control technology used to aerate wastewater for sewage treatment.
Membrane bioreactors are combinations of some membrane processes like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a biological wastewater treatment process, the activated sludge process. These technologies are now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. The two basic membrane bioreactor configurations are the submerged membrane bioreactor and the side stream membrane bioreactor. In the submerged configuration, the membrane is located inside the biological reactor and submerged in the wastewater, while in a side stream membrane bioreactor, the membrane is located outside the reactor as an additional step after biological treatment.
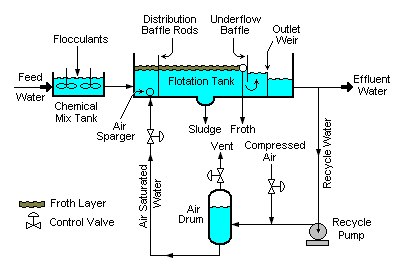
Induced gas flotation (IGF) is a water treatment process that clarifies wastewaters by the removal of suspended matter such as oil or solids. The removal is achieved by injecting gas bubbles into the water or wastewater in a flotation tank or basin. The small bubbles adhere to the suspended matter causing the suspended matter to float to the surface of the water where it may then be removed by a skimming device.

Clarifiers are settling tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation. A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from liquid for clarification and/or thickening. Inside the clarifier, solid contaminants will settle down to the bottom of the tank where it is collected by a scraper mechanism. Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank, are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum.
Dissolved gas flotation (DGF) systems are used for a variety of applications throughout the world. The process floats solids, oils and other contaminants to the surface of liquids. Once on the surface these contaminants are skimmed off and removed from the liquids. Oil and gas production facilities have used flotation systems to remove oil and solids from their produced and processed water (wastewater) for many years. The relative density of candle wax is 0.93, hence objects made of wax float on water.
An oil water separator (OWS) is a piece of equipment used to separate oil and water mixtures into their separate components. There are many different types of oil-water separator. Each has different oil separation capability and are used in different industries. Oil water separators are designed and selected after consideration of oil separation performance parameters and life cycle cost considerations. "Oil" can be taken to mean mineral, vegetable and animal oils, and the many different hydrocarbons.
Microflotation is a further development of standard dissolved air flotation (DAF). Microflotation is a water treatment technology operating with microbubbles of 10–80 μm in size instead of 80-300 μm like conventional DAF units.