Chapter two
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
It is about his personal beliefs.
Einstein and Religion: Physics and Theology (1999) is a book on the religious views of Nobel prize-winning physicist Albert Einstein by Max Jammer, published by Princeton University Press. [1] [2]
The book includes acknowledgments, an introduction, three chapters, an appendix, and an index. Chapter one is "Einstein's Religiosity and the Role of Religion in His Private Life". Chapter two is named "Einstein's Philosophy of Religion", and chapter three is "Einstein's Physics and Theology".
Jammer explains that no biographers have written about the important role of "religious sentiments and theological reflections" in Einstein's life, apart from "occasional references to his early religiosity." [3] Jammer goes on to show that Einstein's scientific work and some of his more personal views have been welcomed by devout, orthodox theologians in all three of the major monotheistic religions: Islam, [4] [5] Christianity, [6] and Judaism. [7] Jammer notes that "extensive use" of "quotations from [sources]" will be used to prevent his own personal biases from creeping into the book. Jammer also notes that although chapter three reflects the opinions of "prominent theologians and scientists", Einstein himself may well have rejected all arguments based upon them. The introduction extends from pages 3 to 11.
Chapter one of the book begins by quoting and comparing three biographical accounts—Einstein's own, that of Maja Winterler-Einstein, and that of Alexander Moszkowski—of Einstein's early religiosity. By all accounts, for three years young Einstein attended a Roman Catholic elementary school. Next, the chapter explores the evidence of whether Einstein's indifference to religious affiliations his refusal to be bar mitzvahed or his first marriage to Mileva Maric, a member of the Greek Orthodox Church) is symptomatic of a defiance to authority—others claim this to be not only so but also a necessary prerequisite to his scientific achievements. [8] [9] Whatever "'hidden complexities'" or "'groping constructive attempts'" might have been necessary for Einstein's watershed physical theories, Jammer concludes that such matters could not have been sociological or political as claimed by Feuer, but could have only involved Einstein's philosophy of religion. [10] David Hilbert's statement "'Do you know why Einstein said the most original and profound things about space and time that have been said in our generation? Because he had learned nothing about all the philosophy and mathematics of time and space." contradicts several of Einstein's own statements regarding the influence of the empiricism of David Hume and Ernst Mach upon his early work in relativity. Jammer suggests this statement is even more improbable given that Einstein is reported to have read Kant's Critique of Pure Reason, which must have been when he was a teenager. [11] By 1920, Jammer states that Baruch Spinoza had become Einstein's most admired philosopher. [12]
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
It is about his personal beliefs.
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (July 2010) |
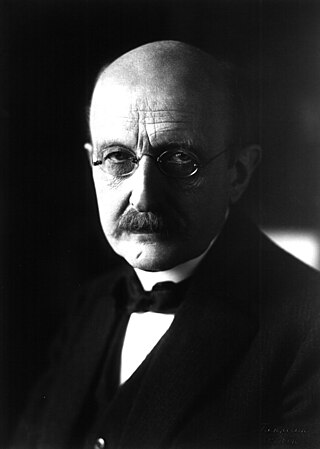
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.

Pantheism is the belief that reality, the universe and the cosmos are identical to divinity and a supreme being or entity, pointing to the universe as being an immanent creator deity who is still expanding and creating, which has existed since the beginning of time, or that all things compose an all-encompassing, immanent god or goddess and regards the universe as a manifestation of a deity. This includes all astronomical objects being viewed as part of a sole deity.

The relationship between religion and science involves discussions that interconnect the study of the natural world, history, philosophy, and theology. Even though the ancient and medieval worlds did not have conceptions resembling the modern understandings of "science" or of "religion", certain elements of modern ideas on the subject recur throughout history. The pair-structured phrases "religion and science" and "science and religion" first emerged in the literature during the 19th century. This coincided with the refining of "science" and of "religion" as distinct concepts in the preceding few centuries—partly due to professionalization of the sciences, the Protestant Reformation, colonization, and globalization. Since then the relationship between science and religion has been characterized in terms of "conflict", "harmony", "complexity", and "mutual independence", among others.
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the supernatural, but also deals with religious epistemology, asks and seeks to answer the question of revelation. Revelation pertains to the acceptance of God, gods, or deities, as not only transcendent or above the natural world, but also willing and able to interact with the natural world and, in particular, to reveal themselves to humankind. While theology has turned into a secular field, religious adherents still consider theology to be a discipline that helps them live and understand concepts such as life and love and that helps them lead lives of obedience to the deities they follow or worship.

Alfred North Whitehead was an English mathematician and philosopher. He is best known as the defining figure of the philosophical school known as process philosophy, which today has found application to a wide variety of disciplines, including ecology, theology, education, physics, biology, economics, and psychology, among other areas.

Religious studies, also known as the study of religion, is an academic field devoted to research into religious beliefs, behaviors, and institutions. It describes, compares, interprets, and explains religion, emphasizing systematic, historically based, and cross-cultural perspectives.

Paul Johannes Tillich was a German-American Christian existentialist philosopher, religious socialist, and Lutheran theologian who is widely regarded as one of the most influential theologians of the twentieth century. Tillich taught at a number of universities in Germany before immigrating to the United States in 1933, where he taught at Union Theological Seminary, Harvard Divinity School, and the University of Chicago.

Rudolf Otto was an eminent German Lutheran theologian, philosopher, and comparative religionist. He is regarded as one of the most influential scholars of religion in the early twentieth century and is best known for his concept of the numinous, a profound emotional experience he argued was at the heart of the world's religions. While his work started in the domain of liberal Christian theology, its main thrust was always apologetical, seeking to defend religion against naturalist critiques. Otto eventually came to conceive of his work as part of a science of religion, which was divided into the philosophy of religion, the history of religion, and the psychology of religion.

Genesis 1:3 is the third verse of the first chapter in the Book of Genesis. In it God made light by declaration: God said, 'Let there be light,' and there was light. It is a part of the Torah portion known as Bereshit.

John F. Haught is an American theologian. He is a Distinguished Research Professor at Georgetown University. He specializes in Roman Catholic systematic theology, with a particular interest in issues pertaining to physical cosmology, evolutionary biology, geology, and Christianity.

Harvey Gallagher Cox Jr. is an American theologian who served as the Hollis Professor of Divinity at Harvard Divinity School, until his retirement in October 2009. Cox's research and teaching focus on theological developments in world Christianity, including liberation theology and the role of Christianity in Latin America.

Max Jammer, was an Israeli physicist and philosopher of physics. He was born in Berlin, Germany. He was Rector and Acting President at Bar-Ilan University from 1967 to 1977.

Issues in Science and Religion is a book by Ian Barbour. A biography provided by the John Templeton Foundation and published by PBS online states this book "has been credited with literally creating the contemporary field of science and religion."

"Is God Dead?" was an April 8, 1966, cover story for the news magazine Time. A previous article, from October 1965, had investigated a trend among 1960s theologians to write God out of the field of theology. The 1966 article looked in greater depth at the problems facing modern theologians, in making God relevant to an increasingly secular society. Modern science seemed to have had eliminated the need for religion to explain the natural world, and God took up less and less space in people's daily lives. The ideas of various scholars were brought in, including the application of contemporary philosophy to the field of theology, and a more personal, individual approach to religion.

Albert Einstein's religious views have been widely studied and often misunderstood. Albert Einstein stated "I believe in Spinoza’s God". He did not believe in a personal God who concerns himself with fates and actions of human beings, a view which he described as naïve. He clarified however that, "I am not an atheist", preferring to call himself an agnostic, or a "religious nonbeliever." Einstein also stated he did not believe in life after death, adding "one life is enough for me." He was closely involved in his lifetime with several humanist groups.
Jesse Ndwiga Kanyua Mugambi is a professor of philosophy and religious studies at the University of Nairobi with professional training in education and philosophy of religion.

Max Bernhard Weinstein was a German physicist and philosopher. He is best known as an opponent of Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity, and for having written a broad examination of various theological theories, including extensive discussion of pandeism.

Heinrich Scholz was a German logician, philosopher, and Protestant theologian. He was a peer of Alan Turing who mentioned Scholz when writing with regard to the reception of "On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem": "I have had two letters asking for reprints, one from Braithwaite at King's and one from a professor [sic] in Germany... They seemed very much interested in the paper. [...] I was disappointed by its reception here."