
A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.

A soft-tissue sarcoma (STS) is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer, that develops in soft tissue. A soft-tissue sarcoma is often a painless mass that grows slowly over months or years. They may be superficial or deep-seated. Any such unexplained mass must be diagnosed by biopsy. Treatment may include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. Bone sarcomas are the other class of sarcomas.

A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or other structural tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Sarcomas are primary connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to secondary connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body spreads to the connective tissue. Sarcomas are one of five different types of cancer, classified by the cell type from which they originate. The word sarcoma is derived from the Greek σάρκωμα sarkōma 'fleshy excrescence or substance', itself from σάρξsarx meaning 'flesh'.

A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroid, kidney and prostate. There may be a lump, pain, or neurological signs from pressure. A bone tumor might present with a pathologic fracture. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia and nausea. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the tumour is found when investigating another problem.

A thymoma is a tumor originating from the epithelial cells of the thymus that is considered a rare malignancy. Thymomas are frequently associated with neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis; thymoma is found in 20% of patients with myasthenia gravis. Once diagnosed, thymomas may be removed surgically. In the rare case of a malignant tumor, chemotherapy may be used.
Spinal tumors are neoplasms located in either the vertebral column or the spinal cord. There are three main types of spinal tumors classified based on their location: extradural and intradural. Extradural tumors are located outside the dura mater lining and are most commonly metastatic. Intradural tumors are located inside the dura mater lining and are further subdivided into intramedullary and extramedullary tumors. Intradural-intramedullary tumors are located within the dura and spinal cord parenchyma, while intradural-extramedullary tumors are located within the dura but outside the spinal cord parenchyma. The most common presenting symptom of spinal tumors is nocturnal back pain. Other common symptoms include muscle weakness, sensory loss, and difficulty walking. Loss of bowel and bladder control may occur during the later stages of the disease.

Meningioma, also known as meningeal tumor, is typically a slow-growing tumor that forms from the meninges, the membranous layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms depend on the location and occur as a result of the tumor pressing on nearby tissue. Many cases never produce symptoms. Occasionally seizures, dementia, trouble talking, vision problems, one sided weakness, or loss of bladder control may occur.

Chondrosarcoma is a bone sarcoma, a primary cancer composed of cells derived from transformed cells that produce cartilage. A chondrosarcoma is a member of a category of tumors of bone and soft tissue known as sarcomas. About 30% of bone sarcomas are chondrosarcomas. It is resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Unlike other primary bone sarcomas that mainly affect children and adolescents, a chondrosarcoma can present at any age. It more often affects the axial skeleton than the appendicular skeleton.

Liposarcomas are the most common subtype of soft tissue sarcomas, accounting for at least 20% of all sarcomas in adults. Soft tissue sarcomas are rare neoplasms with over 150 different histological subtypes or forms. Liposarcomas arise from the precursor lipoblasts of the adipocytes in adipose tissues. Adipose tissues are distributed throughout the body, including such sites as the deep and more superficial layers of subcutaneous tissues as well as in less surgically accessible sites like the retroperitoneum and visceral fat inside the abdominal cavity.

A synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer which occurs primarily in the extremities of the arms or legs, often in proximity to joint capsules and tendon sheaths. It is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma.

A malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is a form of cancer of the connective tissue surrounding nerves. Given its origin and behavior it is classified as a sarcoma. About half the cases are diagnosed in people with neurofibromatosis; the lifetime risk for an MPNST in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 is 8–13%. MPNST with rhabdomyoblastomatous component are called malignant triton tumors.
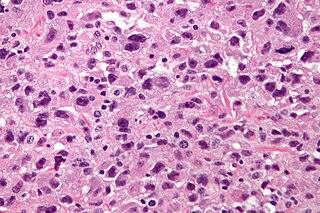
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS), also termed pleomorphic myofibrosarcoma, high-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma, and high-grade myofibrosarcoma, is characterized by the World Health Organization (WHO), 2020, as a rare, poorly differentiated neoplasm, i.e. an abnormal growth of cells that have an unclear identity and/or cell of origin. WHO classified it as one of the undifferentiated/unclassified sarcomas in the category of tumors of uncertain differentiation. Sarcomas are cancers known or thought to derive from mesenchymal stem cells that typically develop in bone, muscle, fat, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, tendons, and ligaments. More than 70 sarcoma subtypes have been described. The UPS subtype of these sarcomas consists of tumor cells that are poorly differentiated and may appear as spindle-shaped cells, histiocytes, and giant cells. UPS is considered a diagnosis that defies formal sub-classification after thorough histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural examinations fail to identify the type of cells involved.
The Ewing family of tumors (EFTs) is a group of small cell sarcomas including Ewing sarcoma of the bone, extra osseous Ewing tumors, and primitive neuroectodermal tumors. They are rare cancers, usually diagnosed in peoples' twenties. The sarcoma of bone is the most common of the variants. All forms are predisposed to metastasis and have had historically high rates of mortality. The family of tumors shares a common translocation mutation of the EWS gene on chromosome 22 to an ETS-type gene, most commonly the FLI1 gene. EFTs are highly malignant, with 5-year survival for patients with metastatic disease at 20%. The current standard of care includes resection, radiation, and chemotherapy.
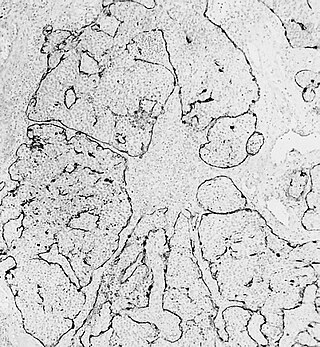
Esthesioneuroblastoma is a rare cancer of the nasal cavity. Arising from the upper nasal tract, esthesioneuroblastoma is believed to originate from sensory neuroepithelial cells, also known as neuroectodermal olfactory cells.
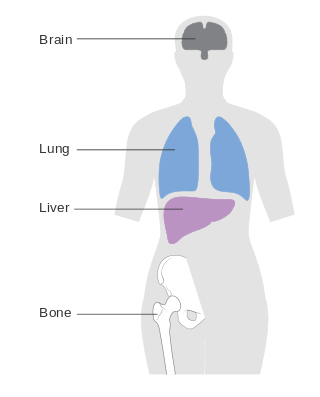
Metastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary lymph nodes. There is no cure for metastatic breast cancer; there is no stage after IV.
Neuro-oncology is the study of brain and spinal cord neoplasms, many of which are very dangerous and life-threatening. Among the malignant brain cancers, gliomas of the brainstem and pons, glioblastoma multiforme, and high-grade astrocytoma/oligodendroglioma are among the worst. In these cases, untreated survival usually amounts to only a few months, and survival with current radiation and chemotherapy treatments may extend that time from around a year to a year and a half, possibly two or more, depending on the patient's condition, immune function, treatments used, and the specific type of malignant brain neoplasm. Surgery may in some cases be curative, but, as a general rule, malignant brain cancers tend to regenerate and emerge from remission easily, especially highly malignant cases. In such cases, the goal is to excise as much of the mass and as much of the tumor margin as possible without endangering vital functions or other important cognitive abilities. The Journal of Neuro-Oncology is the longest continuously published journal in the field and serves as a leading reference to those practicing in the area of neuro-oncology.
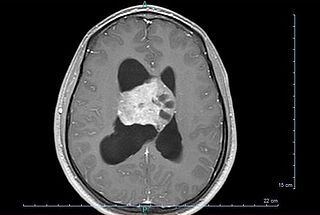
Central neurocytoma (CNC) is an extremely rare, ordinarily benign intraventricular brain tumour that typically forms from the neuronal cells of the septum pellucidum. The majority of central neurocytomas grow inwards into the ventricular system forming interventricular neurocytomas. This leads to two primary symptoms of CNCs, blurred vision and increased intracranial pressure. Treatment for a central neurocytoma typically involves surgical removal, with an approximate 1 in 5 chance of recurrence. Central neurocytomas are classified as a grade II tumor under the World Health Organization's classification of tumors of the nervous system.
Myxofibrosarcoma (MFS), although a rare type of tumor, is one of the most common soft tissue sarcomas, i.e. cancerous tumors, that develop in the soft tissues of elderly individuals. Initially considered to be a type of histiocytoma termed fibrous histiocytoma or myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma, Angervall et al. termed this tumor myxofibrosarcoma in 1977. In 2020, the World Health Organization reclassified MFS as a separate and distinct tumor in the category of malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.
Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma (SEF) is a very rare malignant tumor of soft tissues that on microscopic examination consists of small round or ovoid neoplastic epithelioid fibroblast-like cells, i.e. cells that have features resembling both epithelioid cells and fibroblasts. In 2020, the World Health Organization classified SEF as a distinct tumor type in the category of malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. However, current studies have reported that low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) has many clinically and pathologically important features characteristic of SEF; these studies suggest that LGSFMS may be an early form of, and over time progress to become, a SEF. Since the World Health Organization has classified LGFMS as one of the malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors that is distinctly different than SEF, SEF and LGFMS are here regarded as different tumor forms.
Low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma (LGMS) is a subtype of the malignant sarcomas. As it is currently recognized, LGMS was first described as a rare, atypical myofibroblastic tumor by Mentzel et al. in 1998. Myofibroblastic sarcomas had been divided into low-grade myofibroblastic sarcomas, intermediate‐grade myofibroblasic sarcomas, i.e. IGMS, and high‐grade myofibroblasic sarcomas, i.e. HGMS based on their microscopic morphological, immunophenotypic, and malignancy features. LGMS and IGMS are now classified together by the World Health Organization (WHO), 2020, in the category of intermediate fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. WHO, 2020, classifies HGMS as a soft tissue tumor in the category of tumors of uncertain differentiation. This article follows the WHO classification: here, LGMS includes IGMS but not HGMS which is a more aggressive and metastasizing tumor than LGMS and consists of cells of uncertain origin.














