Related Research Articles

Gestonorone caproate, also known as gestronol hexanoate or norhydroxyprogesterone caproate and sold under the brand names Depostat and Primostat, is a progestin medication which is used in the treatment of enlarged prostate and cancer of the endometrium. It is given by injection into muscle typically once a week.
Combined injectable contraceptives (CICs) are a form of hormonal birth control for women. They consist of monthly injections of combined formulations containing an estrogen and a progestin to prevent pregnancy.

Algestone acetophenide, also known more commonly as dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide (DHPA) and sold under the brand names Perlutal and Topasel among others, is a progestin medication which is used in combination with an estrogen as a form of long-lasting injectable birth control. It has also been used alone, but is no longer available as a standalone medication. DHPA is not active by mouth and is given once a month by injection into muscle.

Norethisterone enanthate (NETE), also known as norethindrone enanthate, is a form of hormonal birth control which is used to prevent pregnancy in women. It is used both as a form of progestogen-only injectable birth control and in combined injectable birth control formulations. It may be used following childbirth, miscarriage, or abortion. The failure rate per year in preventing pregnancy for the progestogen-only formulation is 2 per 100 women. Each dose of this form lasts two months with only up to two doses typically recommended.

Estradiol hexahydrobenzoate (EHHB), sold under a number of brand names including Benzo-Ginoestril A.P., BenzoGynoestryl Retard, Ginestryl-15-Depot, Menodin, and Tardoginestryl, is an estrogen medication which was previously used for indications such as menopausal hormone therapy and gynecological disorders. EHHB is given by injection into muscle at regular intervals, for instance once every few weeks.

Oxogestone phenpropionate, also known as xinogestone, as well as 20β-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone 20β-(3-phenylpropionate), is a progestin related to the 19-norprogesterone derivatives which was developed as an injectable hormonal contraceptive, specifically a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive, in the 1960s and early 1970s but was never marketed. It was studied at a dose of 50 to 75 mg once a month by intramuscular injection but was associated with a high failure rate with this regimen and was not further developed. OPP is the 20β-(3-phenylpropionate) ester of oxogestone, which, similarly, was never marketed.
Progestogen-only injectable contraceptives (POICs) are a form of hormonal contraception and progestogen-only contraception that are administered by injection and providing long-lasting birth control. As opposed to combined injectable contraceptives, they contain only a progestogen without an estrogen, and include two progestin preparations:

Estradiol benzoate butyrate (EBB), sold under the brand names Neolutin N, Redimen, Soluna, and Unijab and formerly known under the developmental code name Unimens, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormonal birth control for women. It is formulated in combination with dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide, a progestin, and is used specifically as a combined injectable contraceptive. EBB is not available for medical use alone. The medication, in combination with DHPA, is given by injection into muscle once a month.

Estradiol/progesterone (E2/P4), sold under the brand names Bijuva and Juvenum, is a combined estrogen and progestogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms in postmenopausal women. It contains estradiol, an estrogen, and progesterone, a progestogen, and is available in both oral and intramuscular formulations. E2/P4 differs from other estrogen–progestogen formulations in that the sex-hormonal agents used are bioidentical.
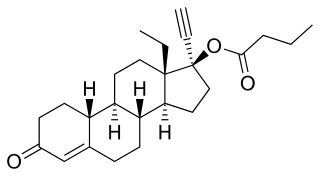
Levonorgestrel butanoate (LNG-B), or levonorgestrel 17β-butanoate, is a steroidal progestin of the 19-nortestosterone group which was developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) in collaboration with the Contraceptive Development Branch (CDB) of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development as a long-acting injectable contraceptive. It is the C17β butanoate ester of levonorgestrel, and acts as a prodrug of levonorgestrel in the body. The drug is at or beyond the phase III stage of clinical development, but has not been marketed at this time. It was first described in the literature, by the WHO, in 1983, and has been under investigation for potential clinical use since then.

Estradiol valerate/hydroxyprogesterone caproate (EV/OHPC), sold under the brand names Gravibinon and Injectable No. 1 among others, is a combined estrogen and progestogen medication which is used in the treatment of threatened miscarriage and other indications and as a form of combined injectable birth control to prevent pregnancy. It contains estradiol valerate (EV), an estrogen, and hydroxyprogesterone caproate (OHPC), a progestin. The medication is given by injection into muscle once a day to once a month depending on the indication.

Estradiol enantate/algestone acetophenide, also known as estradiol enantate/dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide (E2-EN/DHPA) and sold under the brand names Perlutal and Topasel among others, is a form of combined injectable birth control which is used to prevent pregnancy. It contains estradiol enantate (E2-EN), an estrogen, and algestone acetophenide, a progestin. The medication is given once a month by injection into muscle.

Estradiol/megestrol acetate (E2/MGA), sold under the brand names Mego-E and Chinese injectable No. 2, is a form of combined injectable birth control which is used in the People's Republic of China. It contains 3.5 mg estradiol (E2), an estrogen, and 25 mg megestrol acetate (MGA), a progestin. It is a microcrystalline aqueous suspension with a defined particle size range. The medication is given once per month by injection into muscle.

Estradiol benzoate butyrate/algestone acetophenide, also known as estradiol benzoate butyrate/dihydroxyprogesterone acetophenide (EBB/DHPA) and sold under the brand names Neolutin N, Redimen, Soluna, and Unijab, is a form of combined injectable birth control which is used in Peru and Singapore. It contains estradiol benzoate butyrate (EBB), an estrogen, and algestone acetophenide, a progestin. The medication is given once per month by injection into muscle.

Methenmadinone acetate (MMA), also known as methylenedehydroacetoxyprogesterone (MDAP) and sold under the brand names Superlutin and Antigest, is a progestin medication which was developed in Czechoslovakia in the 1960s. It is the C17α acetate ester of methenmadinone.

Methenmadinone caproate is a progestin medication which was developed in Czechoslovakia in the 1960s and was studied for potential use in combined injectable contraceptives in the 1970s but was never marketed. It was studied as a combined injectable contraceptive in combination with estradiol valerate at doses of 60 mg and 10 mg, respectively, once a month by intramuscular injection. MMC is the C17α caproate (hexanoate) ester of methenmadinone and an analogue of methenmadinone acetate. In addition to MMA, analogues of MMC include chlormadinone caproate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone caproate, and megestrol caproate.

Chlormadinone caproate (CMC) is a progestin and a progestogen ester which was studied for potential use in combined injectable contraceptives but was never marketed. It was assessed in combination with estradiol valerate at doses of 80 mg and 3 mg, respectively. In addition to chlormadinone acetate (CMA), analogues of CMC include gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone caproate, megestrol caproate, and methenmadinone caproate.

Lynestrenol phenylpropionate (LPP), also known as ethynylestrenol phenylpropionate, is a progestin and a progestogen ester which was developed for potential use as a progestogen-only injectable contraceptive by Organon but was never marketed. It was assessed at doses of 25 to 75 mg in an oil solution once a month by intramuscular injection. LPP was associated with high contraceptive failure at the low dose and with poor cycle control. The medication was found to produce estrogenic effects in the endometrium in women due to transformation into estrogenic metabolites.

Estradiol valerate/methenmadinone caproate (EV/MMC), known by the tentative brand name Lutofollin, is a combination medication of estradiol valerate (EV), an estrogen, and methenmadinone caproate, a progestin, which was developed for potential use as a once-a-month combined injectable contraceptive but was never marketed. It contained 10 mg EV and 60 mg MMC in 1 mL oil solution and was intended for administration by intramuscular injection once every 4 weeks.

Estradiol valerate/megestrol acetate (EV/MGA) is a combined injectable contraceptive which was developed in China in the 1980s but was never marketed. It is an aqueous suspension of microcapsules containing 5 mg estradiol valerate (EV) and 15 mg megestrol acetate (MGA). It was also studied at doses of EV ranging from 0.5 to 5 mg and at doses of MGA ranging from 15 to 25 mg.
References
- 1 2 Mokhtar K. Toppozada (1983). "Monthly Injectable Contraceptives". In Alfredo Goldsmith; Mokhtar Toppozada (eds.). Long-Acting Contraception. pp. 93–103. OCLC 35018604.