
Parietaria officinalis, the eastern pellitory-of-the-wall, also known as upright pellitory and lichwort, is a plant of the nettle family. Its leaves, however, are non-stinging. The plant grows on rubbish and on walls, hence the name.

Malvidin is an O-methylated anthocyanidin, the 3',5'-methoxy derivative of delphinidin. As a primary plant pigment, its glycosides are highly abundant in nature.

Kaempferia galanga, commonly known as kencur, aromatic ginger, sand ginger, cutcherry, or resurrection lily, is a monocotyledonous plant in the ginger family, and one of four plants called galangal. It is found primarily in open areas in Indonesia, southern China, Taiwan, Cambodia, and India, but is also widely cultivated throughout Southeast Asia.

Nymphaea odorata, also known as the American white waterlily, fragrant water-lily, beaver root, fragrant white water lily, white water lily, sweet-scented white water lily, and sweet-scented water lily, is an aquatic plant belonging to the genus Nymphaea. It can commonly be found in shallow lakes, ponds, and permanent slow moving waters throughout North America where it ranges from Central America to northern Canada. It is also reported from Brazil and Guyana.

Kaempferide is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of chemical compound. It can be found in Kaempferia galanga. It has been noted to inhibit pancreatic cancer growth by blockading an EGFR-related pathway.

Isorhamnetin is an O-methylated flavon-ol from the class of flavonoids. A common food source of this 3'-methoxylated derivative of quercetin and its glucoside conjugates are pungent yellow or red onions, in which it is a minor pigment, quercetin-3,4'-diglucoside and quercetin-4'-glucoside and the aglycone quercetin being the major pigments. Pears, olive oil, wine and tomato sauce are rich in isorhamnetin. Others sources include the spice, herbal medicinal and psychoactive Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida), which is described as accumulating isorhamnetin and its 7-O-glucoside derivate. Nopal is also a good source of isorhamnetin, which can be extracted by supercritical fluid extraction assisted by enzymes.

Trifolin is a chemical compound. It is the kaempferol 3-galactoside. It can be found in Camptotheca acuminata, in Euphorbia condylocarpa or in Consolida oliveriana.
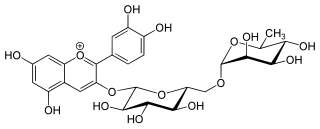
Antirrhinin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-rutinoside of cyanidin.

Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Bergenia ligulata. It exists as at least 2 major epimers.

Selliguea feei is a fern belonging to the genus Selliguea in the family Polypodiaceae. This fern can be collected in Indonesia. The species name feei commemorates the botanist Antoine Laurent Apollinaire Fée.

Selliguea is a fern genus in the family Polypodiaceae. The type species is Selliguea feei.

Bergenia crassifolia is a species of flowering plant of the genus Bergenia in the family Saxifragaceae. Common names for the species include heart-leaved bergenia, heartleaf bergenia, leather bergenia, winter-blooming bergenia, elephant-ears, elephant's ears, Korean elephant-ear, badan, pigsqueak, Siberian tea, and Mongolian tea.

Kaempferol 7-O-glucoside is a flavonol glucoside. It can be found in Smilax china, and in the fern Asplenium rhizophyllum, and its hybrid descendants, as part of a complex with caffeic acid.

Smilax china is a climbing plant species in the genus Smilax. It is native to China, Korea, Taiwan, Japan, Philippines, Vietnam, Thailand, Myanmar, and Assam. Common names for the plant include China root.

Terminalia myriocarpa, the East Indian almond, is a tree species in the genus Terminalia found in Southeast Asia.
The molecular formula C27H30O15, molar mass: 594.52 g/mol, exact mass: 594.15847 u, may refer to:
Propelargonidins are a type of condensed tannins formed from epiafzelechin. They yield pelargonidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.
Alpinia nigra is a medium-sized herb belonging to the ginger family. The rhizome is well known in many Asian cultures as a medicinal and culinary item. In many Asian tribal communities it is a part of the diet along with rice.

3,8-Dihydrodiligustilide is a nonsteroidal phytoprogestogen that is found in Ligusticum chuanxiong. It is a potent agonist of the progesterone receptor (EC50 = 90 nM). Another compound in the plant, riligustilide, is also a phytoprogestogen, but is almost 1,000-fold less potent and is very weak in comparison (EC50 ≈ 81 μM).

Riligustilide is a nonsteroidal phytoprogestogen that is found in Ligusticum chuanxiong. It is a very weak agonist of the progesterone receptor (EC50 ≈ 81 μM). Another compound in the plant, 3,8-dihydrodiligustilide, is also a phytoprogestogen, but is almost 1,000-fold more potent in comparison (EC50 = 90 nM).

















