
Tagetes is a genus of 50 species of annual or perennial, mostly herbaceous plants in the family Asteraceae. They are among several groups of plants known in English as marigolds. The genus Tagetes was described by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
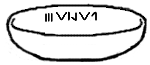
The Vinča symbols, sometimes known as the Danube script, Vinča signs, Vinča script, Vinča–Turdaș script, Old European script, etc., are a set of untranslated symbols found on Neolithic era artifacts from the Vinča culture and related "Old European" cultures of Central Europe and Southeastern Europe. Whether this is one of the earliest writing systems or simply symbols of some sort is disputed. They have sometimes been described as an example of "pre-writing" or "proto-writing". The symbols went out of use around 3500 BC.

The Vinča culture, also known as Turdaș culture, Turdaș–Vinča culture or Vinča-Turdaș culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast Europe, dated to the period 5700–4500 BC or 5300–4700/4500 BC. Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo, a large tell settlement discovered by Serbian archaeologist Miloje Vasić in 1908, it represents the material remains of a prehistoric society mainly distinguished by its settlement pattern and ritual behaviour.

Potentilla erecta is a herbaceous perennial plant belonging to the rose family (Rosaceae).

Catharanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae. Like the genus Vinca, they are known commonly as periwinkles. There are eight known species. Seven are endemic to Madagascar, though one, C. roseus, is widely naturalized around the world. The eighth species, C. pusillus, is native to India and Sri Lanka. The name Catharanthus comes from the Greek for "pure flower".

Vinca is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, native to Europe, northwest Africa and southwest Asia. The English name periwinkle is shared with the related genus Catharanthus.

Tagetes erecta, the Aztec marigold, Mexican marigold, big marigold, cempazúchitl or cempasúchil, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Tagetes native to Mexico. Despite being native to the Americas, it is often called the African marigold. In Mexico, this plant is found in the wild in the states of México, Michoacán, Puebla, and Veracruz.

Vinca minor is a species of flowering plant in the dogbane family, native to central and southern Europe, from Portugal and France north to the Netherlands and the Baltic States, east to the Caucasus, and also southwestern Asia in Turkey. Other vernacular names used in cultivation include small periwinkle, common periwinkle, and sometimes in the United States, myrtle or creeping myrtle.

Rescinnamine, known by the brand names moderil, cinnasil, and anaprel, is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor used as an antihypertensive drug.
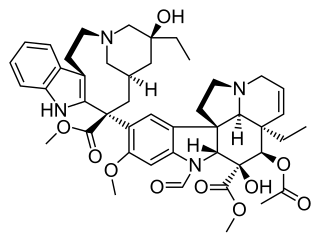
Vinca alkaloids are a set of anti-mitotic and anti-microtubule alkaloid agents originally derived from the periwinkle plant Catharanthus roseus and other vinca plants. They block beta-tubulin polymerization in a dividing cell.

Vindesine, also termed Eldisine, is a semisynthetic vinca alkaloid derived from the flowering plant Catharanthus roseus. Like the natural and semisynthetic vinca alkaloids derived from this plant, vindesine is an inhibitor of mitosis that is used as a chemotherapy drug. By inhibiting mitosis, vinedsine blocks the proliferation of cells, particularly the rapidly proliferation cells of certain types of cancer. It is used, generally in combination with other chemotherapeutic drugs, in the treatment of various malignancies such as leukaemia, lymphoma, melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer.

Eumorpha vitis, known as the vine sphinx, is a moth of the family Sphingidae.

Vinča-Belo Brdo is an archaeological site in Vinča, a suburb of Belgrade, Serbia. The tell of Belo Brdo is almost entirely made up of the remains of human settlement, and was occupied several times from the Early Neolithic through to the Middle Ages. The most substantial archaeological deposits are from the Neolithic-Chalcolithic Vinča culture, of which Vinča-Belo Brdo is the type site.

Duranta is a genus of flowering plants in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. It contains 17 species of shrubs and small trees that are native from southern Florida to Mexico and South America. They are commonly cultivated as hedges and ornamental plants.

Berula erecta, known as lesser water-parsnip or cutleaf waterparsnip or narrow-leaved water-parsnip, is a member of the carrot family. Growing to around 1 m (3 ft) tall, it is found in or by water. It is widespread across much of Europe, Asia, Australia, and North America.

Vinça is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France.

Duranta erecta is a species of flowering shrub in the verbena family Verbenaceae, native from Mexico to South America and the Caribbean. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental plant in tropical and subtropical gardens throughout the world, and has become naturalized in many places. Common names include golden dewdrop, pigeon berry, and skyflower.
Algimantas Vincas Ulba was a Lithuanian politician. In 1990 he was among those who signed the Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania.

The Vinča Institute of Nuclear Sciences is a nuclear physics research institution near Belgrade, Serbia. Since its founding, the institute has also conducted research in the fields in physics, chemistry and biology. The scholarly institute is part of the University of Belgrade.
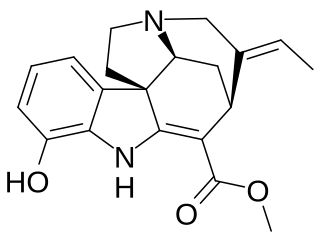
Vinervine is a monoterpene indole alkaloid of the Vinca sub-group. It is a derivative of akuammicine, with one additional hydroxy (OH) group in the indole portion, hence it is also known as 12-hydroxyakuammicine.



















