Additional images
- The Ran-GTP cycle
Karyopherins are proteins involved in transporting molecules between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. The inside of the nucleus is called the karyoplasm (or nucleoplasm). Generally, karyopherin-mediated transport occurs through nuclear pores which act as a gateway into and out of the nucleus. Most proteins require karyopherins to traverse the nuclear pore.
Karyopherins can act as importins (i.e. helping proteins get into the nucleus) or exportins (i.e. helping proteins get out of the nucleus). They belong to the nuclear pore complex family [1] in the transporter classification database (TCDB). Energy for transport is derived from the Ran gradient.
Upon stress, several karyopherins stop shuttling between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and are sequestered in stress granules, cytoplasmic aggregates of ribonucleoprotein complexes. [2] [3]
Importin beta is a variety of karyopherin that facilitates the transport of cargo proteins into the nucleus. First, it is binding importin alpha – another type of karyopherin that binds the cargo protein in the cytoplasm—before the cargo protein is imported into the nucleus through the nuclear pore using energy derived from the Ran gradient. Once inside the nucleus, the cargo dissociates from the karyopherins.
Importin beta can also carry proteins into the nucleus without the aid of the importin alpha adapter protein. [4]

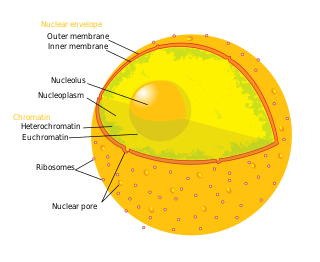
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support.
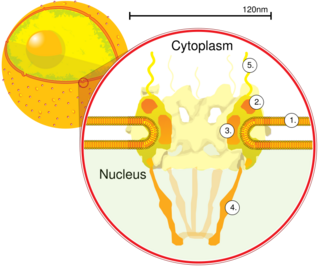
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in the nuclear envelope of a vertebrate cell, but this number varies depending on cell type and the stage in the life cycle. The human nuclear pore complex (hNPC) is a 110 megadalton (MDa) structure. The proteins that make up the nuclear pore complex are known as nucleoporins; each NPC contains at least 456 individual protein molecules and is composed of 34 distinct nucleoporin proteins. About half of the nucleoporins typically contain solenoid protein domains—either an alpha solenoid or a beta-propeller fold, or in some cases both as separate structural domains. The other half show structural characteristics typical of "natively unfolded" or intrinsically disordered proteins, i.e. they are highly flexible proteins that lack ordered tertiary structure. These disordered proteins are the FG nucleoporins, so called because their amino-acid sequence contains many phenylalanine–glycine repeats.
A nuclear localization signalorsequence (NLS) is an amino acid sequence that 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different nuclear localized proteins may share the same NLS. An NLS has the opposite function of a nuclear export signal (NES), which targets proteins out of the nucleus.
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the cell's cytoplasm to the nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS).

Ran also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily.
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherins called importins to enter the nucleus and exportins to exit.
Nuclear pore glycoprotein p62 is a protein complex associated with the nuclear envelope. The p62 protein remains associated with the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. p62 is synthesized as a soluble cytoplasmic precursor of 61 kDa followed by modification that involve addition of N-acetylglucosamine residues, followed by association with other complex proteins. In humans it is encoded by the NUP62 gene.

Nucleoporins are a family of proteins which are the constituent building blocks of the nuclear pore complex (NPC). The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure embedded in the nuclear envelope at sites where the inner and outer nuclear membranes fuse, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nuclear pores enable the passive and facilitated transport of molecules across the nuclear envelope. Nucleoporins, a family of around 30 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. Nucleoporin 62 is the most abundant member of this family. Nucleoporins are able to transport molecules across the nuclear envelope at a very high rate. A single NPC is able to transport 60,000 protein molecules across the nuclear envelope every minute.

Importin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNA2 gene.

Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNB1 gene.

Importin subunit alpha-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KPNA6 gene.
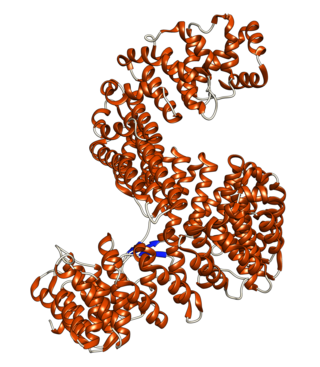
Importin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO5 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the importin beta family. Structurally, the protein adopts the shape of a right hand solenoid and is composed of 24 HEAT repeats.

RAN binding protein 2 (RANBP2) is protein which in humans is encoded by the RANBP2 gene. It is also known as nucleoporin 358 (Nup358) since it is a member nucleoporin family that makes up the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 has a mass of 358 kDa.

Nucleoporin 153 (Nup153) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NUP153 gene. It is an essential component of the basket of nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in vertebrates, and required for the anchoring of NPCs. It also acts as the docking site of an importing karyopherin. On the cytoplasmic side of the NPC, Nup358 fulfills an analogous role.

Transportin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNPO1 gene.

Importin-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IPO7 gene.

Exportin-T is a protein that in humans is encoded by the XPOT gene.

Importin-13 is a protein encoded by the IPO13 gene in humans. Importin-13 is a member of the importin-β family of nuclear transport receptors (NTRs) and was first identified as a transport receptor in 2000. According to PSI-blast based secondary structure PREDiction (PSIPRED), importin-13 contains 38 α-helices. Importin-13 accommodates a range of cargoes due to its flexible superhelical structure and a cargo binding and release system that is distinct from other importin-like transport receptors. IPO13 is broadly expressed in a variety of tissues in the human body, including the heart, cornea, fetal lung, brain, endometrial carcinoma, and testes.
A nuclear export signal (NES) is a short target peptide containing 4 hydrophobic residues in a protein that targets it for export from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore complex using nuclear transport. It has the opposite effect of a nuclear localization signal, which targets a protein located in the cytoplasm for import to the nucleus. The NES is recognized and bound by exportins.
Importin alpha, or karyopherin alpha refers to a class of adaptor proteins that are involved in the import of proteins into the cell nucleus. They are a sub-family of karyopherin proteins.