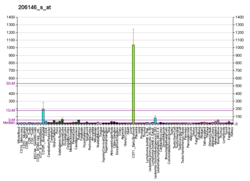
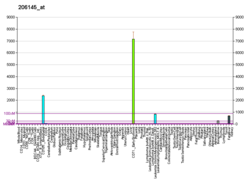
Glycophorin C plays a functionally important role in maintaining erythrocyte shape and regulating membrane material properties, possibly through its interaction with protein 4.1. Moreover, it has previously been shown that membranes deficient in protein 4.1 exhibit decreased content of glycophorin C. It is also an integral membrane protein of the erythrocyte and acts as the receptor for the Plasmodium falciparum protein PfEBP-2.

Duffy antigen/chemokine receptor (DARC), also known as Fy glycoprotein (FY) or CD234, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACKR1 gene.

CD36, also known as platelet glycoprotein 4, fatty acid translocase (FAT), scavenger receptor class B member 3 (SCARB3), and glycoproteins 88 (GP88), IIIb (GPIIIB), or IV (GPIV) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD36 gene. The CD36 antigen is an integral membrane protein found on the surface of many cell types in vertebrate animals. It imports fatty acids inside cells and is a member of the class B scavenger receptor family of cell surface proteins. CD36 binds many ligands including collagen, thrombospondin, erythrocytes parasitized with Plasmodium falciparum, oxidized low density lipoprotein, native lipoproteins, oxidized phospholipids, and long-chain fatty acids.
The term human blood group systems is defined by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT) as systems in the human species where cell-surface antigens—in particular, those on blood cells—are "controlled at a single gene locus or by two or more very closely linked homologous genes with little or no observable recombination between them", and include the common ABO and Rh (Rhesus) antigen systems, as well as many others; 44 human systems are identified as of December 2022.

Aquaporin 1 (AQP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AQP1 gene.

Protein 4.1,, is a protein associated with the cytoskeleton that in humans is encoded by the EPB41 gene. Protein 4.1 is a major structural element of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. It plays a key role in regulating membrane physical properties of mechanical stability and deformability by stabilizing spectrin-actin interaction. Protein 4.1 interacts with spectrin and short actin filaments to form the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Mutations of spectrin and protein 4.1 are associated with elliptocytosis or spherocytosis and anemia of varying severity.

Erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPB42 gene. It is part of the red blood cell cytoskeleton.

Platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha chain also known as glycoprotein Ib (platelet), alpha polypeptide or CD42b, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BA gene.

Blood group Rh(CE) polypeptide is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHCE gene. RHCE has also recently been designated CD240CE.

Glycophorin A (MNS blood group), also known as GYPA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GYPA gene. GYPA has also recently been designated CD235a (cluster of differentiation 235a).

Glycoprotein Ib (platelet), beta polypeptide (GP1BB) also known as CD42c, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GP1BB gene.

Glycoprotein IX (platelet) (GP9) also known as CD42a (Cluster of Differentiation 42a), is a human gene.

Glycophorin B (MNS blood group) (gene designation GYPB) also known as sialoglycoprotein delta and SS-active sialoglycoprotein is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GYPB gene. GYPB has also recently been designated CD235b (cluster of differentiation 235b).

Glycoprotein V (platelet) (GP5) also known as CD42d (Cluster of Differentiation 42d), is a human gene.

Urea transporter 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC14A1 gene.

Rh family, C glycoprotein, also known as RHCG, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHCG gene.

Glycophorin-E is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GYPE gene.

Ankyrin 1, also known as ANK-1, and erythrocyte ankyrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANK1 gene.

Rh deficiency syndrome is a type of hemolytic anemia that involves erythrocytes whom membranes are deficient in Rh antigens. It is considered a rare condition.

Rh blood group, D antigen also known as Rh polypeptide 1 (RhPI) or cluster of differentiation 240D (CD240D) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHD gene.