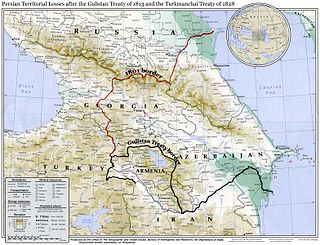
The Treaty of Gulistan was a peace treaty concluded between the Russian Empire and Qajar Iran on 24 October 1813 in the village of Gulistan as a result of the first full-scale Russo-Persian War. The peace negotiations were precipitated by the successful storming of Lankaran by General Pyotr Kotlyarevsky on 1 January 1813. It was the first of a series of treaties signed between Qajar Iran and Imperial Russia that forced Persia to cede the territories that formerly were part of Iran.

The Treaty of Turkmenchay was an agreement between Qajar Iran and the Russian Empire, which concluded the Russo-Persian War (1826–1828). It was second of the series of treaties signed between Qajar Iran and Imperial Russia that forced Persia to cede or recognize Russian influence over the territories that formerly were part of Iran.

The Karabakh Khanate was a khanate under Iranian and later Russian suzerainty, which controlled the historical region of Karabakh, now divided between modern-day Armenia and Azerbaijan. In terms of structure, the Karabakh Khanate was a miniature version of Iranian kingship. The administrative and literary language in Karabakh until the end of the 19th century was Persian, with Arabic being used only for religious studies, despite the fact that most of the Muslims in the region spoke a Turkic dialect.
The Russo-Persian Wars or Russo-Iranian Wars were a series of conflicts between 1651 and 1828, concerning Persia and the Russian Empire. Russia and Persia fought these wars over disputed governance of territories and countries in the Caucasus. The main territories disputed were Aran, Georgia and Armenia, as well as much of Dagestan – generally referred to as Transcaucasia – and considered part of the Safavid Iran prior to the Russo-Persian Wars. Over the course of the five Russo-Persian Wars, the governance of these regions transferred between the two empires. Between the Second and Third Russo-Persian Wars, there was an interbellum period in which a number of treaties were drawn up between the Russian and the Persian Empires, as well as between both parties and the Ottoman Empire. Ottoman interest in these territories further complicated the wars, with both sides forming alliances with the Ottoman Empire at different points throughout the wars. Following the Treaty of Turkmenchay, which concluded the Fifth Russo-Persian War, Persia ceded much of its Transcaucasian territory to the Russian Empire.

The Baku Khanate, was a khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the city of Baku and its surroundings from 1747 to 1806.

The Quba Khanate was one of the most significant semi-independent khanates that existed from 1747 to 1806, under Iranian suzerainty. It bordered the Caspian Sea to the east, Derbent Khanate to the north, Shaki Khanate to the west, and Baku and Shirvan Khanates to the south. In 1755 it captured Salyan from the Karabakh Khanate.

The Ganja Khanate was a khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the town of Ganja and its surroundings, now located in present-day Azerbaijan.

The Shaki Khanate was a khanate under Iranian and later Russian suzerainty, which controlled the town of Shaki and its surroundings, now located in present-day Azerbaijan.

Shirvan Khanate was a Caucasian khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the Shirvan region from 1761 to 1820.

The Nakhichevan Khanate was a khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the city of Nakhichevan and its surroundings from 1747 to 1828.

The Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828 was the last major military conflict between the Russian Empire and Qajar Iran, which was fought over territorial disputes in the South Caucasus region.
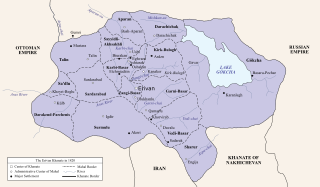
The Erivan Khanate, also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd, was a khanate that was established in Afsharid Iran in the 18th century. It covered an area of roughly 19,500 km2, and corresponded to most of present-day central Armenia, the Iğdır Province and the Kars Province's Kağızman district in present-day Turkey and the Sharur and Sadarak districts of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of present-day Azerbaijan.
Ibrahim Khalil Khan Javanshir was the second khan of the Karabakh Khanate from the Javanshir family. He was the son and successor of Panah-Ali khan Javanshir.

Hossein Qoli Khan Qajar Sardar Iravani was a statesman and commander in Qajar Iran, who was the last khan (governor) of the Erivan Khanate from 1807 to 1828.

The Russian conquest of the Caucasus mainly occurred between 1800 and 1864. The Russian Empire sought to control the region between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea. South of the mountains was the territory that is modern Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Iran and Turkey. North of the mountains was the North Caucasus region of modern Russia. The difficult conquest of the intervening mountains is known as the Caucasian War. Multiple wars were fought against the local rulers of the regions, as well as the dominant powers, the Ottoman Empire and Qajar Iran, for control. By 1864 the last regions were brought under Russian control.

The history of the Caucasus region may be divided by geography into the history of the North Caucasus (Ciscaucasia), historically in the sphere of influence of Scythia and of Southern Russia, and that of the South Caucasus in the sphere of influence of Persia, Anatolia, and Assyria.

The siege of Ganja or assault on Ganja was the result of a Russian offensive in the South Caucasus intended to conquer the Ganja Khanate of Qajar Iran, which contributed to the escalation of the Russo-Persian War (1804–1813).
Mehdi Qoli Khan Javanshir was the last Khan of the Karabakh Khanate, functioning as its head from 1806 to 1822. His only known issue was Khurshidbanu Natavan, a famous Azerbaijani poet.

The Derbent Khanate was a Caucasian khanate that was established in Afsharid Iran. It corresponded to southern Dagestan and its center was at Derbent.
Mostafa Khan was the last khan of Shirvan, until 1820.

















