
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. A cyst is related to an abscess, but it contains a material other than pus, and a cyst has a clearly defined wall.
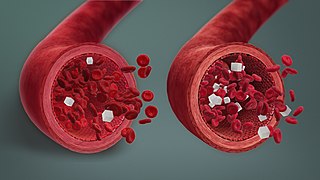
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly.

Glimepiride is an antidiabetic medication within the sulfonylurea class, primarily prescribed for the management of type 2 diabetes. It is regarded as a second-line option compared to metformin, due to metformin's well-established safety and efficacy. Use of glimepiride is recommended in conjunction with lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth, reaching a peak effect within three hours and lasting for about a day.

The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis.

Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Neuroglycopenia is a shortage of glucose (glycopenia) in the brain, usually due to hypoglycemia. Glycopenia affects the function of neurons, and alters brain function and behavior. Prolonged or recurrent neuroglycopenia can result in loss of consciousness, damage to the brain, and eventual death.

Reactive hypoglycemia, postprandial hypoglycemia, or sugar crash is a term describing recurrent episodes of symptomatic hypoglycemia occurring within four hours after a high carbohydrate meal in people with and without diabetes. The term is not necessarily a diagnosis since it requires an evaluation to determine the cause of the hypoglycemia.
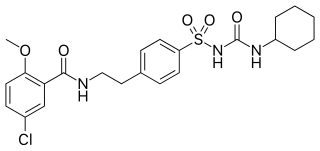
Glibenclamide, also known as glyburide, is an antidiabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is recommended that it be taken together with diet and exercise. It may be used with other antidiabetic medication. It is not recommended for use by itself in type 1 diabetes. It is taken by mouth.

Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for energy and it helps regulate glucose levels in the bloodstream. Before treatment this results in high blood sugar levels in the body. The common symptoms of this elevated blood sugar are frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, and other serious complications. Additional symptoms may include blurry vision, tiredness, and slow wound healing. Symptoms typically develop over a short period of time, often a matter of weeks if not months.
The term diabetes includes several different metabolic disorders that all, if left untreated, result in abnormally high concentrations of a sugar called glucose in the blood. Diabetes mellitus type 1 results when the pancreas no longer produces significant amounts of the hormone insulin, usually owing to the autoimmune destruction of the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas. Diabetes mellitus type 2, in contrast, is now thought to result from autoimmune attacks on the pancreas and/or insulin resistance. The pancreas of a person with type 2 diabetes may be producing normal or even abnormally large amounts of insulin. Other forms of diabetes mellitus, such as the various forms of maturity-onset diabetes of the young, may represent some combination of insufficient insulin production and insulin resistance. Some degree of insulin resistance may also be present in a person with type 1 diabetes.
Many types of glucose tests exist and they can be used to estimate blood sugar levels at a given time or, over a longer period of time, to obtain average levels or to see how fast body is able to normalize changed glucose levels. Eating food for example leads to elevated blood sugar levels. In healthy people, these levels quickly return to normal via increased cellular glucose uptake which is primarily mediated by increase in blood insulin levels.
A diabetic diet is a diet that is used by people with diabetes mellitus or high blood sugar to minimize symptoms and dangerous complications of long-term elevations in blood sugar.
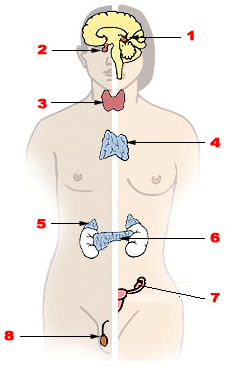
Endocrine diseases are disorders of the endocrine system. The branch of medicine associated with endocrine disorders is known as endocrinology.
An insulin tolerance test (ITT) is a medical diagnostic procedure during which insulin is injected into a patient's vein, after which blood glucose is measured at regular intervals. This procedure is performed to assess pituitary function, adrenal function, insulin sensitivity, and sometimes for other purposes. An ITT is usually ordered and interpreted by an endocrinologist.
A suicide crisis, suicidal crisis or potential suicide is a situation in which a person is attempting to kill themselves or is seriously contemplating or planning to do so. It is considered by public safety authorities, medical practice, and emergency services to be a medical emergency, requiring immediate suicide intervention and emergency medical treatment. Suicidal presentations occur when an individual faces an emotional, physical, or social problem they feel they cannot overcome and considers suicide to be a solution. Clinicians usually attempt to re-frame suicidal crises, point out that suicide is not a solution and help the individual identify and solve or tolerate the problems.
A basic metabolic panel (BMP) is a blood test consisting of a set of seven or eight biochemical tests and is one of the most common lab tests ordered by health care providers. Outside the United States, blood tests made up of the majority of the same biochemical tests are called urea and electrolytes, or urea, electrolytes, creatinine, and are often referred to as 'kidney function tests' as they also include a calculated estimated glomerular filtration rate. The BMP provides key information regarding fluid and electrolyte status, kidney function, blood sugar levels, and response to various medications and other medical therapies. It is frequently employed as a screening tool during a physical exam.

Adrenal gland disorders are conditions that interfere with the normal functioning of the adrenal glands. Your body produces too much or too little of one or more hormones when you have an adrenal gland dysfunction. The type of issue you have and the degree to which it affects your body's hormone levels determine the symptoms.
Caregiver syndrome or caregiver stress is a condition that strongly manifests exhaustion, anger, rage, or guilt resulting from unrelieved caring for a chronically ill patient. This condition is not listed in the United States' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, although the term is often used by many healthcare professionals in that country. The equivalent used in many other countries, the ICD-11, does include the condition.
Complications of diabetes are secondary diseases that are a result of elevated blood glucose levels that occur in diabetic patients. These complications can be divided into two types: acute and chronic. Acute complications are complications that develop rapidly and can be exemplified as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state (HHS), lactic acidosis (LA), and hypoglycemia. Chronic complications develop over time and are generally classified in two categories: microvascular and macrovascular. Microvascular complications include neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy; while cardiovascular disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease are included in the macrovascular complications.
Dapagliflozin/Saxagliptin is a combination medication designed to help manage diabetes mellitus, a chronic condition that affects how the body handles glucose (sugar). This medication combines two active ingredients, dapagliflozin/Saxagliptin, to address different aspects of diabetes control. Dapagliflozin/Saxagliptin sold under the brand name Qtern. It is a combination of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin. It is taken by mouth.









