
Windows Update is a Microsoft service for the Windows 9x and Windows NT families of the Microsoft Windows operating system, which automates downloading and installing Microsoft Windows software updates over the Internet. The service delivers software updates for Windows, as well as the various Microsoft antivirus products, including Windows Defender and Microsoft Security Essentials. Since its inception, Microsoft has introduced two extensions of the service: Microsoft Update and Windows Update for Business. The former expands the core service to include other Microsoft products, such as Microsoft Office and Microsoft Expression Studio. The latter is available to business editions of Windows 10 and permits postponing updates or receiving updates only after they have undergone rigorous testing.

A live CD is a complete bootable computer installation including operating system which runs directly from a CD-ROM or similar storage device into a computer's memory, rather than loading from a hard disk drive. A live CD allows users to run an operating system for any purpose without installing it or making any changes to the computer's configuration. Live CDs can run on a computer without secondary storage, such as a hard disk drive, or with a corrupted hard disk drive or file system, allowing data recovery.
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft Corporation which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software.
Software deployment is all of the activities that make a software system available for use.
Microsoft Servers is a discontinued brand that encompasses Microsoft software products for server computers. This includes the Windows Server editions of the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as products targeted at the wider business market. Microsoft has since replaced this brand with Microsoft Azure, Microsoft 365 and Windows 365.

BartPE is a discontinued tool that customizes Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 into a lightweight environment, similar to Windows Preinstallation Environment, which could be run from a Live CD or Live USB drive. A BartPE system image is created using PE Builder, a freeware program created by Bart Lagerweij.

Windows Preinstallation Environment is a lightweight version of Windows used for the deployment of PCs, workstations, and servers, or troubleshooting an operating system while it is offline. It is intended to replace MS-DOS boot disks and can be booted via USB flash drive, PXE, iPXE, CD, DVD, or hard disk. Traditionally used by large corporations and OEMs, it is now widely available free of charge via Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (WADK).

Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), previously known as Software Update Services (SUS), is a computer program and network service developed by Microsoft Corporation that enables administrators to manage the distribution of updates and hotfixes released for Microsoft products to computers in a corporate environment. WSUS downloads these updates from the Microsoft Update website and then distributes them to computers on a network. WSUS is an integral component of Windows Server.
OpenManage is a product that consists of a number of proprietary network management and systems management applications developed by Dell, Inc.
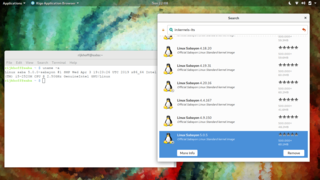
Sabayon Linux or Sabayon, was an Italian Gentoo-based Linux distribution created by Fabio Erculiani and the Sabayon development team. Sabayon followed the "out of the box" philosophy, aiming to give the user a wide number of applications ready to use and a self-configured operating system.
RIS, Remote Installation Services is a Microsoft-supplied server that allows PXE BIOS-enabled computers to remotely execute boot environment variables.

Software remastering is software development that recreates system software and applications while incorporating customizations, with the intent that it is copied and run elsewhere for "off-label" usage. The term comes from remastering in media production, where it is similarly distinguished from mere copying.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
Microsoft Application Virtualization is an application virtualization and application streaming solution from Microsoft. It was originally developed by Softricity, a company based in Boston, Massachusetts, acquired by Microsoft on July 17, 2006. App-V represents Microsoft's entry to the application virtualization market, alongside their other virtualization technologies such as Hyper-V, Microsoft User Environment Virtualization (UE-V), Remote Desktop Services, and System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
Windows Deployment Services (WDS) is a deprecated component of the Windows Server operating system that enables centralized, network-based deployment of operating systems to bare-metal computers. It is the successor to Remote Installation Services (RIS). WDS officially supports remote deployment of Windows Vista and later, as well as Windows Server 2008 and later. However, because WDS uses disk imaging, in particular the Windows Imaging Format (WIM), it could deploy virtually any operating system. This is in contrast with its predecessor, RIS, which was a method of automating the installation process.
A standard operating environment (SOE) is a standard implementation of an operating system and its associated software. Associated names and concepts include:
Turbo is a set of software products and services developed by the Code Systems Corporation for application virtualization, portable application creation, and digital distribution. Code Systems Corporation is an American corporation headquartered in Seattle, Washington, and is best known for its Turbo products that include Browser Sandbox, Turbo Studio, TurboServer, and Turbo.
Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit, formerly Windows Automated Installation Kit, is a collection of tools and technologies produced by Microsoft designed to help deploy Microsoft Windows operating system images to target computers or to a virtual hard disk image in VHD format. It was first introduced with Windows Vista. WAIK is a required component of Microsoft Deployment Toolkit.
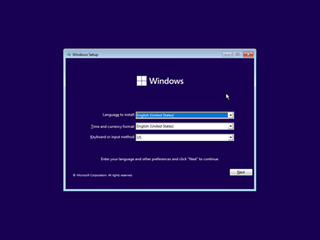
Windows Setup is an installer that prepares a computer for a Microsoft Windows installation by allowing the user to pick installation settings and copying the files to the drive.
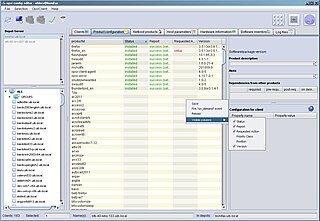
Opsi is a software distribution and management system for Microsoft Windows clients, based on Linux servers. Opsi is developed and maintained by uib GmbH from Mainz, Germany. The main parts of Opsi are open-source licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License.








