Cyan is the color between blue and green on the visible spectrum of light. It is evoked by light with a predominant wavelength between 490 and 520 nm, between the wavelengths of green and blue.

The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue.

Black-and-white images combine black and white to produce a range of achromatic brightnesses of gray.

In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut, is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device or measured by an input device. Devices with a larger gamut can represent more colors. Similarly, gamut may also refer to the colors within a defined color space, which is not linked to a specific device. A trichromatic gamut is often visualized as a color triangle. A less common usage defines gamut as the subset of colors contained within an image, scene or video.

Color photography is a type of photography that uses media capable of capturing and reproducing colors. By contrast, black-and-white or gray-monochrome photography records only a single channel of luminance (brightness) and uses media capable only of showing shades of gray.

This is an index of color topic-related articles.

In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an amount of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscale images, a kind of black-and-white or gray monochrome, are composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest.

False color refers to a group of color rendering methods used to display images in color which were recorded in the visible or non-visible parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. A false-color image is an image that depicts an object in colors that differ from those a photograph would show. In this image, colors have been assigned to three different wavelengths that human eyes cannot normally see.

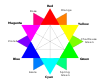
A color wheel or color circle is an abstract illustrative organization of color hues around a circle, which shows the relationships between primary colors, secondary colors, tertiary colors etc.
Color printing or colour printing is the reproduction of an image or text in color.

In infrared photography, the photographic film or image sensor used is sensitive to infrared light. The part of the spectrum used is referred to as near-infrared to distinguish it from far-infrared, which is the domain of thermal imaging. Wavelengths used for photography range from about 700 nm to about 900 nm. Film is usually sensitive to visible light too, so an infrared-passing filter is used; this lets infrared (IR) light pass through to the camera, but blocks all or most of the visible light spectrum.

A spectral color is a color that is evoked by monochromatic light, i.e. either a spectral line with a single wavelength or frequency of light in the visible spectrum, or a relatively narrow spectral band. Every wave of visible light is perceived as a spectral color; when viewed as a continuous spectrum, these colors are seen as the familiar rainbow. Non-spectral colors are evoked by a combination of spectral colors.
Panchromatic emulsion is a type of black-and-white photographic emulsion that is sensitive to all wavelengths of visible light. By extension, a panchromatic sensor is an image sensor sensitive to the whole visible spectrum. A panchromatic image is the resulting picture.
Actinism is the property of solar radiation that leads to the production of photochemical and photobiological effects. Actinism is derived from the Ancient Greek ἀκτίς, ἀκτῖνος. The word actinism is found, for example, in the terminology of imaging technology, medicine, and chemistry, and the concept of actinism is applied, for example, in chemical photography and X-ray imaging.

The Abney effect or the purity-on-hue effect describes the perceived hue shift that occurs when white light is added to a monochromatic light source.

Color motion picture film refers both to unexposed color photographic film in a format suitable for use in a motion picture camera, and to finished motion picture film, ready for use in a projector, which bears images in color.
Monochrome refers to an image or palette comprising shades of a single color. Monochromatic may be used synonymously with monochrome, or may refer to a distinct concept: to describe light that is composed of a single wavelength, which evokes a spectral color.

Monochrome photography is photography where each position on an image can record and show a different amount of light, but not a different hue. It includes all forms of black-and-white photography, which produce images containing shades of neutral grey ranging from black to white. Other hues besides grey, such as sepia, cyan, blue, or brown can also be used in monochrome photography. In the contemporary world, monochrome photography is mostly used for artistic purposes and certain technical imaging applications, rather than for visually accurate reproduction of scenes.

Variations of gray or grey include achromatic grayscale shades, which lie exactly between white and black, and nearby colors with low colorfulness. A selection of a number of these various colors is shown below.