
MIPS Tech LLC, formerly MIPS Computer Systems, Inc. and MIPS Technologies, Inc., is an American fabless semiconductor design company that is most widely known for developing the MIPS architecture and a series of RISC CPU chips based on it. MIPS provides processor architectures and cores for digital home, networking, embedded, Internet of things and mobile applications.
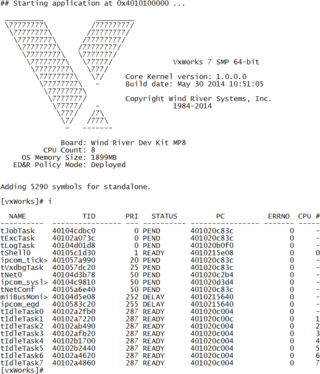
VxWorks is a real-time operating system developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.

Andrew Keith Paul Morton is an Australian software engineer, best known as one of the lead developers of the Linux kernel. He is currently a co-maintainer of the Ext3 file system, the journaling layer for block devices (JBD) and Memory Management.
Wind River Systems, also known as Wind River, is an Alameda, California–based company, subsidiary of Aptiv PLC. The company develops embedded system and cloud software consisting of real-time operating systems software, industry-specific software, simulation technology, development tools and middleware.
Computer operating systems based on the Linux kernel are used in embedded systems such as consumer electronics, in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), networking equipment, machine control, industrial automation, navigation equipment, spacecraft flight software, and medical instruments in general.
MotoMagx was a Linux kernel-based mobile operating system developed and launched in 2007 by Motorola to run on their mid-to-high-end mobile phones. The system was based on MontaVista's Mobilinux. Originally intended for 60% of their upcoming devices, it was soon dropped in favor of Android and Windows Mobile operating systems.

The Motorola A780 is the second cellular PDA running the Linux operating system.
A Bluetooth stack is software that is an implementation of the Bluetooth protocol stack.
Timesys Corporation is a company selling Linux open source software security, engineering services, and development tools, for the embedded software market. The firm also helps software development teams build and maintain a custom Linux platform for embedded processors from integrated circuit manufacturers such as Atmel, Freescale, Intel, Texas Instruments, and Xilinx.

OpenEZX was a project active from 2004 to 2008, which gathered information about the Linux based Motorola EZX phone platform.
Open Kernel Labs is a privately owned company that develops microkernel-based hypervisors and operating systems for embedded systems. The company was founded in 2006 by Steve Subar and Gernot Heiser as a spinout from NICTA. It was headquartered in Chicago, while research and development was located in Sydney, Australia. The company was acquired by General Dynamics in September 2012.
LTTng is a system software package for correlated tracing of the Linux kernel, applications and libraries. The project was originated by Mathieu Desnoyers with an initial release in 2005. Its predecessor is the Linux Trace Toolkit.
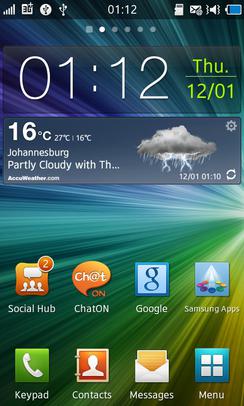
Bada is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Samsung Electronics for devices such as mid- to high-end smartphones and tablet computers. The name is derived from "바다 (bada)", meaning "ocean" or "sea" in Korean. All phones running Bada were branded with the name Wave, unlike Samsung's Android devices which are branded as Galaxy.

The Motorola A910 is a clamshell mobile phone from Motorola, which uses MontaVista Linux as the operating system.

Sailfish OS is a Linux-based operating system based on free software, and open source projects such as Mer as well as including a closed source UI. The project is being developed by the Finnish company Jolla.
Mobilinux is a discontinued Linux distribution by MontaVista. It was announced on April 25, 2005.

OpenAtom OpenHarmony, or abbreviated as OpenHarmony (OHOS), is a family of open-source distributed operating systems based on HarmonyOS derived from LiteOS, donated the L0-L2 branch source code by Huawei to the OpenAtom Foundation. Similar to HarmonyOS, the open-source distributed operating system is designed with a layered architecture, which consists of four layers from the bottom to the top, i.e., the kernel layer, system service layer, framework layer, and application layer. It is also an extensive collection of free software, which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems via Kernel Abstraction Layer subsystems.









