Rooting is the process by which users of Android devices can attain privileged control over various subsystems of the device, usually smartphones and tablets. Because Android is based on a modified version of the Linux kernel, rooting an Android device gives similar access to administrative (superuser) permissions as on Linux or any other Unix-like operating system such as FreeBSD or macOS.
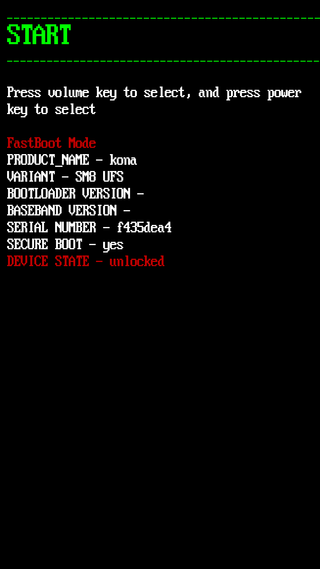
Fastboot is a communication protocol used primarily with Android devices. It is implemented in a command-line interface tool of the same name and as a mode of the bootloader of Android devices. The tool is included with the Android SDK package and used primarily to modify the flash filesystem via a USB connection from a host computer. It requires that the device be started in Fastboot mode. If the mode is enabled, it will accept a specific set of commands, sent through USB bulk transfers. Fastboot on some devices allows unlocking the bootloader, and subsequently, enables installing custom recovery image and custom ROM on the device. Fastboot does not require USB debugging to be enabled on the device. To use fastboot, a specific combination of keys must be held during boot.

Sailfish OS is a Linux-based operating system based on free software, and open source projects such as Mer as well as including a closed source UI. The project is being developed by the Finnish company Jolla.
Fairphone is a Dutch electronics manufacturer that designs and produces smartphones and headphones. It aims to minimise the ethical and environmental impact of its devices by using recycled, fairtrade and conflict-free materials, maintaining fair labor conditions throughout its workforce and suppliers, and enabling users to easily repair their devices through modular design and by providing replacement parts.
The Calyx Institute is a New York-based 501(c)(3) research and education nonprofit organization formed to make privacy and digital security more accessible. It was founded in 2010 by Nicholas Merrill, Micah Anderson, and Kobi Snitz.
Custom firmware, also known as aftermarket firmware, is an unofficial new or modified version of firmware created by third parties on devices such as video game consoles, mobile phones, and various embedded device types to provide new features or to unlock hidden functionality. In the video game console community, the term is often written as custom firmware or simply CFW, referring to an altered version of the original system software inside a video game console such as the PlayStation Portable, PlayStation 3, PlayStation Vita/PlayStation TV, PlayStation 4, Nintendo 3DS and Nintendo Switch. Installing custom firmware on some devices requires bootloader unlocking.

CopperheadOS is a mobile operating system for smartphones, based on the Android mobile platform. It adds privacy and security features to the official releases of the Android Open Source Project by Google. CopperheadOS is developed by Copperhead, a Canadian information security company. It is licensed under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0, although its source code is not available for public download.

LineageOS is an Android-based operating system for smartphones, tablet computers, and set-top boxes, with mostly free and open-source software. It is the successor to CyanogenMod, from which it was forked in December 2016, when Cyanogen Inc. announced it was discontinuing development and shut down the infrastructure behind the project. Since Cyanogen Inc. retained the rights to the Cyanogen name, the project rebranded its fork as LineageOS.

Shiftphone is a modular, easy-to-repair smartphone brand created by the company SHIFT in Germany. The company emphasizes fair trade and ecology, similar to Fairphone. Instead of tantalum capacitors made from coltan, ceramic capacitors are used for their manufacturing. So far, eleven model series have been released. The most recent release was the SHIFT6mq in June 2020. The upcoming device will be the SHIFTphone 8, scheduled for release in 2024.
/e/ is a fork of LineageOS, an Android-based mobile operating system, and associated online services. /e/ is presented as privacy software that does not contain proprietary Google apps or services, and challenges the public to "find any parts of the system or default applications that are still leaking data to Google."

GrapheneOS is an Android-based, open source, privacy and security-focused mobile operating system for selected Google Pixel devices, including smartphones, tablets and foldables that is recommended by Edward Snowden.

MicroG is a free and open-source implementation of proprietary Google libraries that serves as a replacement for Google Play Services on the Android operating system. It is maintained by German developer Marvin Wißfeld. In a presentation, Wißfeld described microG as "the framework to create a fully-compatible Android distribution without any proprietary Google components".

iodéOS is an Android-based mobile operating system developed by French company iodé. The operating system is a fork of LineageOS and does not include Google Play Services, instead using MicroG as a free and open-source replacement.

Bootloader unlocking is the process of disabling the bootloader security that makes secure boot possible. It can make advanced customizations possible, such as installing a custom firmware. On smartphones this can be a custom Android distribution or another mobile operating system. Some bootloaders are not locked at all, others can be unlocked using a standard command, others need assistance from the manufacturer. Some do not include an unlocking method and can only be unlocked through a software exploit.

Fairphone 4 is a smartphone designed and marketed by Fairphone. It succeeds the Fairphone 3+ and was succeeded by the Fairphone 5. It was announced on 30 September 2021, and was available for order on 25 October 2021.

The Google Pixel 6a is an Android smartphone designed, developed, and marketed by Google as part of the Google Pixel product line. It serves as a mid-range variant of the Pixel 6 and Pixel 6 Pro. The device was announced on May 11, 2022 as part of Google I/O's keynote speech.

DivestOS is an operating system based on the Android mobile platform. It is a soft fork of LineageOS that aims to increase security and privacy with support for end-of-life devices. As much as possible, it removes unnecessary proprietary Android components and includes only free-software.

PixelExperience is an open-sourced custom ROM, or Android distribution, based on the stock Android AOSP that aimed to provide a bloat-free, stock-android, Pixel-like experience to a wide range of Android devices. The project, initiated by a community of developers in 2017, focused on delivering a clean, minimalistic, and visually appealing user interface reminiscent of Google's Pixel devices. Pixel Experience was designed to be as close to stock Android as possible, with a focus on reliability, security, stability, performance, battery life, and useful customizations.










