A software development kit (SDK) is a collection of software development tools in one installable package. They facilitate the creation of applications by having a compiler, debugger and sometimes a software framework. They are normally specific to a hardware platform and operating system combination. To create applications with advanced functionalities such as advertisements, push notifications, etc; most application software developers use specific software development kits.
Google I/O, or simply I/O, is an annual developer conference held by Google in Mountain View, California. The name "I/O" is taken from the number googol, with the "I" representing the "1" in googol and the "O" representing the first "0" in the number. The format of the event is similar to Google Developer Day.

The HTC Dream is a smartphone developed by HTC. First released in September 2008 for $179 with a 2-year contract to T-Mobile, the Dream was the first commercially released device to use the Linux-based Android operating system, which was purchased and further developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance to create an open competitor to other major smartphone platforms of the time, such as Symbian, BlackBerry OS, and iPhone OS. The operating system offers a customizable graphical user interface, integration with Google services such as Gmail, a notification system that shows a list of recent messages pushed from apps, and Android Market for downloading additional apps.
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of its first beta on November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released on September 23, 2008. The operating system is developed by Google on a yearly cycle since at least 2011. New major releases are announced at Google I/O along with its first public beta to supported Google Pixel devices. The stable version is then released later in the year.

Android software development is the process by which applications are created for devices running the Android operating system. Google states that "Android apps can be written using Kotlin, Java, and C++ languages" using the Android software development kit (SDK), while using other languages is also possible. All non-Java virtual machine (JVM) languages, such as Go, JavaScript, C, C++ or assembly, need the help of JVM language code, that may be supplied by tools, likely with restricted API support. Some programming languages and tools allow cross-platform app support. Third party tools, development environments, and language support have also continued to evolve and expand since the initial SDK was released in 2008. The official Android app distribution mechanism to end users is Google Play; it also allows staged gradual app release, as well as distribution of pre-release app versions to testers.

Android Ice Cream Sandwich is the fourth major version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google. Unveiled on October 19, 2011, Android 4.0 builds upon the significant changes made by the tablet-only release Android Honeycomb, in an effort to create a unified platform for both smartphones and tablets. The first phone with Android Ice Cream Sandwich was Samsung Galaxy Nexus.

Android Jelly Bean is the codename given to the tenth version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google, spanning three major point releases. Among the devices that run Android 4.1 to 4.3 are the Nexus 7 (2012), Nexus 4, Nexus 10, Nexus 7 (2013), and Hyundai Play X.
This is a comparison of mobile operating systems. Only the latest versions are shown in the table below, even though older versions may still be marketed.
Payanywhere is a payments platform and app that allows merchants in the United States to accept credit and debit card payments while building customer relationships in-store, online, or on the go. Merchants may accept payments on their smartphone via a Bluetooth card reader or on an in-store “Storefront” solution featuring a tablet and stand, which was introduced on April 8, 2014. PayAnywhere offers credit card readers and apps that are compatible with both Apple and Android devices.
Google Cast is a proprietary protocol developed by Google for playing Internet-streamed audiovisual content on a compatible consumer device. The protocol is used to initiate and control playback of content on digital media players, high-definition televisions, and home audio systems using a mobile device, personal computer, or smart speaker. The protocol was first launched on July 24, 2013, to support Google's first-generation Chromecast player. The Google Cast SDK was released on February 3, 2014, allowing third parties to modify their software to support the protocol. According to Google, over 20,000 Google Cast-ready apps were available as of May 2015. Support for Google Cast has since been integrated into subsequent devices, such as the Nexus Player and other Android TV devices, as well as soundbars, speakers, and later models of the Chromecast. Consumer devices that natively support the protocol are marketed as Chromecast built-in. As of October 2017, over 55 million Chromecasts and Chromecast built-in devices have been sold.

Windows Phone 8.1 is the third generation of Microsoft's Windows Phone mobile operating system, succeeding Windows Phone 8. Rolled out at Microsoft's Build Conference in San Francisco, California, on April 2, 2014, it was released in final form to Windows Phone developers on April 14, 2014 and reached general availability on August 4, 2014. All Windows Phones running Windows Phone 8 can be upgraded to Windows Phone 8.1, with release dependent on carrier rollout dates.

Wear OS is a version of Google's Android operating system designed for smartwatches and other wearables. By pairing with mobile phones running Android version 6.0 "Marshmallow" or newer, or iOS version 10.0 or newer with limited support from Google's pairing application, Wear OS integrates Google Assistant technology and mobile notifications into a smartwatch form factor. Wear OS is closed-source, in contrast to the free and open-source Android.

Android Lollipop is the fifth major version of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google and the 12th version of Android, spanning versions between 5.0 and 5.1.1. Unveiled on June 25, 2014 at the Google I/O 2014 conference, it became available through official over-the-air (OTA) updates on November 12, 2014, for select devices that run distributions of Android serviced by Google. Its source code was made available on November 3, 2014. The first phone with Android Lollipop was the Nexus 6.
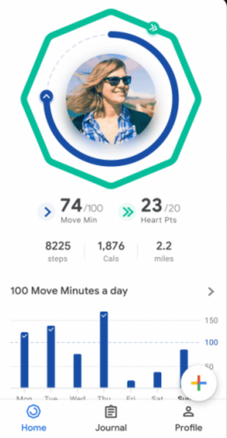
Google Fit is a health-tracking platform developed by Google for the Android operating system, Wear OS, and iOS. It is a single set of APIs that blends data from multiple apps and devices. Google Fit uses sensors in a user's activity tracker or mobile device to record physical fitness activities, which are measured against the user's fitness goals to provide a comprehensive view of their fitness.

Android Eclair is a codename of the Android mobile operating system developed by Google, the fifth operating system for Android and the second major release of Android. Eclair spans the versions 2.0.x and 2.1. Unveiled on October 26, 2009, Android Eclair builds upon the significant changes made in Android 1.6 "Android Donut". The first phone with Android Eclair was the Motorola Droid. Google ceased Android Market support for Android Eclair on June 30, 2017.

Android Nougat is the seventh major version and 14th original version of the Android operating system. First released as an alpha test version on March 9, 2016, it was officially released on August 22, 2016, with Nexus devices being the first to receive the update. The LG V20 was the first smartphone released with Nougat.

Android Oreo is the eighth major release and the 15th version of the Android mobile operating system. It was initially unveiled as an alpha quality developer preview in March 2017 and later made available to the public, on August 21, 2017.
Flutter is an open-source UI software development kit created by Google. It is used to develop cross platform applications from a single codebase for any web browser, Fuchsia, Android, iOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows. First described in 2015, Flutter was released in May 2017.
The version history of the HarmonyOS distributed operating system began with the public release of the HarmonyOS 1.0 for Honor Vision smart TVs on August 9, 2019. The first commercial version of the IoT based operating system, HarmonyOS 2.0, was released on June 2, 2021 for phones, tablets, smartwatches, smart speakers, routers, and internet of things. Beforehand, DevEco Studio, the HarmonyOS app development IDE, was released in September 2020 together with the HarmonyOS 2.0 Beta. HarmonyOS is developed by Huawei. New major releases are announced at the Huawei Developers Conference (HDC) in the fourth quarter of each year together with the first public beta version of the operating system's next major version. The next major stable version is then released in the third to fourth quarter of the following year.











