Educational software is a term used for any computer software which is made for an educational purpose. It encompasses different ranges from language learning software to classroom management software to reference software. The purpose of all this software is to make some part of education more effective and efficient.
Moodle is a free and open-source learning management system written in PHP and distributed under the GNU General Public License. Moodle is used for blended learning, distance education, flipped classroom and other online learning projects in schools, universities, workplaces and other sectors.
Blended learning or hybrid learning, also known as technology-mediated instruction, web-enhanced instruction, or mixed-mode instruction, is an approach to education that combines online educational materials and opportunities for interaction online with physical place-based classroom methods.
A learning management system (LMS) is a software application for the administration, documentation, tracking, reporting, automation, and delivery of educational courses, training programs, materials or learning and development programs. The learning management system concept emerged directly from e-Learning. Learning management systems make up the largest segment of the learning system market. The first introduction of the LMS was in the late 1990s. Learning management systems have faced a massive growth in usage due to the emphasis on remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Educational technology is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning. When referred to with its abbreviation, "EdTech," it often refers to the industry of companies that create educational technology. In EdTech Inc.: Selling, Automating and Globalizing Higher Education in the Digital Age, Tanner Mirrlees and Shahid Alvi (2019) argue "EdTech is no exception to industry ownership and market rules" and "define the EdTech industries as all the privately owned companies currently involved in the financing, production and distribution of commercial hardware, software, cultural goods, services and platforms for the educational market with the goal of turning a profit. Many of these companies are US-based and rapidly expanding into educational markets across North America, and increasingly growing all over the world."
Edline was a learning community management system used for school and class organization. It provided district, school, and classroom level website support for administrators, parents, teachers, and students from kindergarten through 12th grade. It is now discontinued.
An edublog is a blog created for educational purposes. Edublogs archive and support student and teacher learning by facilitating reflection, questioning by self and others, collaboration and by providing contexts for engaging in higher-order thinking. Edublogs proliferated when blogging architecture became more simplified and teachers perceived the instructional potential of blogs as an online resource. The use of blogs has become popular in education institutions including public schools and colleges. Blogs can be useful tools for sharing information and tips among co-workers, providing information for students, or keeping in contact with parents. Common examples include blogs written by or for teachers, blogs maintained for the purpose of classroom instruction, or blogs written about educational policy. Educators who blog are sometimes called edubloggers.
Google Workspace is a collection of cloud computing, productivity and collaboration tools, software and products developed and marketed by Google. It consists of Gmail, Contacts, Calendar, Meet and Chat for communication; Currents for employee engagement; Drive for storage; and the Google Docs Editors suite for content creation. An Admin Panel is provided for managing users and services. Depending on edition Google Workspace may also include the digital interactive whiteboard Jamboard and an option to purchase add-ons such as the telephony service Voice. The education edition adds a learning platform Google Classroom and today has the name Workspace for Education.
Glogster was a cloud-based (SaaS) platform for creating presentations and interactive learning. A platform that allows users, mostly students and educators to combine text, images, video, and audio to create an interactive, Web-based poster called glogs on a virtual canvas. Glogster facilitated the conveyance of social information in many different fields such as art, music, photography. Users also had access to a library of engaging educational content posters created by other students and educators worldwide. Glogster enabled interactive, collaborative education and digital literacy.
Social learning tools are tools used for pedagogical and andragogical purposes that utilize social software and/or social media in order to facilitate learning through interactions between individuals and systems. The idea of setting up "social learning tools" is to make education more convenient and widespread. It also allows an interaction between users and/or the software which can bring a different aspect to learning. People can acquire knowledge by distance learning tools, for instance, Facebook, Twitter, Khan Academy and so on. Social learning tools may mediate in formal or informal learning environments to help create connections between learners, instructors and information. These connections form dynamic knowledge networks. Social learning tools are used in schools for teaching/learning and in businesses for training. Within a school environment, the use of social learning tools can affect not only the user (student) but his/her caretaker as well as his/her instructor. It brings a different approach to the traditional way of learning which affects the student and his/her support circle. Companies also use social learning tools. They used them to improve knowledge transfer within departments and across teams. Businesses use a variety of these tools to create a social learning environment. They are also used in company settings to help improve team work, problem solving, and performance in stressful situations.
Khan Academy is an American non-profit educational organization created in 2006 by Sal Khan. Its goal is to create a set of online tools that help educate students. The organization produces short video lessons. Its website also includes supplementary practice exercises and materials for educators. It has produced over 8,000 video lessons teaching a wide spectrum of academic subjects, including mathematics, sciences, literature, history, and computer science. All resources are available for free to users of the website and application.

Edmodo was an educational technology platform for K-12 schools and teachers. Edmodo enabled teachers to share content, distribute quizzes and assignments, and manage communication with students, colleagues, and parents. It was shut down on September 22, 2022.
Instructure, Inc. is an educational technology company based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It is the developer and publisher of Canvas, a web-based learning management system (LMS), and MasteryConnect, an assessment management system. Prior to its IPO in 2021, the company was owned by private-equity firm Thoma Bravo.
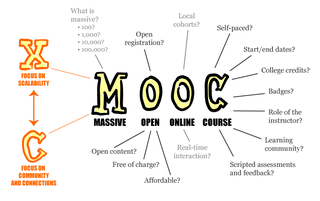
A massive open online course or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012, a year called the "Year of the MOOC".

Kahoot! is a Norwegian online game-based learning platform. It has learning games, also known as "kahoots", which are user-generated multiple-choice quizzes that can be accessed via a web browser or the Kahoot! app.
GoGuardian is an educational technology company founded in 2014 and based in Los Angeles, California. The company's services monitor student activity online, filter content, and alert school officials to possible suicidal or self-harm ideation.
Social media in education is the practice of using social media platforms or technology to enhance the education of students. Social media is defined as "a group of Internet-based applications that build on the ideological and technological foundations of Web 2.0, and that allow the creation and exchange of user-generated content". Social media platforms can be used to complete assignments or projects electronically. These activities can grant students opportunities to develop skills with computers and online platforms.
Itslearning is a digital learning management system (LMS) developed by Norwegian company Itslearning AS. Designed for both K12 and higher education, the itslearning LMS allows teachers to deliver learning materials to students, including assessments, Office 365 documents, and other educational content.

Microsoft Teams is a proprietary cloud-based team collaboration application developed by Microsoft, as part of the Microsoft 365 family of products.

Digital Media in education is measured by a person's ability to access, analyze, evaluate, and produce media content and communication in a variety of forms. These media may involve incorporating multiple digital softwares, devices, and platforms as a tool for learning. The use of digital media in education is growing rapidly in today's age, competing with books for the leading form of communication. This form of education is slowly combating the traditional forms of education that have been around for a long time. With the introduction of virtual education, there has been a need for more incorporation of new digital platforms in online classrooms.





