Microsoft Windows was announced by Bill Gates on November 10, 1983. Microsoft introduced Windows as a graphical user interface for MS-DOS, which had been introduced two years earlier. The product line evolved in the 1990s from an operating environment into a fully complete, modern operating system over two lines of development, each with their own separate codebase.
Microsoft Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For instance, Windows NT for consumer and corporate desktops, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone.

Microsoft Office, or simply Office, is a family of client software, server software, and services developed by Microsoft. It was first announced by Bill Gates on August 1, 1988, at COMDEX in Las Vegas. Initially a marketing term for an office suite, the first version of Office contained Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft PowerPoint. Over the years, Office applications have grown substantially closer with shared features such as a common spell checker, Object Linking and Embedding data integration and Visual Basic for Applications scripting language. Microsoft also positions Office as a development platform for line-of-business software under the Office Business Applications brand.
The Start menu is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, providing a means of opening programs and performing other functions in the Windows shell. The Start menu, and the Taskbar on which it appears, were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on Great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being computers, have similar capabilities, but lack some input/output (I/O) abilities that others have. Modern tablets largely resemble modern smartphones, the only differences being that tablets are relatively larger than smartphones, with screens 7 inches (18 cm) or larger, measured diagonally, and may not support access to a cellular network. Unlike laptops, tablets usually run mobile operating systems, alongside smartphones.

Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance, though its most widely used version is primarily developed by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008.
A mobile operating system is an operating system for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smartglasses, or other non-laptop personal mobile computing devices. While computers such as typical/mobile laptops are "mobile", the operating systems used on them are generally not considered mobile ones, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This line distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile unlike hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers and light-weight laptops and the hybridization of the two in 2-in-1 PCs.

iOS is a mobile operating system based on macOS and on components of the Mach microkernel and FreeBSD, a Unix-like operating system, developed by Apple Inc. exclusively for its smartphones. It was unveiled in January 2007 for the first-generation iPhone, launched in June 2007.

Windows Phone (WP) is a discontinued family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones as the replacement successor to Windows Mobile and Zune. Windows Phone featured a new user interface derived from the Metro design language. Unlike Windows Mobile, it was primarily aimed at the consumer market rather than the enterprise market.

Windows 8 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012, and was made available for download via MSDN and TechNet on August 15, 2012. Nearly three months after its initial release, Windows 8 finally made its first retail appearance on October 26, 2012.

Windows RT is a mobile operating system developed by Microsoft. It is a version of Windows 8 or Windows 8.1 built for the 32-bit ARM architecture (ARMv7). First unveiled in January 2011 at Consumer Electronics Show, the Windows RT 8 operating system was officially launched alongside Windows 8 on October 26, 2012, with the release of three Windows RT-based devices, including Microsoft's original Surface tablet. Unlike Windows 8, Windows RT is only available as preloaded software on devices specifically designed for the operating system by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
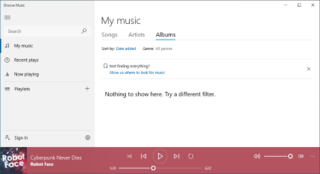
Groove Music is a discontinued audio player software application included with Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10 and Windows 11.
Microsoft mobile services are a set of proprietary mobile services created specifically for mobile devices, they are typically offered through mobile applications and mobile browser for Windows Phone platforms, BREW, and Java. Microsoft's mobile services are typically connected with a Microsoft account and often come preinstalled on Microsoft's own mobile operating systems while they are offered via various means for other platforms. Microsoft started to develop for mobile computing platforms with the launch of Windows CE in 1996 and later added Microsoft's Pocket Office suite to their Handheld PC line of PDAs in April 2000. From December 2014 to June 2015, Microsoft made a number of corporate acquisitions, buying several of the top applications listed in Google Play and the App Store including Acompli, Sunrise Calendar, Datazen, Wunderlist, Echo Notification Lockscreen, and MileIQ.
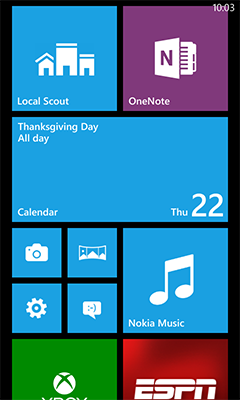
Windows Phone 7 is the first release of the Windows Phone mobile client operating system, released worldwide on October 21, 2010, and in the United States on November 8, 2010. It runs on the Windows CE 6.0 kernel.

Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps are applications that can be used across all compatible Microsoft Windows devices. They are primarily purchased and downloaded via the Microsoft Store, Microsoft's digital application storefront.

Windows Phone 8.1 is the third generation of Microsoft's Windows Phone mobile operating system, succeeding Windows Phone 8. Rolled out at Microsoft's Build Conference in San Francisco, California, on April 2, 2014, it was released in final form to Windows Phone developers on April 14, 2014 and reached general availability on August 4, 2014. All Windows Phones running Windows Phone 8 can be upgraded to Windows Phone 8.1, with release dependent on carrier rollout dates.
The Nokia X platform was a Linux-based mobile operating system and software platform originally developed by Nokia, and subsequently by Microsoft Mobile. Introduced on 24 February 2014, it was forked from Android and used on all the devices of the Nokia X family. It was also the next Nokia Linux project after the ill-fated MeeGo.
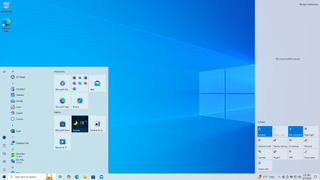
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It is the direct successor to Windows 8.1, which was released nearly two years earlier. It was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on July 29, 2015. Windows 10 was made available for download via MSDN and TechNet, as a free upgrade for retail copies of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 users via the Windows Store, and to Windows 7 users via Windows Update. Windows 10 receives new builds on an ongoing basis, which are available at no additional cost to users, in addition to additional test builds of Windows 10, which are available to Windows Insiders. Devices in enterprise environments can receive these updates at a slower pace, or use long-term support milestones that only receive critical updates, such as security patches, over their ten-year lifespan of extended support. In June 2021, Microsoft announced that support for Windows 10 editions which are not in the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) will end on October 14, 2025.
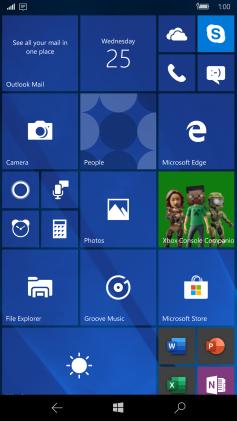
Windows 10 Mobile is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Microsoft. First released in 2015, it is a successor to Windows Phone 8.1, but was marketed by Microsoft as being an edition of its PC operating system Windows 10.