A personal digital assistant (PDA), also known as a handheld PC, is a variety mobile device which functions as a personal information manager. PDAs have been mostly displaced by the widespread adoption of highly capable smartphones, in particular those based on iOS and Android, seeing a rapid decline in use after 2007.

Psion PLC was a designer and manufacturer of mobile handheld computers for commercial and industrial uses. The company was headquartered in London, England, with major operations in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, and other company offices in Europe, the United States, Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. It was a public company listed on the London Stock Exchange and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

A Pocket PC is a class of personal digital assistant (PDA) that runs the Windows Mobile or Windows Embedded Compact operating system that has some of the abilities of modern desktop PCs. The name was introduced by Microsoft in 2000 as a rebranding of the Palm-size PC category. Some of these devices also had integrated phone and data capabilities, which were called Pocket PC Phone Edition or simply "Smartphone".

Palm is a line of personal digital assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones developed by California-based Palm, Inc., originally called Palm Computing, Inc. Palm devices are often remembered as "the first wildly popular handheld computers," responsible for ushering in the smartphone era.

The iPAQ is a discontinued Pocket PC and personal digital assistant which was first unveiled by Compaq in April 2000.
Windows Embedded Compact, formerly Windows Embedded CE, Windows Powered and Windows CE, is an operating system family developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows Embedded family of products.
Casio Cassiopeia was the brand name of a PDA manufactured by Casio. It used Windows CE as the Operating system. Casio was one of the first manufacturers of PDAs, developing at the beginning small pocket-sized computers with keyboards and grayscale displays and subsequently moving to smaller units in response to customer demand.
Windows Mobile was a family of mobile operating systems developed by Microsoft for smartphones and personal digital assistants.

ActiveSync is a mobile data synchronization app developed by Microsoft, originally released in 1996. It synchronizes data with handheld devices and desktop computers. In the Windows Task Manager, the associated process is called wcescomm.exe.

A handheld personal computer (PC) is a pocket-sized computer typically built around a clamshell form factor and is significantly smaller than any standard laptop computer, but based on the same principles. It is sometimes referred to as a palmtop computer, not to be confused with Palmtop PC which was a name used mainly by Hewlett-Packard.
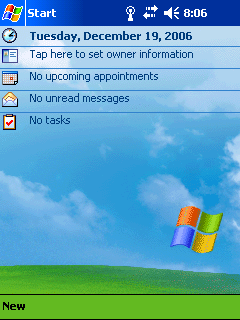
Windows Mobile 2003, originally codenamed "Ozone", was a member of the Windows Mobile family of mobile operating systems, released on June 23, 2003. It was the first Microsoft mobile OS to be called "Windows Mobile" and was based on Windows CE 4.20.
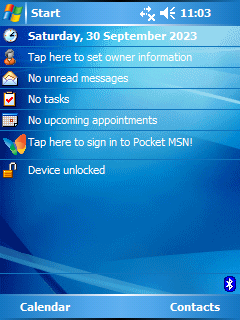
Windows Mobile 5.0, originally codenamed "Magneto", was released at Microsoft's Mobile and Embedded Developers Conference 2005 in Las Vegas, May 9–12, 2005. Microsoft offered mainstream support for Windows Mobile 5 through October 12, 2010, and extended support through October 13, 2015. It was first offered on the Dell Axim x51. It used the .NET Compact Framework 1.0 SP3, an environment for programs based on .NET. Windows Mobile 5.0 included Microsoft Exchange Server "push" functionality improvements that worked with Exchange 2003 SP2. The "push" functionality also required vendor/device support With AKU2 software upgrades all WM 5.0 devices supported DirectPush. This version featured increased battery life due to Persistent storage capability. Previously up to 50% of battery power was reserved just to maintain data in volatile RAM. This continued the trend of Windows-based devices moving from using RAM as their primary storage medium to the use of a combination of RAM and flash memory. Programs and frequently accessed data run in RAM, while most storage is in the flash memory. The OS seamlessly moves data between the two as needed. Everything is backed up in the flash memory, so unlike prior devices, WM5 devices lose no data if power is lost. New to 5.0, OS updates were released as Adaptation kit upgrades, with AKU 3.5 being the final released.

The Jornada was a line of personal digital assistants or PDAs manufactured by Hewlett-Packard. The Jornada was a broad product line that included Palm-Size PCs, Handheld PCs, and Pocket PCs. The first model was the 820, released in 1998, and the last was the 928 model in 2002 when Compaq and HP merged. The Jornada line was then succeeded by the more popular iPAQ model PDAs. All Jornada models ran Microsoft Operating Systems that were based on Windows CE.

Windows IoT, formerly Windows Embedded, is a family of operating systems from Microsoft designed for use in embedded systems. Microsoft has three different subfamilies of operating systems for embedded devices targeting a wide market, ranging from small-footprint, real-time devices to point of sale (POS) devices like kiosks. Windows Embedded operating systems are available to original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), who make it available to end users preloaded with their hardware, in addition to volume license customers in some cases.

Windows Mobile 6, formerly codenamed "Crossbow", was the version of Windows Mobile released on February 12, 2007 at the 3GSM World Congress 2007. It comes in three different versions: "Windows Mobile 6 Standard" for Smartphones, "Windows Mobile 6 Professional" for Pocket PCs with phone functionality, and "Windows Mobile 6 Classic" for Pocket PCs without cellular radios.

Jawbreaker is a port of SameGame for the Pocket PC bundled with the Microsoft Windows Mobile 2003 operating system for PDAs. The operating system, and thus the game, was officially released on April 7, 2003. The game itself was developed by American studio oopdreams software, Inc. Jawbreaker is officially listed as one of the "Core Applications" of the Windows Mobile software family, in a paper released by Microsoft. In Windows Mobile 5.0 and Windows Mobile 6.0 it is called Bubble Breaker. The original non-bundled version of the game is available from the developer itself as Bubblets.
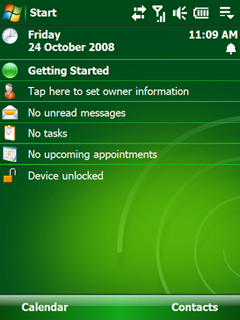
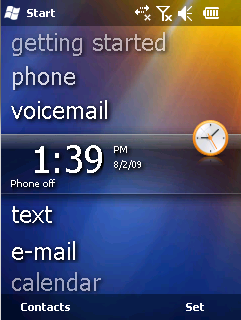
Windows Mobile 6.1 was a version of the Windows Mobile operating system, released on April 1, 2008. It is a minor upgrade to the Windows Mobile 6 platform with various performance enhancements and a redesigned Home screen featuring horizontal tiles that expand on clicking to display more information, although this new home screen is featured only on Windows Mobile Standard edition. This was not supported in the Professional edition. Several other changes such as threaded SMS, full page zooming in Internet Explorer and 'Domain Enroll' were also added, along with a "mobile" version of the Microsoft OneNote program and an interactive "Getting Started" wizard. Domain Enroll is functionality to connect the device to System Center Mobile Device Manager 2008, a product to manage mobile devices. The most apparent of the other differences is that the Standard version still creates automatic links for telephone numbers in Tasks and Appointments, which allows for the easier click and dial of stored telephone numbers within these Outlook items. This feature is not supported in the Professional version. Windows Mobile 6.1 also had improved bandwidth efficiency in its push-email protocol "Activesync" of "up to 40.02%"; this considerably improved battery life in many devices.
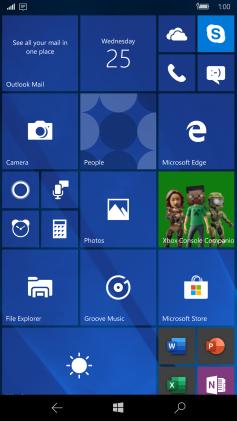
Windows 10 Mobile is a discontinued mobile operating system developed by Microsoft. First released in 2015, it is a successor to Windows Phone 8.1, but was marketed by Microsoft as being an edition of its PC operating system Windows 10.
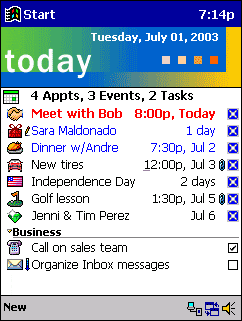
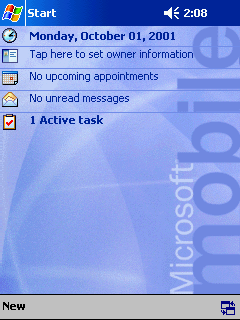
Pocket PC 2000 was the first member of the Windows Mobile family of mobile operating systems that was released on April 19, 2000, and was based on Windows CE 3.0. It is the successor to the operating system aboard Palm-size PCs. Backwards compatibility was retained with such Palm-size PC applications.
Pocket-sized computer describes the post-programmable calculator / pre-smartphone pocket-sized portable-office hardware devices that included the earlier DOS-based palmtops and subsequent Windows-CE handhelds, as well as a few other terms, primarily covering the 1980s through 2007.