
Swahili, also known by its local name Kiswahili, is a Bantu language spoken by the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Tanzania, Kenya and Mozambique.

Hazaragi is an eastern dialect and variety of the Persian language that is spoken by the Hazara people, primarily in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region of central Afghanistan, as well as other Hazara-populated areas of Afghanistan. Hazaragi is also spoken by the Hazaras of Pakistan and Iran, and also by the Hazara diaspora living elsewhere.

The Kansai dialect is a group of Japanese dialects in the Kansai region of Japan. In Japanese, Kansai-ben is the common name and it is called Kinki dialect in technical terms. The dialects of Kyoto and Osaka are known as Kamigata dialect, and were particularly referred to as such in the Edo period. The Kansai dialect is typified by the speech of Osaka, the major city of Kansai, which is referred to specifically as Osaka-ben. It is characterized as being both more melodic and harsher by speakers of the standard language.
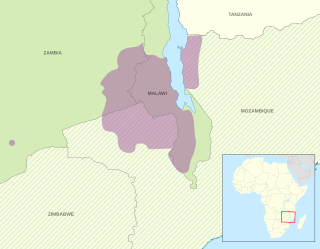
Chewa is a Bantu language spoken in Malawi and a recognised minority in Zambia and Mozambique. The noun class prefix chi- is used for languages, so the language is usually called Chichewa and Chinyanja. In Malawi, the name was officially changed from Chinyanja to Chichewa in 1968 at the insistence of President Hastings Kamuzu Banda, and this is still the name most commonly used in Malawi today. In Zambia, the language is generally known as Nyanja or Cinyanja/Chinyanja '(language) of the lake'.

The Tumbuka is a Bantu ethnic group found in Malawi, Zambia and Tanzania. Tumbuka is classified as a part of the Bantu language family, and with origins in a geographic region between the Dwangwa River to the south, the North Rukuru River to the north, Lake Malawi to the east, and the Luangwa River. They are found in the valleys near the rivers, lake as well as the highlands of Nyika Plateau, where they are frequently referred to as Henga although this is strictly speaking the name of a subdivision.

Mzuzu is the capital of Malawi's Northern Region and is the third largest city by population in Malawi. The city has 221,272 residents and 20,000 commuters with about 1.7 million people in its metropolitan area. It is situated in Mzimba District. Mzuzu lies in a gap in the Viphya Mountains, and the agricultural region surrounding the city specializes in tea, rubber and coffee cultivation. The Viphya Plantation south of the city is the largest man-made forest in Africa, and the Lunyangwa and Kaning'ina forest preserves are east of the city.
The Tumbuka language is a Bantu language which is spoken in Malawi, Zambia, and Tanzania. It is also known by the autonym Chitumbuka also spelled Citumbuka — the chi- prefix in front of Tumbuka means "in the manner of", and is understood in this case to mean "the language of the Tumbuka people". Tumbuka belongs to the same language group as Chewa and Sena.
The Nyakyusa are a Bantu ethnolinguistic group who live in the fertile mountains of southern Mbeya Region of Tanzania and the Northern Region of Malawi. They speak the Nyakyusa language, a member of the Bantu language family. In 1993 the Nyakyusa population was estimated to number 1,050,000, with 750,000 living in Tanzania. Nyakyusa are marked as highly educated and eager agriculturists. The Nyakyusa are colonising people where success and survival depended on individual effort. Nyakyusa have managed to collect vast wealth from trade and agriculture than any tribe in Tanzania..
Chitipa District is the northernmost district in the Northern Region of Malawi. The capital is Chitipa. The district covers an area of 4,288 km.², and has a population of 234,927. Chitipa borders fellow districts Karonga and Rumphi, as well as neighboring countries Tanzania and Zambia. The district is divided into five main areas known as Misuku to the east, Kameme to the north, Bulambia right at the centre while Wenya and Nthalire areas are situated to the south.
Karonga is a district in the Northern Region of Malawi. The district covers an area of 3,355 km.² and has a population of 365,028. It is a border district between Malawi and Tanzania, mainly occupied by the Tumbuka and Nkhonde tribes. Other tribes include Henga tribe.
Nyangumarta, also written Njaŋumada, Njangamada, Njanjamarta and other variants, is a language spoken by the Nyangumarta people and other Aboriginal Australians in the region of Western Australia to the south and east of Lake Waukarlykarly, including Eighty Mile Beach, and part of the Great Sandy Desert inland to near Telfer. As of 2021 there were an estimated 240 speakers of Nyangumarta, down from a 1975 estimate of 1000.

Southwestern Mandarin, also known as Upper Yangtze Mandarin, is a Mandarin Chinese language spoken in much of Southwest China, including in Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Guizhou, most parts of Hubei, the northwestern part of Hunan, the northern part of Guangxi and some southern parts of Shaanxi and Gansu.
Kituba is a widely used lingua franca in Central Africa. It is a creole language based on Kikongo, a Bantu language. It is a national language in Republic of the Congo and Democratic Republic of the Congo.
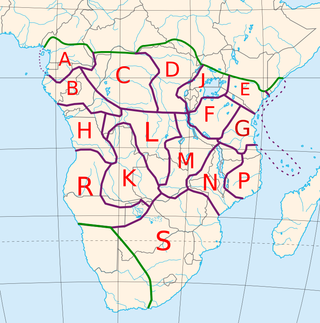
The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades ; individual languages were assigned unit numbers, and dialects further subdivided. This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was a practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes.
Yao is a Bantu language in Africa with approximately two million speakers in Malawi, and half a million each in Tanzania and Mozambique. There are also some speakers in Zambia. In Malawi, the main dialect is Mangochi, mostly spoken around Lake Malawi. In Mozambique, the main dialects are Makale and Massaninga. The language has also gone by several other names in English, including chiYao or ciYao, Achawa, Adsawa, Adsoa, Ajawa, Ayawa, Ayo, Ayao, Djao, Haiao, Hiao, Hyao, Jao, Veiao, and waJao.

Iraqw is a Cushitic language spoken in Tanzania in the Arusha and Manyara Regions. It is expanding in numbers as the Iraqw people absorb neighbouring ethnic groups. The language has many Datooga loanwords, especially in poetic language. The Gorowa language, to the south, shares numerous similarities and is sometimes considered a dialect.
Lambya (Rambia) is a Bantu language of Tanzania and Malawi. In Northern Malawi it is spoken particularly in the Chitipa District.

Tonga is a Bantu language spoken mainly in the Nkhata Bay District of Malawi. The number of speakers is estimated to be 170,000. According to the Mdawuku wa Atonga (MWATO) there are also significant numbers of speakers living elsewhere in Malawi and in neighbouring countries.
The Bible, or portions of it, have been translated into over 1,000 languages of Africa.
Swahili is a Bantu language which is native to or mainly spoken in East African region. It has a grammatical structure that is typical for Bantu languages, bearing all the hallmarks of this language family. These include agglutinativity, a rich array of noun classes, extensive inflection for person, tense, aspect and mood, and generally a subject–verb–object word order.









