
Dementia is the general name for a decline in cognitive abilities that impacts a person's ability to perform everyday activities. This typically involves problems with memory, thinking, and behavior. Aside from memory impairment and a disruption in thought patterns, the most common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and decreased motivation. The symptoms may be described as occurring in a continuum over several stages. Dementia ultimately has a significant effect on the individual, caregivers, and on social relationships in general. A diagnosis of dementia requires the observation of a change from a person's usual mental functioning and a greater cognitive decline than what is caused by normal aging.

Pfizer Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891).

Donepezil, sold under the brand name Aricept among others, is a medication used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer's type. It appears to result in a small benefit in mental function and ability to function. Use, however, has not been shown to change the progression of the disease. Treatment should be stopped if no benefit is seen. It is taken by mouth or via a transdermal patch.

Amyloid beta denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP), which is cleaved by beta secretase and gamma secretase to yield Aβ in a cholesterol-dependent process and substrate presentation. Aβ molecules can aggregate to form flexible soluble oligomers which may exist in several forms. It is now believed that certain misfolded oligomers can induce other Aβ molecules to also take the misfolded oligomeric form, leading to a chain reaction akin to a prion infection. The oligomers are toxic to nerve cells. The other protein implicated in Alzheimer's disease, tau protein, also forms such prion-like misfolded oligomers, and there is some evidence that misfolded Aβ can induce tau to misfold.
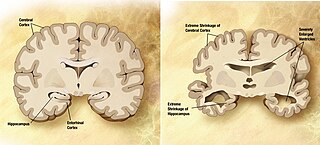
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, tauopathies, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that therapeutic advances against one neurodegenerative disease might ameliorate other diseases as well.
The Alliance for Aging Research is a non-profit organization based in Washington, D.C., that promotes medical research to improve the human experience of aging. Founded in 1986 by Daniel Perry, the Alliance also advocates and implements health education for consumers and health professionals.
Bapineuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that acts on the nervous system and may have potential therapeutic value for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and possibly glaucoma. However, in 2012 it failed to produce significant cognitive improvements in patients in two major trials, despite lowering key biomarkers of AD, amyloid brain plaque and hyperphosphorylated tau protein in CSF.
CD33 or Siglec-3 is a transmembrane receptor expressed on cells of myeloid lineage. It is usually considered myeloid-specific, but it can also be found on some lymphoid cells.

Latrepirdine is an antihistamine drug which has been used clinically in Russia since 1983.

Gantenerumab is a monoclonal antibody for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease being developed by Hoffmann-La Roche pharmaceuticals.
Sir Menelaos (Mene) Nicolas Pangalos is a British neuroscientist of Greek descent.

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens, and is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.

Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs), also known as anti-cholinesterase, are chemicals that prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine or butyrylcholine. This increases the amount of the acetylcholine or butyrylcholine in the synaptic cleft that can bind to muscarinic receptors, nicotinic receptors and others. This group of inhibitors is divided into two subgroups, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors (BChEIs).

Gladstone Institutes is an independent, non-profit biomedical research organization whose focus is to better understand, prevent, treat and cure cardiovascular, viral and neurological conditions such as heart failure, HIV/AIDS and Alzheimer's disease. Its researchers study these diseases using techniques of basic and translational science. Another focus at Gladstone is building on the development of induced pluripotent stem cell technology by one of its investigators, 2012 Nobel Laureate Shinya Yamanaka, to improve drug discovery, personalized medicine and tissue regeneration.

PF-03654746 is a potent and selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist developed by Pfizer and currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of ADHD, Tourette syndrome as well as potential anti-allergy applications.

Cerlapirdine is a drug which was under development by Wyeth/Pfizer for the treatment of cognitive disorders associated with Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia. In a phase II clinical trial it demonstrated a trend toward efficacy along with a good side effect profile and no incidence of serious adverse events, but no further development has occurred since 2011.
Medivation was an American biopharmaceutical company focused on development of novel therapies to treat serious diseases for which there are limited treatment options. Medivation was headquartered in San Francisco, California, beginning operations in December 2004 with the acquisition of Medivation Neurology, Inc. Its final CEO was David Hung.
Rinat Neuroscience Corporation was a privately held biotechnology company that discovered and developed antibody-based drugs, including:

Phenserine is a synthetic drug which has been investigated as a medication to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD), as the drug exhibits neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects.

SAGE-718 is experimental drug being investigated for the treatment of neurological disorders and cognitive impairment. It acts as a positive allosteric modulator of the NMDA receptor, whose activity is essential for learning, memory, and cognition. SAGE-718 is an analog of the neurosteroid 24S-hydroxycholesterol.














