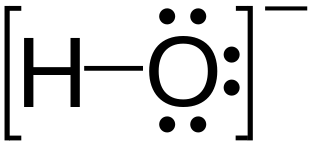
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Iron(II) hydroxide or ferrous hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Fe(OH)2. It is produced when iron(II) salts, from a compound such as iron(II) sulfate, are treated with hydroxide ions. Iron(II) hydroxide is a white solid, but even traces of oxygen impart a greenish tinge. The air-oxidised solid is sometimes known as "green rust".
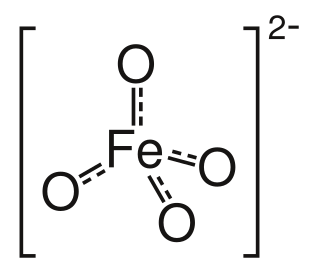
Ferrate(VI) is the inorganic anion with the chemical formula [FeO4]2−. It is photosensitive, contributes a pale violet colour to compounds and solutions containing it and is one of the strongest water-stable oxidizing species known. Although it is classified as a weak base, concentrated solutions containing ferrate(VI) are corrosive and attack the skin and are only stable at high pH. It is similar to the somewhat more stable permanganate.
Potassium hypomanganate is the inorganic compound with the formula K3MnO4. Also known as potassium manganate(V), this bright blue solid is a rare example of a salt with the hypomanganate or manganate(V) anion, where the manganese atom is in the +5 oxidation state. It is an intermediate in the production of potassium permanganate and the industrially most important Mn(V) compound.

Chromium compounds are compounds containing the element chromium (Cr). Chromium is a member of group 6 of the transition metals. The +3 and +6 states occur most commonly within chromium compounds, followed by +2; charges of +1, +4 and +5 for chromium are rare, but do nevertheless occasionally exist.
Indium(III) hydroxide is the chemical compound with the formula In(OH)3. Its prime use is as a precursor to indium(III) oxide, In2O3. It is sometimes found as the rare mineral dzhalindite.

Promethium(III) chloride is a chemical compound of promethium and chlorine with the formula PmCl3. It is an ionic, water soluble, crystalline salt that glows in the dark with a pale blue or green light due to promethium's intense radioactivity.

Promethium(III) fluoride or promethium trifluoride is a salt of promethium and fluorine with the formula PmF3.

Americium(III) hydroxide is a radioactive inorganic compound with the chemical formula Am(OH)3. It consists of one americium atom and three hydroxy groups. It was first discovered in 1944, closely related to the Manhattan Project. However, these results were confidential and were only released to the public in 1945. It was the first isolated sample of an americium compound, and the first americium compound discovered.
Praseodymium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with a chemical formula Pr(OH)3.
Scandium(III) hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Sc(OH)3, the trivalent hydroxide of scandium. It is an amphoteric compound. It is slightly soluble in water, and its saturated solution contains Sc(OH)3 and a small amount of Sc(OH)+2. The solubility of scandium(III) hydroxide in water is 0.0279 mol/L. It will convert to ScO(OH) after aging, greatly reducing the solubility (0.0008 mol/L). Scandium(III) hydroxide can be produced by reacting scandium salts and alkali hydroxides. In the reaction, different starting ingredients can generate different intermediates such as Sc(OH)1.75Cl1.25, Sc(OH)2NO3 and Sc(OH)2.32(SO4)0.34.
Promethium(III) nitrate is an inorganic compound, a salt of promethium and nitric acid with the chemical formula Pm(NO3)3. The compound is radioactive, soluble in water and forms crystalline hydrates.
Promethium(III) iodide is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of PmI3. It is a red radioactive solid with a melting point of 695 °C.

Promethium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula of PmBr3. It is radioactive salt. It is a crystal of the hexagonal crystal system, with the space group of P63/mc (No. 176).
Promethium compounds are compounds containing the element promethium, which normally take the +3 oxidation state. Promethium belongs to the cerium group of lanthanides and is chemically very similar to the neighboring elements. Because of its instability, chemical studies of promethium are incomplete. Even though a few compounds have been synthesized, they are not fully studied; in general, they tend to be pink or red in color. Treatment of acidic solutions containing Pm3+ ions with ammonia results in a gelatinous light-brown sediment of hydroxide, Pm(OH)3, which is insoluble in water. When dissolved in hydrochloric acid, a water-soluble yellow salt, PmCl3, is produced; similarly, when dissolved in nitric acid, a nitrate results, Pm(NO3)3. The latter is also well-soluble; when dried, it forms pink crystals, similar to Nd(NO3)3. The electron configuration for Pm3+ is [Xe] 4f4, and the color of the ion is pink. The ground state term symbol is 5I4. The sulfate is slightly soluble, like the other cerium group sulfates. Cell parameters have been calculated for its octahydrate; they lead to conclusion that the density of Pm2(SO4)3·8 H2O is 2.86 g/cm3. The oxalate, Pm2(C2O4)3·10 H2O, has the lowest solubility of all lanthanide oxalates.
Neptunium compounds are compounds containg the element neptunium (Np). Neptunium has five ionic oxidation states ranging from +3 to +7 when forming chemical compounds, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. It is the heaviest actinide that can lose all its valence electrons in a stable compound. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
Americium compounds are compounds containing the element americium (Am). These compounds can form in the +2, +3, and +4, although the +3 oxidation state is the most common. The +5, +6 and +7 oxidation states have also been reported.
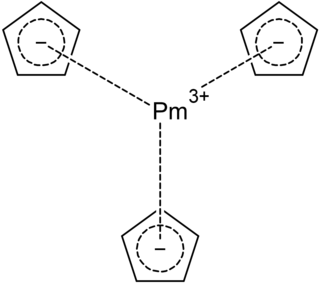
Promethocene is a metal-organic compound of promethium with the chemical formula Pm(C5H5)3. It is radioactive and stable in dry air. Promethocene is different from cyclopentadiene complexes of general transition metals and is considered to be ionically bonded. Theoretical calculations show that its Pm natural population analysis (NPA) electronic configuration is 6s0.115d1.194f2.21.










