
Honolulu is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. An unincorporated city, it is the county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oʻahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions.
Punchbowl is an alternative spelling of punch bowl, a large bowl for serving drinks, or may refer to:

The National Memorial Cemetery of the Pacific is a national cemetery located at Punchbowl Crater in Honolulu, Hawaii. It serves as a memorial to honor those men and women who served in the United States Armed Forces, and those who have been killed in doing so. It is administered by the National Cemetery Administration of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. Millions of visitors visit the cemetery each year, and it is one of the most popular tourist attractions in Hawaii.

The Hawaii State Capitol is the official statehouse or capitol building of the U.S. state of Hawaii. From its chambers, the executive and legislative branches perform the duties involved in governing the state. The Hawaii State Legislature—composed of the twenty-five member Hawaii State Senate led by the President of the Senate and the fifty-one member Hawaii State House of Representatives led by the Speaker of the House—convenes in the building. Its principal tenants are the Governor of Hawaii and Lieutenant Governor of Hawaii, as well as all legislative offices and the Legislative Reference Bureau.

Salt Lake is a neighborhood of Honolulu, Hawaii on the island of O‘ahu. The area is also known as Āliamanu after a nearby crater, although Salt Lake itself is in a crater called Ālia pa‘akai — meaning "salt pond" in the Hawaiian language. The Salt Lake community was developed in the 1960s during a construction boom, providing residents with an expansive view of downtown Honolulu and the sugarcane plantations of the central plain of O‘ahu. It is a community of high-rise condominiums, mid-rise town-dwellings, and houses snaking around the remnants of a now freshwater lake.

Diamond Head is a volcanic tuff cone on the Hawaiian island of Oʻahu. It is known to Hawaiians as Lēʻahi, which is most likely derived from lae plus ʻahi (tuna) because the shape of the ridgeline resembles the shape of a tuna's dorsal fin. Its English name was given by British sailors in the 19th century, who named it for the calcite crystals on the adjacent beach.

Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park is an American national park located in the U.S. state of Hawaii on the island of Hawaii. The park encompasses two active volcanoes: Kīlauea, one of the world's most active volcanoes, and Mauna Loa, the world's largest shield volcano. The park provides scientists with insight into the development of the Hawaiian Islands and access for studies of volcanism. For visitors, the park offers dramatic volcanic landscapes, glimpses of rare flora and fauna, and a view into the traditional Hawaiian culture connected to these landscapes.
The following is an alphabetical list of articles related to the U.S. state of Hawaii:

The USS Arizona. Memorial, at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Hawaii, marks the resting place of 1,102 of the 1,177 sailors and Marines killed on USS Arizona during the attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, and commemorates the events of that day. The attack on Pearl Harbor led to the United States' involvement in World War II.

Lorrin Andrews Thurston was an American-Hawaiian lawyer, politician, and businessman. Thurston played a prominent role in the revolution that caused the Overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom that replaced Queen Liliʻuokalani with the Republic of Hawaii, guided by American ideas. He published the Pacific Commercial Advertiser, and owned other enterprises. From 1906 to 1916, he and his network lobbied with national politicians to create a national park to preserve the Hawaiian volcanoes.

Hanauma is a marine embayment formed within a tuff ring and located along the southeast coast of the Island of Oʻahu in the Hawaii Kai neighborhood of East Honolulu, in the Hawaiian Islands.

Koʻolau Range is a name given to the dormant fragmented remnant of the eastern or windward shield volcano of the Hawaiian island of Oʻahu. It was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1972.
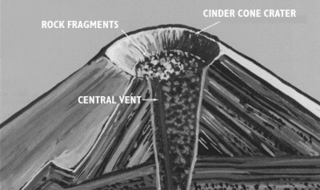
A cinder cone is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or scoria that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30 and 40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit.

Pearl Harbor is an American lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. It was often visited by the Naval fleet of the United States, before it was acquired from the Hawaiian Kingdom by the U.S. with the signing of the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands are now a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the United States Pacific Fleet. The U.S. government first obtained exclusive use of the inlet and the right to maintain a repair and coaling station for ships here in 1887. The surprise attack by the Imperial Japanese Navy on December 7, 1941, led the United States to declare war on the Empire of Japan, making the attack on Pearl Harbor the immediate cause of the United States' entry into World War II.

Volcano House is the name of a series of historic hotels built at the edge of Kīlauea, within the grounds of Hawai'i Volcanoes National Park on the Island of Hawai'i. The original 1877 building is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and now houses the Volcano Art Center. The hotel in use today was built in 1941 and expanded in 1961.

The Oʻahu Cemetery is the resting place of many notable early residents of the Honolulu area. They range from missionaries and politicians to sports pioneers and philosophers. Over time it was expanded to become an area known as the Nuʻuanu Cemetery.

Mount Tantalus is an extinct cinder cone in the southern Koʻolau Range on the Hawaiian Island of Oʻahu. It also has a summit crater, Tantalus Crater. The cinder cone formed after the demise of Koʻolau Volcano, during a time of rejuvenated-stage volcanism in southeastern Oʻahu that also formed Punchbowl Crater, Diamond Head and Koko Head as part of the Honolulu Volcanics. Tantalus overlooks the modern city of Honolulu, which is built on top of Tantalus cinders.

Ulupaʻu Crater is a tuff cone in the U.S. state of Hawaii, located near Marine Corps Base Hawaii on the Mokapu Peninsula.

The Honolulu Volcanics are a group of volcanoes which form a volcanic field on the island of Oʻahu, Hawaiʻi, more specifically in that island's southeastern sector and in the city of Honolulu from Pearl Harbor to the Mokapu Peninsula. It is part of the rejuvenated stage of Hawaiian volcanic activity, which occurred after the main stage of volcanic activity that on Oʻahu built the Koʻolau volcano. These volcanoes formed through dominantly explosive eruptions and gave rise to cinder cones, lava flows, tuff cones and volcanic islands. Among these are well known landmarks such as Diamond Head and Punchbowl Crater.

Naval Base Hawaii was a number of United States Navy bases in the Territory of Hawaii during World War II. At the start of the war, much of the Hawaiian Islands was converted from tourism to a United States Armed Forces base. With the loss of US Naval Base Philippines in Philippines campaign of 1941 and 1942, Hawaii became the US Navy's main base for the early part of the island-hopping Pacific War against Empire of Japan. Naval Station Pearl Harbor was founded in 1899 with the annexation of Hawaii.





















