A prefecture is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain international church structures, as well as in antiquity a Roman district.
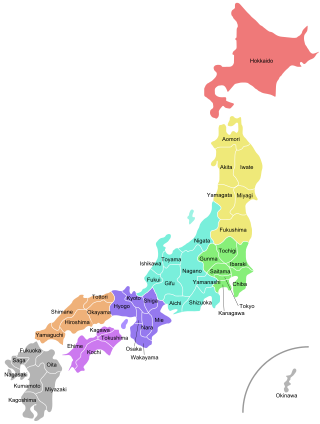
Japan is divided into 47 prefectures, which rank immediately below the national government and form the country's first level of jurisdiction and administrative division. They include 43 prefectures proper, two urban prefectures, one "circuit" or "territory" and one metropolis. In 1868, the Meiji Fuhanken sanchisei administration created the first prefectures to replace the urban and rural administrators in the parts of the country previously controlled directly by the shogunate and a few territories of rebels/shogunate loyalists who had not submitted to the new government such as Aizu/Wakamatsu. In 1871, all remaining feudal domains (han) were also transformed into prefectures, so that prefectures subdivided the whole country. In several waves of territorial consolidation, today's 47 prefectures were formed by the turn of the century. In many instances, these are contiguous with the ancient ritsuryō provinces of Japan.
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since ancient times, due to China's large population and geographical area. The constitution of China provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there are five levels of local government; the provincial, prefecture, county, township, and village.

The regions of Greece are the country's thirteen first-level administrative entities, each comprising several second-level units, originally known as prefectures and, since 2011, as regional units.
ISO 3166-2:GN is the entry for Guinea in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.

Guinea is divided into 8 regions among which the national capital Conakry ranks as a special zone. The other 7 regions are further subdivided into 33 prefectures and thence into sub-prefectures; which are later subdivided into local units and further subdivided into smaller units.

The Nzérékoré Region is a region in the southern part of Guinea. Its capital and largest city is Nzérékoré. It is one of the eight regions of Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Sierra Leone, Liberia, and Ivory Coast, and the Guinean regions of Kankan and Faranah.

The Kankan region now has more than 6,167,904 inhabitants (2021) the most popular region of Guinea The region has five (5) prefectures, 53 sub-prefectures, 5 urban communes, 53 rural communes, 878 arrondissements, 68 neighborhoods and 1864 sectors.

Faranah Region is located in east-central Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Sierra Leone and Mali and the Guinean regions of Kankan, Mamou, Nzérékoré, and Labé.

Boké Region is located in western Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Senegal and Guinea-Bissau and the Guinean regions of Kindia and Labé. Its capital is the city of Boké.

Mamou Region is located in central Guinea. It is bordered by the country of Sierra Leone and the Guinean regions of Faranah, Labé, and Kindia.

Kindia Region is located in western Guinea. It is bordered by the country of Sierra Leone and the Guinean regions of Conakry, Labé, Mamou, and Boké.

Labé Region is located in north-central Guinea. It is bordered by the countries of Senegal and Mali and the Guinean regions of Faranah, Kindia, Mamou, and Boké.

The traditional geographic regions of Greece are the country's main historical-geographic regions, and were also official administrative regional subdivisions of Greece until the 1987 administrative reform. Despite their replacement as first-level administrative units by only partly identical administrative regions, the nine traditional geographic regions—six on the mainland and three island groups—are still widely referred to in unofficial contexts and in daily discourse.
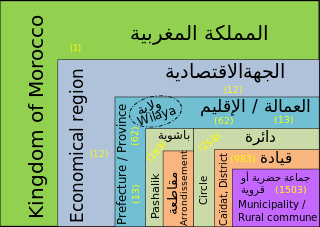
In Morocco, the 75 second-level administrative subdivisions are 13 prefectures and 62 provinces. They are subdivisions of the 12 regions of Morocco. Each prefecture or province is subdivided into arrondissements, municipalities or urban municipalities in other urban areas, and districts in rural areas. The districts are subdivided into rural municipalities. One prefecture (Casablanca) is also subdivided into préfectures d'arrondissements, similar to districts (cercles) except they are grouping a few arrondissements instead of rural municipalities.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Guinea:

The sub-prefectures are the third-level administrative divisions in Guinea. As of 2009 there were 303 rural sub-prefectures of Guinea and 38 urban sub-prefectures, 5 of which compose the Conakry greater urban area; Kaloum, Dixinn, Matam, Ratoma and Matoto.
Ivory Coast is a relatively decentralised state. The country divided into 14 districts, of which two are cities organised as autonomous districts. The 12 non-autonomous districts are subdivided into 31 second-level regions. The autonomous districts and the regions are divided into 108 third-level departments. The departments are divided into 510 fourth-level sub-prefectures. Sub-prefectures contain villages and, in some instances, several villages are combined into fifth-level communes. There are 197 communes.

Guinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic, and climatic characteristics:

Following the implementation on 1 January 2011 of the Kallikratis Plan, the administrative divisions of Greece consist of two main levels: the regions and the municipalities. In addition, a number of decentralized administrations overseeing the regions exist as part of the Ministry of the Interior, but are not entities of local government. The old prefectures were either abolished and divided or transformed into regional units in 2011. The administrative regions are divided into regional units which are further subdivided into municipalities. The Eastern Orthodox monastic community on Mount Athos is an autonomous self-governing entity.
















