
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature.

Sulfuric acid or sulphuric acid, known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a colorless, odorless and viscous liquid that is miscible with water.

Sulfide (British English also sulphide) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. Sulfide also refers to chemical compounds large families of inorganic and organic compounds, e.g. lead sulfide and dimethyl sulfide. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and bisulfide (SH−) are the conjugate acids of sulfide.

Cerium(IV) sulfate, also called ceric sulfate, is an inorganic compound. It exists as the anhydrous salt Ce(SO4)2 as well as a few hydrated forms: Ce(SO4)2(H2O)x, with x equal to 4, 8, or 12. These salts are yellow to yellow/orange solids that are moderately soluble in water and dilute acids. Its neutral solutions slowly decompose, depositing the light yellow oxide CeO2. Solutions of ceric sulfate have a strong yellow color. The tetrahydrate loses water when heated to 180-200 °C.

Wilkinson's catalyst is the common name for chloridotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I), a coordination complex of rhodium with the formula [RhCl(PPh3)3] (Ph = phenyl). It is a red-brown colored solid that is soluble in hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, and more so in tetrahydrofuran or chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane. The compound is widely used as a catalyst for hydrogenation of alkenes. It is named after chemist and Nobel laureate Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson, who first popularized its use.

Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.
Selenic acid is the inorganic compound with the formula H2SeO4. It is an oxoacid of selenium, and its structure is more accurately described as O2Se(OH)2. It is a colorless compound. Although it has few uses, one of its salts, sodium selenate is used in the production of glass and animal feeds.
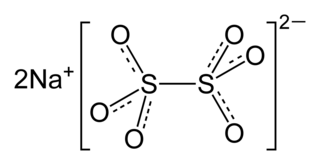
Sodium dithionate Na2S2O6 is an important compound for inorganic chemistry. It is also known under names disodium dithionate, sodium hyposulfate, and sodium metabisulfate. The sulfur can be considered to be in its +5 oxidation state.

Terbium(III,IV) oxide, occasionally called tetraterbium heptaoxide, has the formula Tb4O7, though some texts refer to it as TbO1.75. There is some debate as to whether it is a discrete compound, or simply one phase in an interstitial oxide system. Tb4O7 is one of the main commercial terbium compounds, and the only such product containing at least some Tb(IV) (terbium in the +4 oxidation state), along with the more stable Tb(III). It is produced by heating the metal oxalate, and it is used in the preparation of other terbium compounds. Terbium forms three other major oxides: Tb2O3, TbO2, and Tb6O11.

Chlorosulfuric acid (IUPAC name: sulfurochloridic acid) is the inorganic compound with the formula HSO3Cl. It is also known as chlorosulfonic acid, being the sulfonic acid of chlorine. It is a distillable, colorless liquid which is hygroscopic and a powerful lachrymator. Commercial samples usually are pale brown or straw colored.
Indium(III) sulfate (In2(SO4)3) is a sulfate salt of the metal indium. It is a sesquisulfate, meaning that the sulfate group occurs 11/2 times as much as the metal. It may be formed by the reaction of indium, its oxide, or its carbonate with sulfuric acid. An excess of strong acid is required, otherwise insoluble basic salts are formed. As a solid indium sulfate can be anhydrous, or take the form of a pentahydrate with five water molecules or a nonahydrate with nine molecules of water. Indium sulfate is used in the production of indium or indium containing substances. Indium sulfate also can be found in basic salts, acidic salts or double salts including indium alum.
Vanadium(III) sulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula V2(SO4)3. It is a pale yellow solid that is stable to air, in contrast to most vanadium(III) compounds. It slowly dissolves in water to give the green aquo complex [V(H2O)6]3+.

Iron(III) sulfate (or ferric sulfate), is a family of inorganic compounds with the formula Fe2(SO4)3(H2O)n. A variety of hydrates are known, including the most commonly encountered form of "ferric sulfate". Solutions are used in dyeing as a mordant, and as a coagulant for industrial wastes. Solutions of ferric sulfate are also used in the processing of aluminum and steel.

Ammonium iron(III) sulfate, NH4Fe(SO4)2·12 H2O, or NH4[Fe(H2O)6](SO4)2·6 H2O, also known as ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS) or iron alum, is a double salt in the class of alums, which consists of compounds with the general formula AB(SO4)2 · 12 H2O. It has the appearance of weakly violet, octahedrical crystals. There has been some discussion regarding the origin of the crystals' colour, with some ascribing it to impurities in the compound, and others claiming it to be a property of the crystal itself.

Antimony sulfate, Sb2(SO4)3, is a hygroscopic salt formed by reacting antimony or its compounds with hot sulfuric acid. It is used in doping of semiconductors and in the production of explosives and fireworks.

Compounds of lead exist with lead in two main oxidation states: +2 and +4. The former is more common. Inorganic lead(IV) compounds are typically strong oxidants or exist only in highly acidic solutions.

Chloropentamminecobalt chloride is the dichloride salt of the coordination complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+. It is a red-violet, diamagnetic, water-soluble salt. The compound has been of academic and historical interest.

Hydroxylamine-O-sulfonic acid (HOSA) is the inorganic compound with molecular formula H3NO4S that is formed by the sulfonation of hydroxylamine with oleum. It is a white, water-soluble and hygroscopic, solid, commonly represented by the condensed structural formula H2NOSO3H, though it actually exists as a zwitterion and thus is more accurately represented as +H3NOSO3−. It is used as a reagent for the introduction of amine groups (–NH2), for the conversion of aldehydes into nitriles and alicyclic ketones into lactams (cyclic amides), and for the synthesis of variety of nitrogen-containing heterocycles.
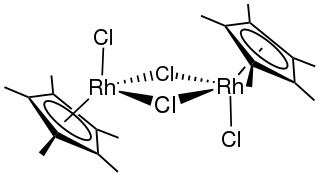
Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride dimer is an organometallic compound with the formula [(C5(CH3)5RhCl2)]2, commonly abbreviated [Cp*RhCl2]2 This dark red air-stable diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry.

Rhodium(III) perchlorate refers to the inorganic compound with the formula Rh(H2O)6(ClO4)3. It is a hygroscopic yellow solid. It is the perchlorate salt of the tricationic aquo complex [Rh(H2O)6]3+. The compound is prepared by treating hydrated rhodium(III) chloride and perchloric acid at elevated temperatures:

















