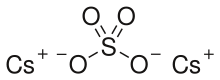
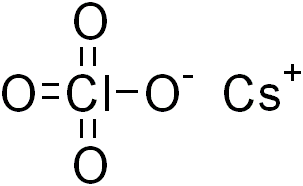Caesium is a chemical element; it has symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of 28.5 °C (83.3 °F), which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at or near room temperature. Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. It is pyrophoric and reacts with water even at −116 °C (−177 °F). It is the least electronegative element, with a value of 0.79 on the Pauling scale. It has only one stable isotope, caesium-133. Caesium is mined mostly from pollucite. Caesium-137, a fission product, is extracted from waste produced by nuclear reactors. It has the largest atomic radius of all elements whose radii have been measured or calculated, at about 260 picometers.

Rubidium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have a density higher than water. On Earth, natural rubidium comprises two isotopes: 72% is a stable isotope 85Rb, and 28% is slightly radioactive 87Rb, with a half-life of 48.8 billion years—more than three times as long as the estimated age of the universe.

Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a hygroscopic white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all known elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements.

Caesium hydroxide is a strong base containing the highly reactive alkali metal caesium, much like the other alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. It is the strongest of the five alkali metal hydroxides. Fused Caesium hydroxide dissolves glass by attacking silica framework and it has applications in bringing glass samples into a solution for analytical purposes in commercial glass industry and defense waste processing facility. The melting process is carried out in a nickel or zirconium crucible. Cesium hydroxide fusion at 750°C produces complete dissolution of glass pellets.

Caesium iodide or cesium iodide is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly efficient at extreme ultraviolet wavelengths.

Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula CsCl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural type where each caesium ion is coordinated by 8 chloride ions. Caesium chloride dissolves in water. CsCl changes to NaCl structure on heating. Caesium chloride occurs naturally as impurities in carnallite, sylvite and kainite. Less than 20 tonnes of CsCl is produced annually worldwide, mostly from a caesium-bearing mineral pollucite.
Caesium (55Cs) has 40 known isotopes, making it, along with barium and mercury, one of the elements with the most isotopes. The atomic masses of these isotopes range from 112 to 151. Only one isotope, 133Cs, is stable. The longest-lived radioisotopes are 135Cs with a half-life of 2.3 million years, 137
Cs
with a half-life of 30.1671 years and 134Cs with a half-life of 2.0652 years. All other isotopes have half-lives less than 2 weeks, most under an hour.
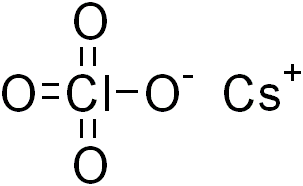
Caesium perchlorate or cesium perchlorate (CsClO4), is a perchlorate of caesium. It forms white crystals, which are sparingly soluble in cold water and ethanol. It dissolves more easily in hot water.

Caesium-137, cesium-137 (US), or radiocaesium, is a radioactive isotope of caesium that is formed as one of the more common fission products by the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and other fissionable isotopes in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Trace quantities also originate from spontaneous fission of uranium-238. It is among the most problematic of the short-to-medium-lifetime fission products. Caesium-137 has a relatively low boiling point of 671 °C (1,240 °F) and easily becomes volatile when released suddenly at high temperature, as in the case of the Chernobyl nuclear accident and with atomic explosions, and can travel very long distances in the air. After being deposited onto the soil as radioactive fallout, it moves and spreads easily in the environment because of the high water solubility of caesium's most common chemical compounds, which are salts. Caesium-137 was discovered by Glenn T. Seaborg and Margaret Melhase.
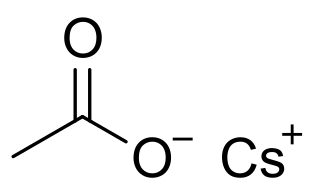
Caesium acetate or cesium acetate is an ionic caesium compound with the molecular formula CH3COOCs. It is a white solid that may be formed by the reaction of caesium hydroxide or caesium carbonate with acetic acid.

Caesium chromate or cesium chromate is an inorganic compound with the formula Cs2CrO4. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is the caesium salt of chromic acid, and it crystallises in the orthorhombic system.
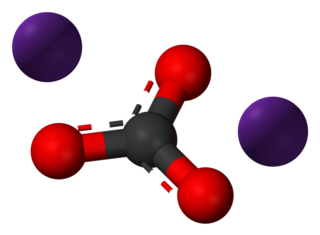
Caesium carbonate or cesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid compound. Caesium carbonate has a high solubility in polar solvents such as water, alcohol and DMF. Its solubility is higher in organic solvents compared to other carbonates like potassium and sodium carbonates, although it remains quite insoluble in other organic solvents such as toluene, p-xylene, and chlorobenzene. This compound is used in organic synthesis as a base. It also appears to have applications in energy conversion.

Thallium(I) chloride, also known as thallous chloride, is a chemical compound with the formula TlCl. This colourless salt is an intermediate in the isolation of thallium from its ores. Typically, an acidic solution of thallium(I) sulfate is treated with hydrochloric acid to precipitate insoluble thallium(I) chloride. This solid crystallizes in the caesium chloride motif.

Caesium bromide or cesium bromide is an ionic compound of caesium and bromine with the chemical formula CsBr. It is a white or transparent solid with melting point at 636 °C that readily dissolves in water. Its bulk crystals have the cubic CsCl structure, but the structure changes to the rocksalt type in nanometer-thin film grown on mica, LiF, KBr or NaCl substrates.

Caesium hydride or cesium hydride (CsH) is a compound of caesium and hydrogen. It is an alkali metal hydride. It was the first substance to be created by light-induced particle formation in metal vapor, and showed promise in early studies of an ion propulsion system using caesium. It is the most reactive stable alkaline metal hydride of all. It is a powerful superbase and reacts with water extremely vigorously.

Caesium nitrate or cesium nitrate is a salt with the chemical formula Cs N O3. An alkali metal nitrate, it is used in pyrotechnic compositions, as a colorant and an oxidizer, e.g. in decoys and illumination flares. The caesium emissions are chiefly due to two powerful spectral lines at 852.113 nm and 894.347 nm.

Caesium bicarbonate or cesium bicarbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CsHCO3. It can be produced through the following reaction:

Caesium oxalate (standard IUPAC spelling) dicesium oxalate, or cesium oxalate (American spelling) is the oxalate of caesium. Caesium oxalate has the chemical formula of Cs2C2O4.

Caesium azide or cesium azide is an inorganic compound of caesium and nitrogen. It is a salt of azide with the formula CsN3.
Caesium telluride or Caesium telluridocaesium is an inorganic salt with a chemical formula Cs2Te. Caesium telluride is used to make photo cathodes.