Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula SO. It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 (disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise.

Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SOCl2. It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately 45,000 tonnes per year being produced during the early 1990s, but is occasionally also used as a solvent. It is toxic, reacts with water, and is also listed under the Chemical Weapons Convention as it may be used for the production of chemical weapons.

Tetrasulfur tetranitride is an inorganic compound with the formula S4N4. This vivid orange, opaque crystalline compound is the most important binary sulfur nitride, which are compounds that contain only the elements sulfur and nitrogen. It is a precursor to many S-N compounds and has attracted wide interest for its unusual structure and bonding.
Sulfur compounds are chemical compounds formed the element sulfur (S). Common oxidation states of sulfur range from −2 to +6. Sulfur forms stable compounds with all elements except the noble gases.

Sulfur dichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SCl2. This cherry-red liquid is the simplest sulfur chloride and one of the most common, and it is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds. It is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, and it reacts on contact with water to form chlorine-containing acids.
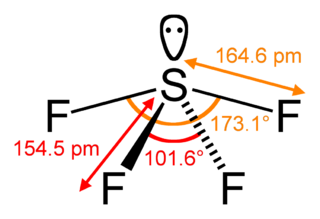
Sulfur tetrafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula SF4. It is a colorless corrosive gas that releases dangerous HF upon exposure to water or moisture. Despite these unwelcome characteristics, this compound is a useful reagent for the preparation of organofluorine compounds, some of which are important in the pharmaceutical and specialty chemical industries.

Disulfur dichloride is the inorganic compound of sulfur and chlorine with the formula S2Cl2. It is an amber oily liquid.

Thiophosgene is a red liquid with the formula CSCl2. It is a molecule with trigonal planar geometry. There are two reactive C–Cl bonds that allow it to be used in diverse organic syntheses.

Gold(V) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula Au2F10. This fluoride compound features gold in its highest known oxidation state. This red solid dissolves in hydrogen fluoride but these solutions decompose, liberating fluorine.
A polysulfane is a chemical compound of formula H2Sn, where n > 1. Compounds containing 2 – 8 sulfur atoms have been isolated, longer chain compounds have been detected, but only in solution. H2S2 is colourless, higher members are yellow with the colour increasing with the sulfur content. In the chemical literature the term polysulfanes is sometimes used for compounds containing −(S)n−, e.g. organic polysulfanes R1−(S)n−R2.

The lower sulfur oxides are a group of inorganic compounds with the formula SmOn, where 2m > n. These species are often unstable and thus rarely encountered in everyday life. They are significant intermediates in the combustion of elemental sulfur. Some well characterized examples include sulfur monoxide (SO), its dimer S2O2, and a series of cyclic sulfur oxides, SnOx (x = 1, 2), based on cyclic Sn rings.

The element sulfur exists as many allotropes. In number of allotropes, sulfur is second only to carbon. In addition to the allotropes, each allotrope often exists in polymorphs delineated by Greek prefixes.

Disulfur is the diatomic molecule with the formula S2. It is analogous to the dioxygen molecule but rarely occurs at room temperature. This violet gas is the dominant species in hot sulfur vapors. S2 is one of the minor components of the atmosphere of Io, which is predominantly composed of SO2. The instability of S2 is usually described in the context of the double bond rule.
Selenium monochloride or diselenium dichloride is an inorganic compound with the formula Se2Cl2. Although a common name for the compound is selenium monochloride, reflecting its empirical formula, IUPAC does not recommend that name, instead preferring the more descriptive diselenium dichloride.

Disulfur monoxide or sulfur suboxide is an inorganic compound with the formula S2O, one of the lower sulfur oxides. It is a colourless gas and condenses to give a roughly dark red coloured solid that is unstable at room temperature.

Sulfur difluoride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SF2. It can be generated by the reaction of sulfur dichloride and potassium fluoride or mercury(II) fluoride at low pressures:

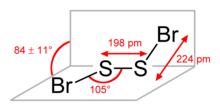
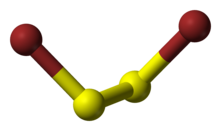
Disulfur dioxide, dimeric sulfur monoxide or SO dimer is an oxide of sulfur with the formula S2O2. The solid is unstable with a lifetime of a few seconds at room temperature.

Titanocene pentasulfide is the organotitanium compound with the formula (C5H5)2TiS5, commonly abbreviated as Cp2TiS5. This metallocene exists as a bright red solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is of academic interest as a precursor to unusual allotropes of elemental sulfur as well as some related inorganic rings.

Thiothionyl fluoride is a chemical compound of fluorine and sulfur, with the chemical formula S=SF2. It is an isomer of disulfur difluoride (difluorodisulfane) F−S−S−F.

Disulfur diiodide is an unstable inorganic chemical compound with the chemical formula S2I2. It is a red-brown solid that decomposes above −30 °C to elemental sulfur and iodine.