General anaesthetics are often defined as compounds that induce a loss of consciousness in humans or loss of righting reflex in animals. Clinical definitions are also extended to include an induced coma that causes lack of awareness to painful stimuli, sufficient to facilitate surgical applications in clinical and veterinary practice. General anaesthetics do not act as analgesics and should also not be confused with sedatives. General anaesthetics are a structurally diverse group of compounds whose mechanisms encompass multiple biological targets involved in the control of neuronal pathways. The precise workings are the subject of some debate and ongoing research.

Anesthesia or anaesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized.

General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a method of medically inducing loss of consciousness that renders a patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general anaesthetic medications, which often act in combination with an analgesic and neuromuscular blocking agent. Spontaneous ventilation is often inadequate during the procedure and intervention is often necessary to protect the airway. General anaesthesia is generally performed in an operating theater to allow surgical procedures that would otherwise be intolerably painful for a patient, or in an intensive care unit or emergency department to facilitate endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation in critically ill patients. Depending on the procedure, general anaesthesia may be optional or required. Regardless of whether a patient may prefer to be unconscious or not, certain pain stimuli could result in involuntary responses from the patient that may make an operation extremely difficult. Thus, for many procedures, general anaesthesia is required from a practical perspective.

Midazolam, sold under the brand name Dormicum and Versed among others, is a benzodiazepine medication used for anesthesia and procedural sedation, and to treat severe agitation. It induces sleepiness, decreases anxiety, and causes anterograde amnesia.

An anesthetic or anaesthetic is a drug used to induce anesthesia — in other words, to result in a temporary loss of sensation or awareness. They may be divided into two broad classes: general anesthetics, which result in a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body without necessarily affecting consciousness.
Awareness under anesthesia, also referred to as intraoperative awareness or accidental awareness during general anesthesia (AAGA), is a rare complication of general anesthesia where patients regain varying levels of consciousness during their surgical procedures. While anesthesia awareness is possible without resulting in any long-term memory of the experience, it is also possible for victims to have awareness with explicit recall, where they can remember the events related to their surgery.
Premedication is using medication before some other therapy to prepare for that forthcoming therapy. Typical examples include premedicating with a sedative or analgesic before surgery; using prophylactic (preventive) antibiotics before surgery; and using antiemetics or antihistamines before chemotherapy.
In anaesthesia and advanced airway management, rapid sequence induction (RSI) – also referred to as rapid sequence intubation or as rapid sequence induction and intubation (RSII) or as crash induction – is a special process for endotracheal intubation that is used where the patient is at a high risk of pulmonary aspiration. It differs from other techniques for inducing general anesthesia in that several extra precautions are taken to minimize the time between giving the induction drugs and securing the tube, during which period the patient's airway is essentially unprotected.
Veterinary anesthesia is anesthesia performed on non-human animals by a veterinarian or a Registered Veterinary Technician. Anesthesia is used for a wider range of circumstances in animals than in people, due to animals' inability to cooperate with certain diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Veterinary anesthesia includes anesthesia of the major species: dogs, cats, horses, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs, as well as all other animals requiring veterinary care such as birds, pocket pets, and wildlife.

Dental fear, or dentophobia, is a normal emotional reaction to one or more specific threatening stimuli in the dental situation. However, dental anxiety is indicative of a state of apprehension that something dreadful is going to happen in relation to dental treatment, and it is usually coupled with a sense of losing control. Similarly, dental phobia denotes a severe type of dental anxiety, and is characterised by marked and persistent anxiety in relation to either clearly discernible situations or objects or to the dental setting in general. The term ‘dental fear and anxiety’ (DFA) is often used to refer to strong negative feelings associated with dental treatment among children, adolescents and adults, whether or not the criteria for a diagnosis of dental phobia are met. Dental phobia can include fear of dental procedures, dental environment or setting, fear of dental instruments or fear of the dentist as a person. People with dental phobia often avoid the dentist and neglect oral health, which may lead to painful dental problems and ultimately force a visit to the dentist. The emergency nature of this appointment may serve to worsen the phobia. This phenomenon may also be called the cycle of dental fear. Dental anxiety typically starts in childhood. There is the potential for this to place strains on relationships and negatively impact on employment.
Procedural sedation and analgesia (PSA) is a technique in which a sedating/dissociative medication is given, usually along with an analgesic medication, in order to perform non-surgical procedures on a patient. The overall goal is to induce a decreased level of consciousness while maintaining the patient's ability to breathe on their own. Airway protective reflexes are not compromised by this process and therefore endotracheal intubation is not required. PSA is commonly used in the emergency department, in addition to the operating room.

Twilight anesthesia is an anesthetic technique where a mild dose of sedation is applied to induce anxiolysis, hypnosis, and anterograde amnesia. The patient is not unconscious, but sedated. During surgery or other medical procedures, the patient is under what is known as a "twilight state", where the patient is relaxed and "sleepy", able to follow simple directions by the doctor, and is responsive. Generally, twilight anesthesia causes the patient to forget the surgery and the time right after. It is used for a variety of surgical procedures and for various reasons. Just like regular anesthesia, twilight anesthesia is designed to help a patient feel more comfortable and to minimize pain associated with the procedure being performed and to allow the medical practitioner to practice without interruptions.
Sedation dentistry refers to the use of pharmacological agents to induce sleep in a patient prior to and during a dental appointment. The pharmacological agents usually belong to a class of drugs called sedatives, which exert their action by depressing the central nervous system, specifically those areas concerned with conscious awareness.
In periodontics, there are four reasons to seek medication. Those four reasons include infection, swelling, pain, and sedation. Although some patients may experience pain, swelling, and infection as a result of an acute periodontal problem such as advanced periodontal disease, periodontic patients usually do not need medication until they are faced with surgery. For successful surgery, medication is then introduced prior to the operation, usually the morning before the procedure and is continued for up to two weeks after.
Oral sedation dentistry is a medical procedure involving the administration of sedative drugs via an oral route, generally to facilitate a dental procedure and reduce patients anxiety related to the experience. Oral sedation is one of the available methods of conscious sedation dentistry, along with inhalation sedation and conscious intravenous sedation. Benzodiazepines are commonly used, specifically triazolam. Triazolam is commonly selected for its rapid onset and limited duration of effect. An initial dose is usually taken approximately one hour before the dental appointment. Treatment may include additional dosing on the night proceeding the procedure, to mitigate anxiety-related insomnia. The procedure is generally recognized as safe, with the effective dosages being below levels sufficient to impair breathing.
The American Dental Society of Anesthesiology (ADSA) is an American professional association established in 1953 and based in Chicago.
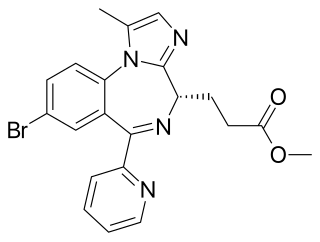
Remimazolam, sold under the brand name Byfavo, is a medication for the induction and maintenance of procedural sedation in adults for invasive diagnostic or surgical procedures lasting 30 minutes or less. It is a benzodiazepine drug, developed by PAION AG in collaboration with several regional licensees as an alternative to the short-acting imidazobenzodiazepine midazolam, for use in the induction of anesthesia and conscious sedation for minor invasive procedures. Remimazolam was found to have both a more rapid onset and a shorter duration than midazolam, and human clinical trials showed a faster recovery time and predictable, consistent pharmacokinetics, suggesting some advantages over existing drugs for these applications.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to anesthesia:
Sedoanalgesia is the practice of combining sedation with local anesthesia, usually in the case of surgery. In medical studies, administering sedoanalgesia has been shown to be cost- and time-effective when compared to general or regional anesthesia, and it can reduce the amount of nursing staff, anesthetists, and equipment required for a given procedure. Frequently used in patients who present with considerable risk from conventional anesthesia and with elderly patients with co-morbid medical conditions.

Inhalation sedation is a form of conscious sedation where an inhaled drug should:
- Depress the central nervous system (CNS) to an extent that surgeons can operate with minimal physiological and psychological stress to the patient
- Modify the patient's state of mind such that communication is maintained and the patient can respond to verbal command
- Carry a margin of safety wide enough to render the unintended loss of consciousness and loss of protective reflexes unlikely.







