Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements, that indicates dysfunction of parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum.
Paroxysmal attacks or paroxysms are a sudden recurrence or intensification of symptoms, such as a spasm or seizure. These short, frequent symptoms can be observed in various clinical conditions. They are usually associated with multiple sclerosis or pertussis, but they may also be observed in other disorders such as encephalitis, head trauma, stroke, autism, asthma, trigeminal neuralgia, breath-holding spells, epilepsy, malaria, tabes dorsalis, and Behçet's disease, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). It has also been noted as a symptom of gratification disorder in children.
General paresis, also known as general paralysis of the insane (GPI), paralytic dementia, or syphilitic paresis is a severe neuropsychiatric disorder, classified as an organic mental disorder, and is caused by late-stage syphilis and the chronic meningoencephalitis and cerebral atrophy that are associated with this late stage of the disease when left untreated. GPI differs from mere paresis, as mere paresis can result from multiple other causes and usually does not affect cognitive function. Degenerative changes caused by GPI are associated primarily with the frontal and temporal lobar cortex. The disease affects approximately 7% of individuals infected with syphilis, and is far more common in developing countries where fewer options for timely treatment are available. It is more common among men.
The ankle jerk reflex, also known as the Achilles reflex, occurs when the Achilles tendon is tapped while the foot is dorsiflexed. It is a type of stretch reflex that tests the function of the gastrocnemius muscle and the nerve that supplies it. A positive result would be the jerking of the foot towards its plantar surface. Being a deep tendon reflex, it is monosynaptic. It is also a stretch reflex. These are monosynaptic spinal segmental reflexes. When they are intact, integrity of the following is confirmed: cutaneous innervation, motor supply, and cortical input to the corresponding spinal segment.

Locomotor ataxia is the inability to precisely control one's own bodily movements.
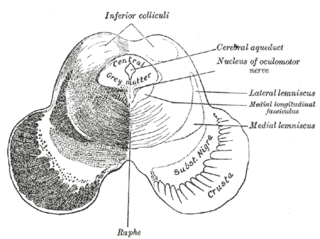
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is an area of crossed over tracts, on each side of the brainstem. These bundles of axons are situated near the midline of the brainstem. They are made up of both ascending and descending fibers that arise from a number of sources and terminate in different areas, including the superior colliculus, the vestibular nuclei, and the cerebellum. It contains the interstitial nucleus of Cajal, responsible for oculomotor control, head posture, and vertical eye movement.
A demyelinating disease refers to any disease affecting the nervous system where the myelin sheath surrounding neurons is damaged. This damage disrupts the transmission of signals through the affected nerves, resulting in a decrease in their conduction ability. Consequently, this reduction in conduction can lead to deficiencies in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on the nerves affected.

Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degenerative process in osteoarthritis chiefly affects the vertebral bodies, the neural foramina and the facet joints. If severe, it may cause pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots with subsequent sensory or motor disturbances, such as pain, paresthesia, imbalance, and muscle weakness in the limbs.

Moritz Heinrich Romberg was a German physician and neurologist who published a classic multi-volume textbook between 1840 and 1846. Considered a pioneer of neurology, he was the first to describe Romberg's sign, a medical sign of impaired proprioception in a patient.

Aseptic meningitis is the inflammation of the meninges, a membrane covering the brain and spinal cord, in patients whose cerebral spinal fluid test result is negative with routine bacterial cultures. Aseptic meningitis is caused by viruses, mycobacteria, spirochetes, fungi, medications, and cancer malignancies. The testing for both meningitis and aseptic meningitis is mostly the same. A cerebrospinal fluid sample is taken by lumbar puncture and is tested for leukocyte levels to determine if there is an infection and goes on to further testing to see what the actual cause is. The symptoms are the same for both meningitis and aseptic meningitis but the severity of the symptoms and the treatment can depend on the certain cause.

Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) is a progressive, degenerative, genetic disease with multiple types, each of which could be considered a neurological condition in its own right. An estimated 150,000 people in the United States have a diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia at any given time. SCA is hereditary, progressive, degenerative, and often fatal. There is no known effective treatment or cure. SCA can affect anyone of any age. The disease is caused by either a recessive or dominant gene. In many cases people are not aware that they carry a relevant gene until they have children who begin to show signs of having the disorder.

Romberg's test, Romberg's sign, or the Romberg maneuver is a test used in an exam of neurological function for balance. The exam is based on the premise that a person requires at least two of the three following senses to maintain balance while standing: proprioception ; vestibular function ; and vision.

Neurosyphilis is the infection of the central nervous system in a patient with syphilis. In the era of modern antibiotics, the majority of neurosyphilis cases have been reported in HIV-infected patients. Meningitis is the most common neurological presentation in early syphilis. Tertiary syphilis symptoms are exclusively neurosyphilis, though neurosyphilis may occur at any stage of infection.

The vestibulospinal tract is a neural tract in the central nervous system. Specifically, it is a component of the extrapyramidal system and is classified as a component of the medial pathway. Like other descending motor pathways, the vestibulospinal fibers of the tract relay information from nuclei to motor neurons. The vestibular nuclei receive information through the vestibulocochlear nerve about changes in the orientation of the head. The nuclei relay motor commands through the vestibulospinal tract. The function of these motor commands is to alter muscle tone, extend, and change the position of the limbs and head with the goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of the body and head.

Karl Friedrich Otto Westphal was a German psychiatrist from Berlin. He was the son of Otto Carl Friedrich Westphal (1800–1879) and Karoline Friederike Heine and the father of Alexander Karl Otto Westphal (1863-1941). He was married to Klara, daughter of the banker Alexander Mendelssohn.
Focal neurologic signs also known as focal neurological deficits or focal CNS signs are impairments of nerve, spinal cord, or brain function that affects a specific region of the body, e.g. weakness in the left arm, the right leg, paresis, or plegia.

Leptomeningeal cancer is a rare complication of cancer in which the disease spreads from the original tumor site to the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This leads to an inflammatory response, hence the alternative names neoplastic meningitis (NM), malignant meningitis, or carcinomatous meningitis. The term leptomeningeal describes the thin meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater, between which the cerebrospinal fluid is located. The disorder was originally reported by Eberth in 1870. It is also known as leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, leptomeningeal disease (LMD), leptomeningeal metastasis, meningeal metastasis and meningeal carcinomatosis.

Posterior spinal artery syndrome(PSAS), also known as posterior spinal cord syndrome, is a type of incomplete spinal cord injury. PSAS is the least commonly occurring of the six clinical spinal cord injury syndromes, with an incidence rate of less than 1%.

Tarlov cysts, are type II innervated meningeal cysts, cerebrospinal-fluid-filled (CSF) sacs most frequently located in the spinal canal of the sacral region of the spinal cord (S1–S5) and much less often in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. They can be distinguished from other meningeal cysts by their nerve-fiber-filled walls. Tarlov cysts are defined as cysts formed within the nerve-root sheath at the dorsal root ganglion. The etiology of these cysts is not well understood; some current theories explaining this phenomenon have not yet been tested or challenged but include increased pressure in CSF, filling of congenital cysts with one-way valves, inflammation in response to trauma and disease. They are named for American neurosurgeon Isadore Tarlov, who described them in 1938.

Meningeal syphilis is a chronic form of syphilis infection that affects the central nervous system. Treponema pallidum, a spirochate bacterium, is the main cause of syphilis, which spreads drastically throughout the body and can infect all its systems if not treated appropriately. Treponema pallidum is the main cause of the onset of meningeal syphilis and other treponemal diseases, and it consists of a cytoplasmic and outer membrane that can cause a diverse array of diseases in the central nervous system and brain.














