Related Research Articles

A Leyden jar is an electrical component that stores a high-voltage electric charge between electrical conductors on the inside and outside of a glass jar. It typically consists of a glass jar with metal foil cemented to the inside and the outside surfaces, and a metal terminal projecting vertically through the jar lid to make contact with the inner foil. It was the original form of the capacitor.
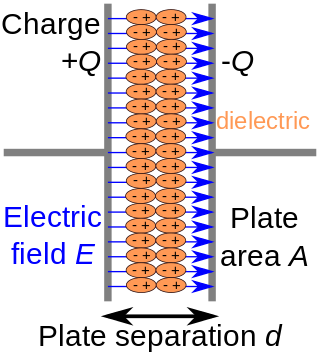
In electromagnetism, a dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in an electrical conductor, because they have no loosely bound, or free, electrons that may drift through the material, but instead they shift, only slightly, from their average equilibrium positions, causing dielectric polarisation. Because of dielectric polarisation, positive charges are displaced in the direction of the field and negative charges shift in the direction opposite to the field. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarised, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.
In physics, the term dielectric strength has the following meanings:

The triboelectric effect is a type of contact electrification on which certain materials become electrically charged after they are separated from a different material with which they were in contact. Rubbing the two materials with each other increases the contact between their surfaces, and hence the triboelectric effect. Rubbing glass with fur for example, or a plastic comb through the hair, can build up triboelectricity. Most everyday static electricity is triboelectric. The polarity and strength of the charges produced differ according to the materials, surface roughness, temperature, strain, and other properties.

Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: self capacitance and mutual capacitance. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit.

Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material or between materials. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, where the electric charge flows through an electrical conductor or space, and transmits energy.

In electromagnetism, an electrophorus or electrophore is a simple, manual, capacitive, electrostatic generator used to produce charge via the process of electrostatic induction. A first version of it was invented in 1762 by Swedish professor Johan Carl Wilcke. Italian scientist Alessandro Volta improved and popularized the device in 1775, and is sometimes erroneously credited with its invention. The word electrophorus was coined by Volta from the Greek ήλεκτρον, elektron, and ϕέρω, phero, meaning 'electricity bearer'.
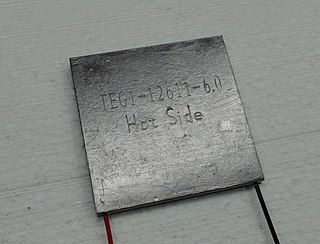
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when a voltage is applied to it, heat is transferred from one side to the other, creating a temperature difference. At the atomic scale, an applied temperature gradient causes charge carriers in the material to diffuse from the hot side to the cold side.

A Lichtenberg figure, or Lichtenberg dust figure, is a branching electric discharge that sometimes appears on the surface or in the interior of insulating materials. Lichtenberg figures are often associated with the progressive deterioration of high voltage components and equipment. The study of planar Lichtenberg figures along insulating surfaces and 3D electrical trees within insulating materials often provides engineers with valuable insights for improving the long-term reliability of high-voltage equipment. Lichtenberg figures are now known to occur on or within solids, liquids, and gases during electrical breakdown.
An electret is a dielectric material that has a quasi-permanent electric charge or dipole polarisation. An electret generates internal and external electric fields, and is the electrostatic equivalent of a permanent magnet. Although Oliver Heaviside coined this term in 1885, materials with electret properties were already known to science and had been studied since the early 1700s. One particular example is the electrophorus, a device consisting of a slab with electret properties and a separate metal plate. The electrophorus was originally invented by Johan Carl Wilcke in Sweden and again by Alessandro Volta in Italy.
Electrohydrodynamics (EHD), also known as electro-fluid-dynamics (EFD) or electrokinetics, is the study of the dynamics of electrically charged fluids. It is the study of the motions of ionized particles or molecules and their interactions with electric fields and the surrounding fluid. The term may be considered to be synonymous with the rather elaborate electrostrictive hydrodynamics. ESHD covers the following types of particle and fluid transport mechanisms: electrophoresis, electrokinesis, dielectrophoresis, electro-osmosis, and electrorotation. In general, the phenomena relate to the direct conversion of electrical energy into kinetic energy, and vice versa.
In quantum field theory, and specifically quantum electrodynamics, vacuum polarization describes a process in which a background electromagnetic field produces virtual electron–positron pairs that change the distribution of charges and currents that generated the original electromagnetic field. It is also sometimes referred to as the self-energy of the gauge boson (photon).
Polarization or polarisation may refer to:

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
A ferroelectret, also known as a piezoelectret, is a thin film of polymer foams, exhibiting piezoelectric and pyroelectric properties after electric charging. Ferroelectret foams usually consist of a cellular polymer structure filled with air. Polymer-air composites are elastically soft due to their high air content as well as due to the size and shape of the polymer walls. Their elastically soft composite structure is one essential key for the working principle of ferroelectrets, besides the permanent trapping of electric charges inside the polymer voids. The elastic properties allow large deformations of the electrically charged voids. However, the composite structure can also possibly limit the stability and consequently the range of applications.
Sedimentation potential occurs when dispersed particles move under the influence of either gravity or centrifugation in a medium. This motion disrupts the equilibrium symmetry of the particle's double layer. While the particle moves, the ions in the electric double layer lag behind due to the liquid flow. This causes a slight displacement between the surface charge and the electric charge of the diffuse layer. As a result, the moving particle creates a dipole moment. The sum of all of the dipoles generates an electric field which is called sedimentation potential. It can be measured with an open electrical circuit, which is also called sedimentation current.
Microvias are used as the interconnects between layers in high density interconnect (HDI) substrates and printed circuit boards (PCBs) to accommodate the high input/output (I/O) density of advanced packages. Driven by portability and wireless communications, the electronics industry strives to produce affordable, light, and reliable products with increased functionality. At the electronic component level, this translates to components with increased I/Os with smaller footprint areas, and on the printed circuit board and package substrate level, to the use of high density interconnects (HDIs).
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.
Polysilicon depletion effect is the phenomenon in which unwanted variation of threshold voltage of the MOSFET devices using polysilicon as gate material is observed, leading to unpredicted behavior of the electronic circuit. Because of this variation High-k Dielectric Metal Gates (HKMG) were introduced to solve the issue.
Dielectric absorption is the name given to the effect by which a capacitor, that has been charged for a long time, discharges only incompletely when briefly discharged. Although an ideal capacitor would remain at zero volts after being discharged, real capacitors will develop a small voltage from time-delayed dipole discharging, a phenomenon that is also called dielectric relaxation, "soakage", or "battery action". For some dielectrics, such as many polymer films, the resulting voltage may be less than 1–2% of the original voltage, but it can be as much as 15% for electrolytic capacitors. The voltage at the terminals generated by the dielectric absorption may possibly cause problems in the function of an electronic circuit or can be a safety risk to personnel. In order to prevent shocks, most very large capacitors are shipped with shorting wires that need to be removed before they are used and/or permanently connected bleeder resistors. When disconnected at one or both ends, DC high-voltage cables can also "recharge themselves" to dangerous voltages.
References
- Gross, B. (1954). "Theory of Thermodielectric effect". Physical Review. 94 (6): 1545–1551. Bibcode:1954PhRv...94.1545G. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.94.1545.
- Saldaña, Juan José (2006). Science in Latin America: a history. ISBN 978-0-292-71271-3.