
Negros Occidental, officially the Province of Negros Occidental (Hiligaynon: Kapuoran sang Nakatungdang Negros (Negros Occidental; Tagalog: Lalawigan ng Kanlurang Negros, is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the city of Bacolod, of which it is geographically situated and grouped under by the Philippine Statistics Authority, but remains politically independent from the provincial government. It occupies the northwestern half of the large island of Negros, and borders Negros Oriental, which comprises the southeastern half. Known as the "Sugarbowl of the Philippines", Negros Occidental produces more than half the nation's sugar output.

Asturias, officially the Municipality of Asturias, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Cebu, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 55,397 people.

Binalbagan, officially the Municipality of Binalbagan, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 71,407 people.

Cadiz, officially the City of Cadiz, is a 2nd class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. It was the capital of the short-lived province of Negros del Norte, before the creation of the province was declared unconstitutional on August 18, 1986.

Calatrava, officially the Municipality of Calatrava, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 82,540 people.

Escalante, officially the City of Escalante, is a 4th class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 96,159 people.

Isabela, officially the Municipality of Isabela, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 64,516 people.

Kabankalan, officially the City of Kabankalan, is a 1st class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 200,198 people making it the second most populous city in Negros Occidental next to Bacolod.

Moises Padilla, officially the Municipality of Moises Padilla, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 43,462 people.

Murcia, officially the Municipality of Murcia, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 88,868 people. It is 17 kilometres (11 mi) east of Bacolod.

Pulupandan, officially the Municipality of Pulupandan, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 30,117 people.

Sagay, officially the City of Sagay, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 148,894 people.

Don Salvador Benedicto, officially the Municipality of Don Salvador Benedicto or simply Salvador Benedicto and abbreviated as DSB, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 26,922 people.

San Carlos, officially the City of San Carlos, is a second-class component city in the province of Negros Occidental in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 132,650 people.

Sipalay, officially the City of Sipalay, is a 4th class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 72,448 people. It is the top tourist destination in the province of Negros Occidental.

Talisay, officially the City of Talisay, is a 4th class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 108,909 people.

The legislative districts of Negros Occidental are the representations of the province of Negros Occidental in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first, second, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth congressional districts.
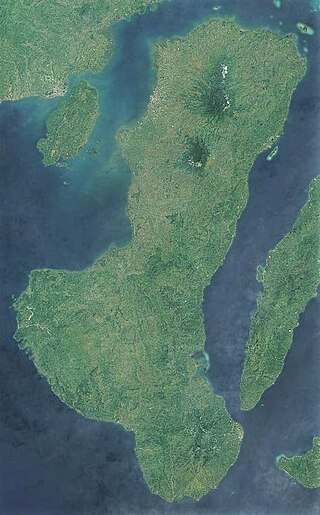
Negros is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of 13,309 km2 (5,139 sq mi). The coastal zone of the southern part of Negros is identified as a site of highest marine biodiversity importance in the Coral Triangle.

Central Visayas is an administrative region in the Philippines, numerically designated as Region VII. It consists of four provinces: Cebu, Bohol, Negros Oriental, and Siquijor. The region also has three highly urbanized cities: Cebu City, Lapu-Lapu, and Mandaue.
The Negros Occidental Provincial Board is the Sangguniang Panlalawigan of the Philippine province of Negros Occidental.
























