
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The glossopharyngeal nerve, also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue.

The somatic nervous system (SNS) is made up of nerves that link the brain and spinal cord to voluntary or skeletal muscles that are under conscious control as well as to skin sensory receptors. Specialized nerve fiber ends called sensory receptors are responsible for detecting information within and outside of the body.
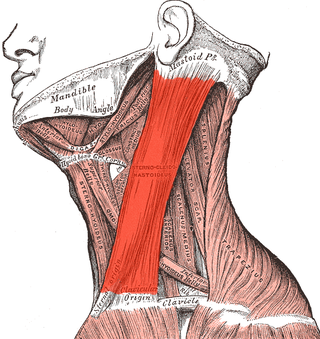
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve.

The levator scapulae is a slender skeletal muscle situated at the back and side of the neck. It originates from the transverse processes of the four uppermost cervical vertebrae; it inserts onto the upper portion of the medial border of the scapula. It is innervated by the cervical nerves C3-C4, and frequently also by the dorsal scapular nerve. As the Latin name suggests, its main function is to lift the scapula.

The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory innervation to parts of the head, neck, and chest.
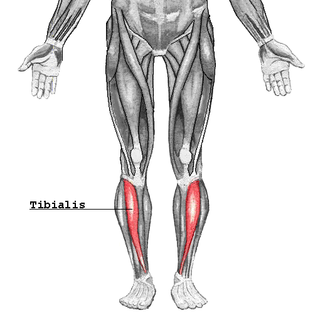
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin.
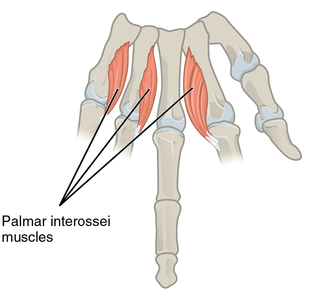
In human anatomy, the palmar or volar interossei are four muscles, one on the thumb that is occasionally missing, and three small, unipennate, central muscles in the hand that lie between the metacarpal bones and are attached to the index, ring, and little fingers. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand.

The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding the tongue.

The hyoglossus is a thin and quadrilateral extrinsic muscle of the tongue. It originates from the hyoid bone; it inserts onto the side of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. It acts to depress and retract the tongue.

The styloglossus muscle is a bilaterally paired muscle of the tongue. It originates at the styloid process of the temporal bone. It inserts onto the side of the tongue. It acts to elevate and retract the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve.

The palatoglossal muscle is a muscle of the soft palate and an extrinsic muscle of the tongue. Its surface is covered by oral mucosa and forms the visible palatoglossal arch.

The superior longitudinal muscle of tongue or superior lingualis is a thin layer of oblique and longitudinal fibers immediately underlying the mucous membrane on the dorsum of the tongue.
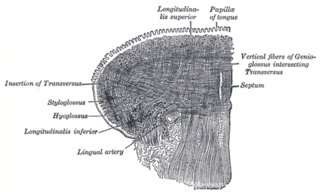
The inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue. It is situated on the under surface of the tongue between the genioglossus and hyoglossus. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. Its contraction shortens and thickens the tongue.

The vertical muscle of the tongue is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue. Its fibers extend from the upper to the under surface of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve. Its contraction flattens, widens and elongates the tongue.

The middle cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of the brain. It connects the pons to the cerebellum, with fibres originating from the pontine nucleus and travelling to the opposite hemisphere of the cerebellar cortex. It is supplied by the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) and branches from the basilar artery. It conveys information from the cerebrum and the pons to the cerebellum.
Bulbar palsy refers to a range of different signs and symptoms linked to impairment of function of the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, the accessory nerve, and the hypoglossal nerve. It is caused by a lower motor neuron lesion in the medulla oblongata, or from lesions to these nerves outside the brainstem, and also botulism. This may be caused by any of a number of genetic, vascular, degenerative, inflammatory, and other underlying conditions. It can be differentiated from pseudobulbar palsy. When there is airway obstruction, intubation is used.

The cranial nerve exam is a type of neurological examination. It is used to identify problems with the cranial nerves by physical examination. It has nine components. Each test is designed to assess the status of one or more of the twelve cranial nerves (I-XII). These components correspond to testing the sense of smell (I), visual fields and acuity (II), eye movements and pupils, sensory function of face (V), strength of facial (VII) and shoulder girdle muscles (XI), hearing and balance, taste, pharyngeal movement and reflex, tongue movements (XII).

















