
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.

Ergocalciferol, also known as vitamin D2 and nonspecifically calciferol, is a type of vitamin D found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to prevent and treat vitamin D deficiency. This includes vitamin D deficiency due to poor absorption by the intestines or liver disease. It may also be used for low blood calcium due to hypoparathyroidism. It is used by mouth or injection into a muscle.
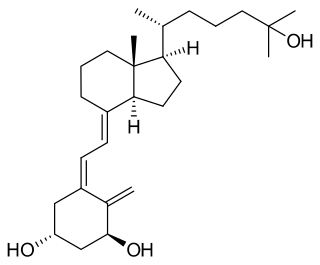
Calcitriol is the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It is a hormone which binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the expression of many genes. Calcitriol increases blood calcium (Ca2+) mainly by increasing the uptake of calcium from the intestines.

Vitamin D toxicity, or hypervitaminosis D is the toxic state of an excess of vitamin D. The normal range for blood concentration in adults is 20 to 50 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).

Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a protein and member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family which participates in the regulation of phosphate in plasma and vitamin D metabolism. In humans it is encoded by the FGF23 gene. FGF23 decreases reabsorption of phosphate in the kidney. Mutations in FGF23 can lead to its increased activity, resulting in autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets.

The vitamin D receptor (VDR also known as the calcitriol receptor) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D, 1,25-(OH)2vitamin D3) binds to VDR, which then forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor. The VDR heterodimer then enters the nucleus and binds to Vitamin D responsive elements (VDRE) in genomic DNA. VDR binding results in expression or transrepression of many specific gene products. VDR is also involved in microRNA-directed post transcriptional mechanisms. In humans, the vitamin D receptor is encoded by the VDR gene located on chromosome 12q13.11.

Calcifediol, also known as calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (abbreviated 25(OH)D3), is a form of vitamin D produced in the liver by hydroxylation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) by the enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylase. Calcifediol can be further hydroxylated by the enzyme 25(OH)D-1α-hydroxylase, primarily in the kidney, to form calcitriol (1,25-(OH)2D3), which is the active hormonal form of vitamin D.

25-Hydroxyvitamin D 1-alpha-hydroxylase also known as calcidiol 1-monooxygenase or cytochrome p450 27B1 (CYP27B1) or simply 1-alpha-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP27B1 gene.

Calcitroic acid (1α-hydroxy-23-carboxy-24,25,26,27-tetranorvitamin D3) is a major metabolite of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol). Often synthesized in the liver and kidneys, calcitroic acid is generated in the body after vitamin D is first converted into calcitriol, an intermediate in the fortification of bone through the formation and regulation of calcium in the body. These pathways managed by calcitriol are thought to be inactivated through its hydroxylation by the enzyme CYP24A1, also called calcitriol 24-hydroxylase. Specifically, It is thought to be the major route to inactivate vitamin D metabolites.

Tacalcitol (1,24-dihydroxyvitamin D3) is a synthetic vitamin D3 analog. Tacalcitol is marketed under several names, including Curatoderm and Bonalfa.
In enzymology, a cholestanetriol 26-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1 (abbreviated CYP24A1) is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes encoded by the CYP24A1 gene. It is a mitochondrial monooxygenase which catalyzes reactions including 24-hydroxylation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). It has also been identified as vitamin D3 24-hydroxylase.(EC 1.14.15.16)

Adrenodoxin reductase, was first isolated from bovine adrenal cortex where it functions as the first enzyme in the mitochondrial P450 systems that catalyze essential steps in steroid hormone biosynthesis. Examination of complete genome sequences revealed that adrenodoxin reductase gene is present in most metazoans and prokaryotes.

CYP2R1 is cytochrome P450 2R1, an enzyme which is the principal vitamin D 25-hydroxylase. In humans it is encoded by the CYP2R1 gene located on chromosome 11p15.2. It is expressed in the endoplasmic reticulum in liver, where it performs the first step in the activation of vitamin D by catalyzing the formation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D.
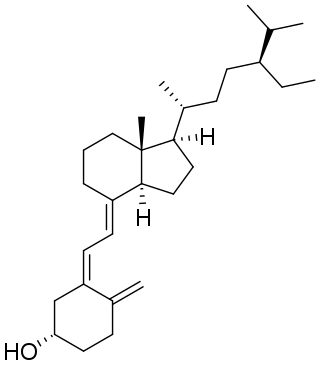
Vitamin D5 (sitocalciferol) is a form of vitamin D.

24,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol, also known as 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and (24R)-hydroxycalcidiol (abbreviated as 24(R),25-(OH)2D3), is a compound which is closely related to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, the active form of vitamin D3. Like vitamin D3 itself and calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D3), it is inactive as a hormone both in vitro and in vivo. It was first identified in 1972 in the laboratory of Hector DeLuca and Michael F. Holick.

Alfacalcidol is an analogue of vitamin D used for supplementation in humans and as a poultry feed additive.
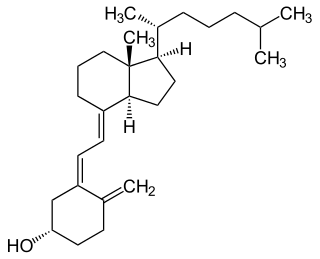
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).

Michael F. Holick is an American adult endocrinologist, specializing in vitamin D, such as the identification of both calcidiol, the major circulating form of vitamin D, and calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D. His work has been the basis for diagnostic tests and therapies for vitamin D-related diseases. He is a professor of medicine at the Boston University Medical Center and editor-in-chief of the journal Clinical Laboratory.
Vitamin D3 dihydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme purified from the actinobacterium Streptomyces griseolus, with EC number EC 1.14.15.22 and CYP Symbol CYP105A1, catalyses oxidation of cholecalciferol(vitamin D3) to calcitriol.

















