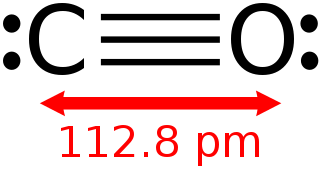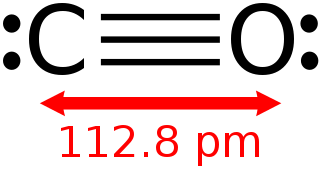
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.

Bilirubin (BR) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the destruction of aged or abnormal red blood cells. In the first step of bilirubin synthesis, the heme molecule is stripped from the hemoglobin molecule. Heme then passes through various processes of porphyrin catabolism, which varies according to the region of the body in which the breakdown occurs. For example, the molecules excreted in the urine differ from those in the feces. The production of biliverdin from heme is the first major step in the catabolic pathway, after which the enzyme biliverdin reductase performs the second step, producing bilirubin from biliverdin.

Heme, or haem, is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecular component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver.

Stercobilin is a tetrapyrrolic bile pigment and is one end-product of heme catabolism. It is the chemical responsible for the brown color of human feces and was originally isolated from feces in 1932. Stercobilin can be used as a marker for biochemical identification of fecal pollution levels in rivers.
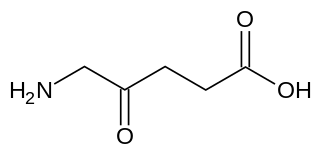
δ-Aminolevulinic acid, an endogenous non-proteinogenic amino acid, is the first compound in the porphyrin synthesis pathway, the pathway that leads to heme in mammals, as well as chlorophyll in plants.
Carboxyhemoglobin is a stable complex of carbon monoxide and hemoglobin (Hb) that forms in red blood cells upon contact with carbon monoxide. Carboxyhemoglobin is often mistaken for the compound formed by the combination of carbon dioxide (carboxyl) and hemoglobin, which is actually carbaminohemoglobin. Carboxyhemoglobin terminology emerged when carbon monoxide was known by its historic name, "carbonic oxide", and evolved through Germanic and British English etymological influences; the preferred IUPAC nomenclature is carbonylhemoglobin.

Nitric oxide synthases (NOSs) are a family of enzymes catalyzing the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule. It helps modulate vascular tone, insulin secretion, airway tone, and peristalsis, and is involved in angiogenesis and neural development. It may function as a retrograde neurotransmitter. Nitric oxide is mediated in mammals by the calcium-calmodulin controlled isoenzymes eNOS and nNOS. The inducible isoform, iNOS, involved in immune response, binds calmodulin at physiologically relevant concentrations, and produces NO as an immune defense mechanism, as NO is a free radical with an unpaired electron. It is the proximate cause of septic shock and may function in autoimmune disease.

HMOX1 is a human gene that encodes for the enzyme heme oxygenase 1. Heme oxygenase mediates the first step of heme catabolism, it cleaves heme to form biliverdin.
Gasotransmitters is a class of neurotransmitters. The molecules are distinguished from other bioactive endogenous gaseous signaling molecules based on a need to meet distinct characterization criteria. Currently, only nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide are accepted as gasotransmitters. According to in vitro models, gasotransmitters, like other gaseous signaling molecules, may bind to gasoreceptors and trigger signaling in the cells.

Biliverdin reductase (BVR) is an enzyme found in all tissues under normal conditions, but especially in reticulo-macrophages of the liver and spleen. BVR facilitates the conversion of biliverdin to bilirubin via the reduction of a double bond between the second and third pyrrole ring into a single bond.

Protoporphyrin IX is an organic compound, classified as a porphyrin, that plays an important role in living organisms as a precursor to other critical compounds like heme (hemoglobin) and chlorophyll. It is a deeply colored solid that is not soluble in water. The name is often abbreviated as PPIX.
The chemical substance 1,2-dioxetane is a heterocyclic, organic compound with formula C2O2H4, containing a ring of two adjacent oxygen atoms and two adjacent carbon atoms. It is therefore an organic peroxide, and can be viewed as a dimer of formaldehyde.

Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), also known as nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2, is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the NFE2L2 gene. NRF2 is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) protein that may regulate the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage triggered by injury and inflammation, according to preliminary research. In vitro, NRF2 binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoter regions of genes encoding cytoprotective proteins. NRF2 induces the expression of heme oxygenase 1 in vitro leading to an increase in phase II enzymes. NRF2 also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome.

Heme oxygenase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HMOX2 gene.
In chemistry, decarbonylation is a type of organic reaction that involves the loss of carbon monoxide (CO). It is often an undesirable reaction, since it represents a degradation. In the chemistry of metal carbonyls, decarbonylation describes a substitution process, whereby a CO ligand is replaced by another ligand.
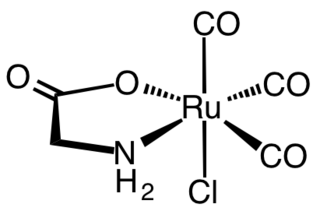
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecules (CORMs) are chemical compounds designed to release controlled amounts of carbon monoxide (CO). CORMs are being developed as potential therapeutic agents to locally deliver CO to cells and tissues, thus overcoming limitations of CO gas inhalation protocols.
Gaseous signaling molecules are gaseous molecules that are either synthesized internally (endogenously) in the organism, tissue or cell or are received by the organism, tissue or cell from outside and that are used to transmit chemical signals which induce certain physiological or biochemical changes in the organism, tissue or cell. The term is applied to, for example, oxygen, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxide, hydrogen cyanide, ammonia, methane, hydrogen, ethylene, etc.

Biliverdin reductase B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BLVRB gene.
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases are a major class of non-heme iron proteins that catalyse a wide range of reactions. These reactions include hydroxylation reactions, demethylations, ring expansions, ring closures, and desaturations. Functionally, the αKG-dependent hydroxylases are comparable to cytochrome P450 enzymes. Both use O2 and reducing equivalents as cosubstrates and both generate water.
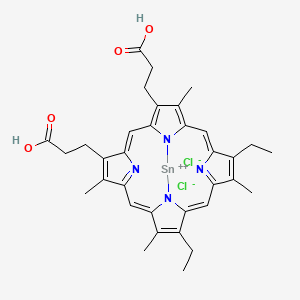
Tin mesoporphyrin (SnMP), also known as stannsoporfin, is a synthetic metalloporphyrin, which consists of a group of competitive inhibitors of heme oxygenase, a rate-limiting enzyme in the heme catabolic pathway. Tin mesoporphyrin is one of the more potent metalloporphyrin compound out of all the others.