Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a colorless, dense, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the formation of xenon hexafluoroplatinate, the first noble gas compound to be synthesized.
Noble gas compounds are chemical compounds that include an element from the noble gases, group 18 of the periodic table. Although the noble gases are generally unreactive elements, many such compounds have been observed, particularly involving the element xenon. From the standpoint of chemistry, the noble gases may be divided into two groups: the relatively reactive krypton, xenon (12.1 eV), and radon (10.7 eV) on one side, and the very unreactive argon (15.8 eV), neon (21.6 eV), and helium (24.6 eV) on the other. Consistent with this classification, Kr, Xe, and Rn form compounds that can be isolated in bulk at or near standard temperature and pressure, whereas He, Ne, Ar have been observed to form true chemical bonds using spectroscopic techniques, but only when frozen into a noble gas matrix at temperatures of 40 K or lower, in supersonic jets of noble gas, or under extremely high pressures with metals.
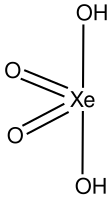
In chemistry, perxenates are salts of the yellow xenon-containing anion XeO4−
6. This anion has octahedral molecular geometry, as determined by Raman spectroscopy, having O–Xe–O bond angles varying between 87° and 93°. The Xe–O bond length was determined by X-ray crystallography to be 1.875 Å.
Xenon tetroxide is a chemical compound of xenon and oxygen with molecular formula XeO4, remarkable for being a relatively stable compound of a noble gas. It is a yellow crystalline solid that is stable below −35.9 °C; above that temperature it is very prone to exploding and decomposing into elemental xenon and oxygen (O2).

Zinc chloride is the name of chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. Zinc chlorides, of which nine crystalline forms are known, are colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. This white salt is hygroscopic and even deliquescent. Samples should therefore be protected from sources of moisture, including the water vapor present in ambient air. Zinc chloride finds wide application in textile processing, metallurgical fluxes, and chemical synthesis. No mineral with this chemical composition is known aside from the very rare mineral simonkolleite, Zn5(OH)8Cl2·H2O.
In chemistry, the phosphonium cation describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.
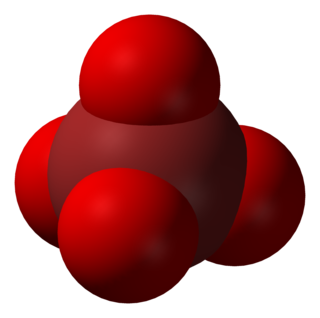
In chemistry, the perbromate ion is the anion having the chemical formula BrO−
4. It is an oxyanion of bromine, the conjugate base of perbromic acid, in which bromine has the oxidation state +7. Unlike its chlorine and iodine analogs, it is difficult to synthesize. It has tetrahedral molecular geometry.

Telluric acid is a chemical compound with the formula Te(OH)6. It is a white solid made up of octahedral Te(OH)6 molecules which persist in aqueous solution. There are two forms, rhombohedral and monoclinic, and both contain octahedral Te(OH)6 molecules. Telluric acid is a weak acid which is dibasic, forming tellurate salts with strong bases and hydrogen tellurate salts with weaker bases or upon hydrolysis of tellurates in water. It is used as tellurium-source in the synthesis of oxidation catalysts.
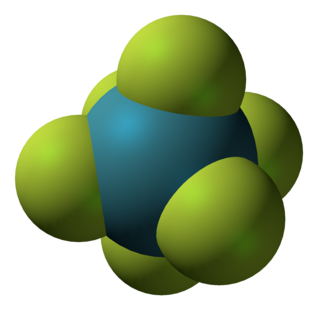
Xenon hexafluoride is a noble gas compound with the formula XeF6. It is one of the three binary fluorides of xenon, the other two being XeF2 and XeF4. All known are exergonic and stable at normal temperatures. XeF6 is the strongest fluorinating agent of the series. It is a colorless solid that readily sublimes into intensely yellow vapors.
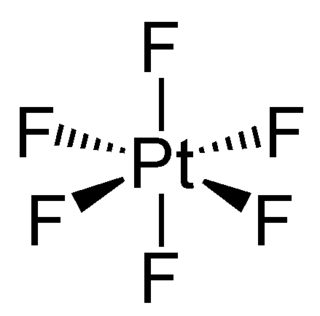
Platinum hexafluoride is the chemical compound with the formula PtF6, and is one of seventeen known binary hexafluorides. It is a dark-red volatile solid that forms a red gas. The compound is a unique example of platinum in the +6 oxidation state. With only four d-electrons, it is paramagnetic with a triplet ground state. PtF6 is a strong fluorinating agent and one of the strongest oxidants, capable of oxidising xenon and O2. PtF6 is octahedral in both the solid state and in the gaseous state. The Pt-F bond lengths are 185 picometers.

Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions. This substance is a superacid that can be in excess of a quadrillion times stronger than 100% pure sulfuric acid, depending on the proportion of its ingredients. It has been shown to protonate even hydrocarbons to afford pentacoordinate carbocations. Extreme care must be taken when handling fluoroantimonic acid. It is exceptionally corrosive, but can be stored in containers lined with PTFE (Teflon).

Teflic acid is the chemical compound with the formula HOTeF5. This strong acid is related to orthotelluric acid, Te(OH)6. Teflic acid has a slightly distorted octahedral geometry.

Xenon trioxide is an unstable compound of xenon in its +6 oxidation state. It is a very powerful oxidizing agent, and liberates oxygen from water slowly, accelerated by exposure to sunlight. It is dangerously explosive upon contact with organic materials. When it detonates, it releases xenon and oxygen gas.

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.

Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH or TMAOH) is a quaternary ammonium salt with molecular formula N(CH3)4+ OH−. It is commonly encountered in form of concentrated solutions in water or methanol. TMAH in solid state and its aqueous solutions are all colorless, but may be yellowish if impure. Although TMAH has virtually no odor when pure, samples often have a strong fishy smell due to presence of trimethylamine which is a common impurity. TMAH has several diverse industrial and research applications.

Potassium nonahydridorhenate(VII) is an inorganic compound having the formula K2ReH9. This colourless salt is soluble in water but only poorly soluble in most alcohols. The ReH2−
9 anion is a rare example of a coordination complex bearing only hydride ligands.

Barium ferrate is the chemical compound of formula BaFeO4. This is a rare compound containing iron in the +6 oxidation state. The ferrate(VI) ion has two unpaired electrons, making it paramagnetic. It is isostructural with BaSO4, and contains the tetrahedral [FeO4]2− anion.

Cobalt(II) hydroxide or cobaltous hydroxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Co(OH)
2, consisting of divalent cobalt cations Co2+
and hydroxide anions HO−
. The pure compound, often called the "beta form" is a pink solid insoluble in water.

The tetrafluoroammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with chemical formula NF+
4. It is equivalent to the ammonium ion where the hydrogen atoms surrounding the central nitrogen atom have been replaced by fluorine. Tetrafluoroammonium ion is isoelectronic with tetrafluoromethane CF
4, trifluoramine oxide ONF
3 and the tetrafluoroborate BF−
4 anion.

Monosodium xenate is the sodium salt of xenic acid with formula NaHXeO4·1.5H2O. It is a powerful oxidizer. It is a highly reactive compound of xenon. The dialkali xenates do not appear to exist, as xenate disproportions in more alkaline conditions.