The Poales are a large order of flowering plants in the monocotyledons, and includes families of plants such as the grasses, bromeliads, rushes and sedges. Sixteen plant families are currently recognized by botanists to be part of Poales.

Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.
A glucoside is a glycoside that is chemically derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

Paepalanthus bromelioides is a species in the flowering plant family Eriocaulaceae. This family is placed in the Poales, close to the Bromeliaceae, whose morphology this genus shares. Paepalanthus bromelioides is native to Cerrado. There is some speculation that the occasional insects trapped in the urn of this plant are evidence of its being a carnivorous plant or protocarnivorous, possible deriving nutrients from termite mounds that termites frequently make in the plants' roots.

The Eriocaulaceae are a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants in the order Poales, commonly known as the pipewort family. The family is large, with about 1207 known species described in seven genera. They are widely distributed, with the centers of diversity for the group occurring in tropical regions, particularly the Americas. Very few species extend to temperate regions, with only 16 species in the United States, mostly in the southern states from California to Florida, only two species in Canada, and only one species in Europe. They tend to be associated with wet soils, many growing in shallow water. This is also reported from the southern part of India and the regions of Western Ghats hot spots.

Monodactylus argenteus is a species of fish in the family Monodactylidae, the moonyfishes. Its common names include silver moonyfish, or silver moony, butter bream, and diamondfish. It is native to the western Pacific and Indian Oceans, including the Persian Gulf, Red Sea, and associated estuaries, such as the Mekong Delta.
Paepalanthus celsus is a species of plant in the Eriocaulaceae family. It is endemic to Ecuador. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests and subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Isorhamnetin is an O-methylated flavon-ol from the class of flavonoids. A common food source of this 3'-methoxylated derivative of quercetin and its glucoside conjugates are pungent yellow or red onions, in which it is a minor pigment, quercetin-3,4'-diglucoside and quercetin-4'-glucoside and the aglycone quercetin being the major pigments. Pears, olive oil, wine and tomato sauce are rich in isorhamnetin. Almond skin is a rich source of isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, in some cultivars they comprise 75% of the polyphenol content, the total of which can exceed 10 mg/100 gram almond. Others sources include the spice, herbal medicinal and psychoactive Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida), which is described as accumulating isorhamnetin and its 7-O-glucoside derivate. Nopal is also a good source of isorhamnetin, which can be extracted by supercritical fluid extraction assisted by enzymes.

Biochanin A is an O-methylated isoflavone. It is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as flavonoids. Biochanin A can be found in red clover in soy, in alfalfa sprouts, in peanuts, in chickpea and in other legumes.

Genistin is an isoflavone found in a number of dietary plants like soy and kudzu. It was first isolated in 1931 from the 90% methanol extract of a soybean meal, when it was found that hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid produced 1 mole each of genistein and glucose. Chemically it is the 7-O-beta-D-glucoside form of genistein and is the predominant form of the isoflavone naturally occurring in plants. In fact, studies in the 1970s revealed that 99% of the isoflavonoid compounds in soy are present as their glucosides. The glucosides are converted by digestive enzymes in the digestive system to exert their biological effects. Genistin is also converted to a more familiar genistein, thus, the biological activities including antiatherosclerotic, estrogenic and anticancer effects are analogous.

The flavanonols are a class of flavonoids that use the 3-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone.

Aromadendrin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in the wood of Pinus sibirica.

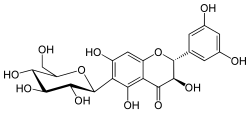
Phellamurin, a flavonoid, is the 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, 8-C-prenyl derivative of the flavan-on-ol Aromadendrin, and may be seen as the 7-O-glucoside of noricaritin. Being a flavanonol, it has two stereocenters on the C-ring, so four stereoisomers of phellamurin are possible.

Oenin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of malvidin. It is one of the red pigments found in the skin of purple grapes and in wine.
The pyranoanthocyanins are a type of pyranoflavonoids. They are chemical compounds formed in red wines by yeast during fermentation processes or during controlled oxygenation processes during the aging of wine. The different classes of pyranoanthocyanins are carboxypyranoanthocyanins, methylpyranoanthocyanins, pyranoanthocyanin-flavanols, pyranoanthocyanin-phenols, portisins, oxovitisins and pyranoanthocyanin dimers; their general structure includes an additional ring that may have different substituents linked directly at C-10.

Norartocarpetin is a flavone. It is found in Artocarpus dadah.

Paepalanthus is a genus of plants in the family Eriocaulaceae. It has about 300-400 species, native mostly to tropical Africa and Latin America, with a few species in Japan and Madagascar.

Pipturus argenteus, known as false stinger, native mulberry, white mulberry, white nettle, amahatyan (Chamorro), and ghasooso (Carolinian), is a small tree native to tropical Asia, northern and eastern Australia and the Pacific.

The Três Pontas Mountains is a geological formation located in the Brazilian municipality of Três Pontas, in the southern region of Minas Gerais. Its altitude, which reaches a maximum of 1,234 metres (4,049 ft) above sea level, stands out in relation to the surrounding terrain, with altitudes varying around 900 metres (3,000 ft). Although it seems like an isolated mountain system, the mountain range is considered an extension of the Bocaina Mountains, located about 38 kilometres (24 mi) away in the municipality of Lavras, which, in turn, is considered a counterfort of the Mantiqueira Mountains.