
Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood. Adolescence is usually associated with the teenage years, but its physical, psychological or cultural expressions may begin earlier or end later. Puberty typically begins during preadolescence, particularly in females. Physical growth and cognitive development can extend past the teens. Age provides only a rough marker of adolescence, and scholars have not agreed upon a precise definition. Some definitions start as early as 10 and end as late 30. The World Health Organization definition officially designates an adolescent as someone between the ages of 10 and 19.

Conduct disorder (CD) is a mental disorder diagnosed in childhood or adolescence that presents itself through a repetitive and persistent pattern of behavior that includes theft, lies, physical violence that may lead to destruction, and reckless breaking of rules, in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate norms are violated. These behaviors are often referred to as "antisocial behaviors", and is often seen as the precursor to antisocial personality disorder; however, the latter, by definition, cannot be diagnosed until the individual is 18 years old. Conduct disorder may result from parental rejection and neglect and can be treated with family therapy, as well as behavioral modifications and pharmacotherapy. Conduct disorder is estimated to affect 51.1 million people globally as of 2013.

An adult is a human or other animal that has reached full growth. The biological definition of the word means an animal reaching sexual maturity and thus capable of reproduction. In the human context, the term adult has meanings associated with social and legal concepts. In contrast to a non-adult or "minor", a legal adult is a person who has attained the age of majority and is therefore regarded as independent, self-sufficient, and responsible. They may also be regarded as a "major". The typical age of attaining legal adulthood is 18, although definition may vary by legal rights, country, and psychological development.

Juvenile delinquency, also known as juvenile offending, is the act of participating in unlawful behavior as a minor or individual younger than the statutory age of majority. These acts would otherwise be considered crimes if the individuals committing them were older. The term delinquent usually refers to juvenile delinquency, and is also generalised to refer to a young person who behaves an unacceptable way.
Abuse is the improper usage or treatment of a thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, crimes, or other types of aggression. To these descriptions, one can also add the Kantian notion of the wrongness of using another human being as means to an end rather than as ends in themselves. Some sources describe abuse as "socially constructed", which means there may be more or less recognition of the suffering of a victim at different times and societies.
Antisocial behaviours, sometimes called dissocial behaviours, are actions which are considered to violate the rights of or otherwise harm others by committing crime or nuisance, such as stealing and physical attack or noncriminal behaviours such as lying and manipulation. It is considered to be disruptive to others in society. This can be carried out in various ways, which includes, but is not limited to, intentional aggression, as well as covert and overt hostility. Anti-social behaviour also develops through social interaction within the family and community. It continuously affects a child's temperament, cognitive ability and their involvement with negative peers, dramatically affecting children's cooperative problem-solving skills. Many people also label behaviour which is deemed contrary to prevailing norms for social conduct as anti-social behaviour. However, researchers have stated that it is a difficult term to define, particularly in the United Kingdom where many acts fall into its category. The term is especially used in Irish English and British English.
Relational aggression, alternative aggression, or relational bullying is a type of aggression in which harm is caused by damaging someone's relationships or social status.

Childhood obesity is a condition where excess body fat negatively affects a child's health or well-being. As methods to determine body fat directly are difficult, the diagnosis of obesity is often based on BMI. Due to the rising prevalence of obesity in children and its many adverse health effects it is being recognized as a serious public health concern. The term overweight rather than obese is often used when discussing childhood obesity, as it is less stigmatizing, although the term overweight can also refer to a different BMI category. The prevalence of childhood obesity is known to differ by sex and gender.
Transitional age youth can reference both a developmental period and be a descriptor regarding eligibility for certain services. While there are variations in definitions, the age ranges do consistently overlap and include late adolescence to early adulthood. This range is considered a critical period in human development characterized by several changes socially, environmentally, and cognitively. During this time, individuals can experience changes in their social roles and function, family and peer supports, exposure to substance use, educational and vocational programs, as well as changes in healthcare providers from pediatric to adult settings.
Childhood trauma is often described as serious adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Children may go through a range of experiences that classify as psychological trauma; these might include neglect, abandonment, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, and physical abuse, witnessing abuse of a sibling or parent, or having a mentally ill parent. These events have profound psychological, physiological, and sociological impacts and can have negative, lasting effects on health and well-being such as unsocial behaviors, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and sleep disturbances. Similarly, children whose mothers have experienced traumatic or stressful events during pregnancy have an increased risk of mental health disorders and other neurodevelopmental disorders.
Adolescent health, or youth health, is the range of approaches to preventing, detecting or treating young people's health and well-being.
Youth suicide is when a young person, generally categorized as someone below the legal age of majority, deliberately ends their own life. Rates of youth suicide and attempted youth suicide in Western societies and other countries are high. Youth suicide attempts are more common among girls, but adolescent males are the ones who usually carry out suicide. Suicide rates in youths have nearly tripled between the 1960s and 1980s. For example, in Australia suicide is second only to motor vehicle accidents as its leading cause of death for people aged 15 to 25.
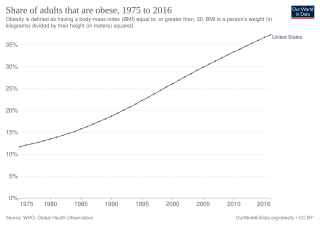
Obesity is common in the United States and is a major health issue associated with numerous diseases, specifically an increased risk of certain types of cancer, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke, and cardiovascular disease, as well as significant increases in early mortality and economic costs.

Major depressive disorder, often simply referred to as depression, is a mental disorder characterized by prolonged unhappiness or irritability. It is accompanied by a constellation of somatic and cognitive signs and symptoms such as fatigue, apathy, sleep problems, loss of appetite, loss of engagement, low self-regard/worthlessness, difficulty concentrating or indecisiveness, or recurrent thoughts of death or suicide.
Disability abuse is when a person with a disability is abused physically, financially, sexually and/or psychologically due to the person having a disability. This type of abuse has also been considered a hate crime. The abuse is not limited to those who are visibly disabled or physically deformed, but also includes those with learning, intellectual and developmental disabilities or mental illnesses.
Cyberbullying or cyberharassment is a form of bullying or harassment using electronic means. Cyberbullying and cyberharassment are also known as online bullying. It has become increasingly common, especially among teenagers and adolescents, due to the communication technology advancements and young people's increased use of such technologies. Cyberbullying is when someone, typically a teenager, bullies or harasses others on the internet and other digital spaces, particularly on social media sites.
Youth is an age group in the demographics of the United States. In 2010, it was estimated that 20.2% of the population of the United States were 0–14 years old.
Alcohol is a liquid form substance which contains ethyl alcohol that can cause harm and even damage to a person's DNA. "Alcohol consumption is recognized worldwide as a leading risk factor for disease, disability, and death" and is rated as the most used substance by adolescences. Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and psychological changes, usually a time in a person life in which they go through puberty. Combining these transitional stages and the intake of alcohol can leave a number of consequences for an adolescent.
Risky sexual behavior is the description of the activity that will increase the probability that a person engaging in sexual activity with another person infected with a sexually transmitted infection will be infected or become unintended pregnant, or make a partner pregnant. It can mean two similar things: the behavior itself, and the description of the partner's behavior.
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) include childhood emotional, physical, or sexual abuse and household dysfunction during childhood. The categories are verbal abuse, physical abuse, contact sexual abuse, a battered mother, household substance abuse, household mental illness, incarcerated household members, and parental separation or divorce. The experiences chosen were based upon prior research that has shown to them to have significant negative health or social implications, and for which substantial efforts are being made in the public and private sector to reduce their frequency of occurrence. Scientific evidence is mounting that such adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) have a profound long-term effect on health. Research shows that exposure to abuse and to serious forms of family dysfunction in the childhood family environment are likely to activate the stress response, thus potentially disrupting the developing nervous, immune, and metabolic systems of children. ACEs are associated with lifelong physical and mental health problems that emerge in adolescence and persist into adulthood, including cardiovascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, substance abuse, and depression.















