
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I. The Second Republic ceased to exist in 1939, after Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany, the Soviet Union, and the Slovak Republic, marking the beginning of the European theatre of the Second World War. The Polish government-in-exile was established in Paris and later London after the fall of France in 1940.

Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with population of over 39 million people, and the seventh-largest EU country, covering a combined area of 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi). It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordering seven countries. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and temperate transitional climate. The capital and largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk.

Polish is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group within the Indo-European language family written in the Latin script. It is primarily spoken in Poland and serves as the official language of the country, as well as the language of the Polish diaspora around the world. In 2023, there were over 40.6 million Polish native speakers. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals.

Pomerania is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The central and eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian, Pomeranian and Kuyavian-Pomeranian voivodeships of Poland, while the western part belongs to the German states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg.

Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at 1.86 million residents within a greater metropolitan area of 3.27 million residents, which makes Warsaw the 7th most-populous city in the European Union. The city area measures 517 km2 (200 sq mi) and comprises 18 districts, while the metropolitan area covers 6,100 km2 (2,355 sq mi). Warsaw is classified as an alpha global city, a major cultural, political and economic hub, and the country's seat of government. It is also capital of the Masovian Voivodeship.

Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the Sudeten Mountains to the south. As of 2023, the official population of Wrocław is 674,132 making it the third largest city in Poland. The population of the Wrocław metropolitan area is around 1.25 million.

The Polish United Workers' Party, commonly abbreviated to PZPR, was the communist party which ruled the Polish People's Republic as a one-party state from 1948 to 1989. The PZPR had led two other legally permitted subordinate minor parties together as the Front of National Unity and later Patriotic Movement for National Rebirth. Ideologically, it was based on the theories of Marxism-Leninism, with a strong emphasis on left-wing nationalism. The Polish United Workers' Party had total control over public institutions in the country as well as the Polish People's Army, the UB and SB security agencies, the Citizens' Militia (MO) police force and the media.

A voivodeship is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province".

The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations.

Józef Klemens Piłsudski[a] was a Polish statesman who served as the Chief of State (1918–1922) and first Marshal of Poland. In the aftermath of World War I, he became an increasingly dominant figure in Polish politics and exerted significant influence on shaping the country's foreign policy. Piłsudski is viewed as a father of the Second Polish Republic, which was re-established in 1918, 123 years after the final partition of Poland in 1795, and was considered de facto leader (1926–1935) of the Second Republic as the Minister of Military Affairs.

Polish people, or Poles, are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Central Europe. The preamble to the Constitution of the Republic of Poland defines the Polish nation as comprising all the citizens of Poland, regardless of heritage or ethnicity. The majority of Poles adhere to Roman Catholicism.

Poland–Lithuania, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and also referred to as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth or the First Polish Republic, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch in real union, who was both King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. It was one of the largest and most populous countries of 16th- to 17th-century Europe. At its largest territorial extent, in the early 17th century, the Commonwealth covered almost 1,000,000 km2 (400,000 sq mi) and as of 1618 sustained a multi-ethnic population of almost 12 million. Polish and Latin were the two co-official languages, and Catholicism served as the state religion.

The Polish–Soviet War was fought primarily between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic before it became a union republic in the aftermath of World War I and the Russian Revolution, on territories which were previously held by the Russian Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy following the Partitions of Poland.

The Polish People's Republic (1952–1989), formerly the Republic of Poland (1947–1952), was a country in Central Europe that existed as the predecessor of the modern-day democratic Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million near the end of its existence, it was the second most-populous communist and Eastern Bloc country in Europe, and one of the main signatories of the Warsaw Pact alliance. The largest city and official capital since 1947 was Warsaw, followed by the industrial city of Łódź and cultural city of Kraków. The country was bordered by the Baltic Sea to the north, the Soviet Union to the east, Czechoslovakia to the south, and East Germany to the west.
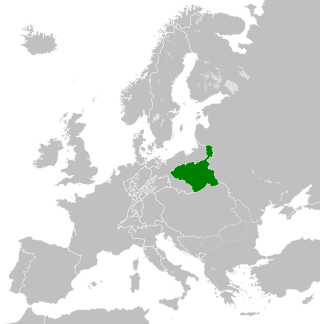
The Duchy of Warsaw, also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars. It initially comprised the ethnically Polish lands ceded to France by Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit, and was augmented in 1809 with territory ceded by Austria in the Treaty of Schönbrunn. It was the first attempt to re-establish Poland as a sovereign state after the 18th-century partitions and covered the central and southeastern parts of present-day Poland.

The Kingdom of Poland was a monarchy in Central Europe during the medieval period from 1025 until 1385.

Galicia is a historical and geographic region spanning what is now southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, long part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It covers much of the other historic regions of Red Ruthenia and Lesser Poland.

The Order of Polonia Restituta is a Polish state order established 4 February 1921. It is conferred on both military and civilians as well as on foreigners for outstanding achievements in the fields of education, science, sport, culture, art, economics, national defense, social work, civil service, or for furthering good relations between countries. It is Poland's second-highest civilian state award in the order of precedence, behind the Order of the White Eagle.
Polsat Comedy Central Extra is a Polish channel focusing on comedy owned by Paramount Networks EMEAA. It was launched on 29 April 2010 as a programming block on VH1 Poland. On 14 January 2011, VH1 Poland was rebranded as Comedy Central Family.

The Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland, also called the Polish Armed Forces and popularly called Wojsko Polskie in Poland are the national armed forces of the Republic of Poland. The name has been used since the early 19th century, but can also be applied to earlier periods.


















