| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in Norway | ||||
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in Norway | ||||
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2017) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2017) |
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (December 2017) |

The Taiping Rebellion, also known as the Taiping Civil War or the Taiping Revolution, was a massive civil war in China between the Manchu-led Qing dynasty and the Hakka-led Taiping Heavenly Kingdom. It lasted from 1850 until the fall of Tianjing in 1864, although the last rebel army was not wiped out until August 1871. The conflict resulted in approximately 20 million deaths. The established Qing government won decisively, although at great cost to its fiscal and political structure.

The Mandate of Heaven is a Chinese political philosophy that was used in ancient and imperial China to legitimize the rule of the King or Emperor of China. According to this doctrine, heaven bestows its mandate on a just ruler of China. If a ruler was overthrown, this was interpreted as an indication that the ruler was unworthy and had lost the mandate. It was also a common belief that natural disasters such as famine and flood were divine retributions bearing signs of Heaven's displeasure with the ruler, so there would often be revolts following major disasters as the people saw these calamities as signs that the Mandate of Heaven had been withdrawn.

Wei (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was a dynastic state of China and one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period. With its capital initially located at Xuchang, and thereafter Luoyang, the state was established by Cao Pi in 220, based upon the foundations laid by his father, Cao Cao, towards the end of the Eastern Han dynasty. The name "Wei" first became associated with Cao Cao when he was named the Duke of Wei by the Eastern Han government in 213, and became the name of the state when Cao Pi proclaimed himself emperor in 220. Historians often add the prefix "Cao" to distinguish it from other Chinese states known as "Wei". The authority of the ruling Cao family dramatically weakened in the aftermath of the deposing and execution of Cao Shuang and his siblings, the former being one of the regents for the third Cao Wei emperor, Cao Fang, with state authority gradually falling into the hands of Sima Yi, another Cao Wei regent, and his family, from 249 onwards. The last Wei emperors would remain largely as puppet rulers under the control of the Simas until Sima Yi's grandson, Sima Yan, forced the last Wei ruler, Cao Huan, to abdicate the throne and established the Western Jin dynasty.
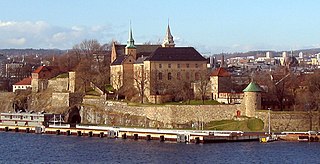
Akershus Fortress or Akershus Castle is a medieval castle in the Norwegian capital Oslo that was built to protect and provide a royal residence for the city. Since the Middle Ages the fortress has been the namesake and centre of the main fief and later main county of Akershus, which was originally one of Norway's four main regions and which included most of Eastern Norway. The fortress itself was located within the Akershus main county until 1919, and also within the smaller Akershus sub county until 1842.

The Chu–Han Contention (楚漢相爭), also known as the Chu–Han War (楚漢戰爭), was an interregnum period in ancient China between the fall of the Qin dynasty and the establishment of the Han dynasty. After the third and last Qin ruler, Ziying, unconditionally surrendered to rebel forces in 206 BCE, the former Qin Empire was divided by rebel leader Xiang Yu into the Eighteen Kingdoms, which were ruled by various rebel leaders and surrendered Qin generals. A civil war soon broke out, most prominently between two major contending powers – Xiang Yu's Western Chu and Liu Bang's Han. Some of the other kingdoms also waged war among themselves but these were largely insignificant compared to the main conflict between Chu and Han. The war ended in 202 BCE with a Han victory at the Battle of Gaixia, during which Xiang Yu committed suicide after making a last stand. Liu Bang subsequently proclaimed himself emperor and established the Han dynasty as the ruling dynasty of China.

After Liu Bang defeated Xiang Yu and proclaimed himself emperor of the Han dynasty, he followed the practice of Xiang Yu and enfeoffed many generals, noblemen, and imperial relatives as kings, the same title borne by the sovereigns of the Shang and Zhou dynasties and by the rulers of the Warring States. Each king had his own semi-autonomous kingdom. This was a departure from the policy of the Qin dynasty, which divided China into commanderies governed by non-hereditary governors.

Sudreim claim is an entitlement to the Throne of the Kingdome Norway held among members of the powerful and influential House of Sudreim and House of Rosensverd in Norway since the late Middle Ages.
Mette Iversdotter Dyre was a Danish noble, nominal sheriff and chancellor. She was married three times to powerful men: two royal councillors and finally Svante, Regent of Sweden. As such she was a de facto queen consort. Mette Dyre is credited with political influence on the affairs of state through her spouse.

Anti-Qing sentiment refers to a sentiment principally held in China against the rule of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty (1636–1912), which was criticized by opponents as being "barbaric". The Qing was accused of destroying traditional Han culture by enforcing policies such as forcing Han to wear their hair in a queue in the Manchu style. It was blamed for suppressing Chinese science, causing China to be transformed from the world's premiere power to a poor, backwards nation. The people of the Eight Banners lived off government pensions unlike the general Han civilian population.

Henrich Krummedige, was born circa 1464 in Norway and died in 1530. He was a Danish-Norwegian nobleman and a member of both the Norwegian and Danish National Councils (Rigsråd) and played an extensive role in the politics of the era. He served as commanding officer of the Bohus Fortress in Norway from 1489 to 1503.
Knut Alvsson was a Norwegian nobleman and landowner. He was the country's foremost Norwegian-born noble in his time and served as fief-holder in southern-central Norway.

Görvel Fadersdotter (Sparre) was a Swedish noblewoman and county administrator. She was a major landowner in Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
Events in the year 1502 in Norway.

The Dano-Swedish War from 1501 to 1512 was a military conflict between Denmark and Sweden within the Kalmar Union.
Nils Ravaldsson was a leader of the Alvsson's rebellion. He was the leader of the rebellion after Knut Alvsson was murdered. Ravaldsson was also responsible for the construction of Olsborg Castle in 1502.
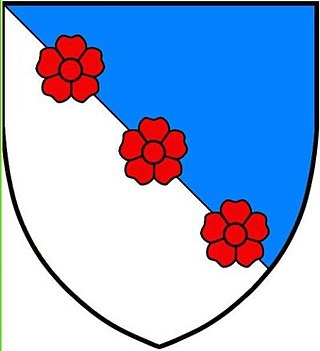
The Krummedige-Tre Rosor feud was a feud that took place from 1448 to 1502 between the Norwegian noble families, Krummedige and Tre Rosor. The feud ended with the extinction of the male Tre Rosor line in Norway, and a stronger monarchy in Norway.